|
Interstate System (world-systems Theory)
The interstate system is a concept used within world-systems theory to describe the system of state relationships that arose either as a concomitant process or as a consequence of the development of the capitalist world-system over the course of the "long" 16th century. The theory of the interstate system holds that all states are defined through their relationship to other states or through participation in the world economy, and that divisions between states help to divide the world into a core, periphery and semi-periphery. Concepts Development of an interstate system Immanuel Wallerstein wrote that the development of a capitalist world-economy created all of the major institutions of the modern world, including social classes, nations, households and states. These institutions also created each other, as nations, classes, and households came to be defined by their relations to the state, and were subsequently able to shape the state. Out of this structural chaos on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World-systems Theory
World-systems theory (also known as world-systems analysis or the world-systems perspective)Immanuel Wallerstein, (2004), "World-systems Analysis." In ''World System History'', ed. George Modelski, in ''Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems'' (EOLSS), Developed under the Auspices of the UNESCO, Eolss Publishers, Oxford, UK is a multidisciplinary approach to world history and social change which emphasizes the world-system (and not nation states) as the primary (but not exclusive) unit of social analysis. "World-system" refers to the inter-regional and transnational division of labor, which divides the world into core countries, semi-periphery countries, and the periphery countries. Core countries focus on higher-skill, capital-intensive production, and the rest of the world focuses on low-skill, labor-intensive production and extraction of raw materials. This constantly reinforces the dominance of the core countries. Nonetheless, the system has dynamic characteristics, in part a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bourgeois Nationalism
In Marxism, bourgeois nationalism is the practice by the ruling classes of deliberately dividing people by nationality, race, ethnicity, or religion, so as to distract them from engaging in class struggle. It is seen as a divide-and-conquer strategy used by the ruling classes to prevent the working class from uniting against them; hence the Marxist slogan, ''Workers of all countries, unite!'' Usage Soviet Union After the October Revolution, the Bolshevik government based its nationalities policy ( korenization) on the principles of Marxism. According to these principles, all nations should disappear with time, and nationalism was considered a bourgeois ideology. By the mid-1930s these policies were replaced with more extreme assimilationist and russification policies. In his Report on the 50th anniversary of the formation of the USSR, Leonid Brezhnev emphasized: "That is why Communists and all fighters for socialism believe that the main aspect of the national question ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Chase-Dunn
Christopher K. Chase-Dunn (born January 10, 1944, Corvallis, Oregon) is an American sociologist best known for his contributions to world-systems theory. Education and career Chase-Dunn earned his PhD in 1975 at Stanford University (studying under John W. Meyer) and has taught at The Johns Hopkins University (1975–2000) and at the University of California, Riverside (2000–present). He is a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science and served as President (2002–06) of Research Committee 02 (Economy and Society) of the International Sociological Association from 2002 to 2006. He was chair of the Section on International Political Economy of the International Studies Association from 1984 to 1986, and chair of the Section on the Political Economy of the World-System of the American Sociological Association in 1982. He founded the Institute for Research on World-Systems at the University of California, Riverside. He is founding editor of the ''Journal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Accumulation
Capital accumulation is the dynamic that motivates the pursuit of profit, involving the investment of money or any financial asset with the goal of increasing the initial monetary value of said asset as a financial return whether in the form of profit, rent, interest, royalties or capital gains. The aim of capital accumulation is to create new fixed and working capitals, broaden and modernize the existing ones, grow the material basis of social-cultural activities, as well as constituting the necessary resource for reserve and insurance. The process of capital accumulation forms the basis of capitalism, and is one of the defining characteristics of a capitalist economic system.''Capital'', Encyclopedia on Marxists.org: http://marxists.org/glossary/terms/c/a.htm#capital Definition The definition of capital accumulation is subject to controversy and ambiguities, because it could refer to: *a ''net addition'' to existing wealth *a ''redistribution'' of wealth. Most often, capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicos Poulantzas
Nicos Poulantzas ( el, Νίκος Πουλαντζάς ; 21 September 1936 – 3 October 1979) was a Greek-French Marxist political sociologist and philosopher. In the 1970s, Poulantzas was known, along with Louis Althusser, as a leading structural Marxist; while at first a Leninist, he eventually became a proponent of democratic socialism Democratic socialism is a Left-wing politics, left-wing political philosophy that supports political democracy and some form of a socially owned economy, with a particular emphasis on economic democracy, workplace democracy, and workers' self- .... He is best known for his theoretical work on the state, but he also offered Marxist contributions to the analysis of fascism, social class in the contemporary world, and the collapse of dictatorships in Southern Europe in the 1970s (such as Francisco Franco's rule in Spain, António de Oliveira Salazar's in Portugal, and Georgios Papadopoulos' in Greece). Life Poulantzas studied law in Greece a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economism
Economism, sometimes spelled economicism, is a term referring to the distraction of working class political activism from a global political project to purely economic demands. The concept encompasses rewarding workers in socialism with money incentives, rather than incentivizing workers through revolutionary politics. The term is originally associated with Vladimir Lenin's critique of trade unionism. In Marxist analysis The term economism was used by Lenin in his critique of the trade union movement, in reference to how working class demands for a more global political project can become supplanted by purely economic demands. Economistic demands include higher wages, shorter working hours, secure employment, health care, and other benefits. In his criticism of economism, Lenin's view was that the political figure of the worker could not necessarily be inferred from the worker's social position. Under capitalism, the worker's labor power is commodified and sold in exchange for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Marxists
Western Marxism is a current of Marxist theory that arose from Western and Central Europe in the aftermath of the 1917 October Revolution in Russia and the ascent of Leninism Leninism is a political ideology developed by Russian Marxist revolutionary Vladimir Lenin that proposes the establishment of the Dictatorship of the proletariat#Vladimir Lenin, dictatorship of the proletariat led by a revolutionary Vanguardis .... The term denotes a loose collection of theorists who advanced an interpretation of Marxism distinct from both classical Marxism, classical and Orthodox Marxism and the Soviet Marxism, Marxism-Leninism of the Soviet Union. Less concerned with economic analysis than earlier schools of Marxist thought, Western Marxism placed greater emphasis on the study of the cultural trends of capitalist society, deploying the more philosophy, philosophical and subjectivity, subjective aspects of Marxism, and incorporating non-Marxist approaches to investigating culture an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commodity Fetishism
In Marxist philosophy, the term commodity fetishism describes the economic relationships of production and exchange as being social relationships that exist among things (money and merchandise) and not as relationships that exist among people. As a form of reification, commodity fetishism presents economic value as inherent to the commodities, and not as arising from the workforce, from the human relations that produced the commodity, the goods and the services. In the first chapter of '' Capital: Critique of Political Economy'' (1867) commodity fetishism explicates that the social organization of labour occurs through the buying and selling of commodities (goods and services); therefore, in the marketplace, capitalist social relations among people—who makes what, who works for whom, the production-time for a commodity, etc.—are social relations among ''objects'', not among individual persons. At market, the commodities appear in a depersonalized form, as material goods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed during the Cold War (1947–1991). These states followed the ideology of Marxism–Leninism, in opposition to the Capitalism, capitalist Western Bloc. The Eastern Bloc was often called the Second World, whereas the term "First World" referred to the Western Bloc and "Third World" referred to the Non-Aligned Movement, non-aligned countries that were mainly in Africa, Asia, and Latin America but notably also included former Tito–Stalin split, pre-1948 Soviet ally SFR Yugoslavia, which was located in Europe. In Western Europe, the term Eastern Bloc generally referred to the USSR and Central and Eastern European countries in the Comecon (East Germany, Polish People's Republic, Poland, Czechoslovak Socialist Republic, Czechoslovakia, Hungarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Socialist
State socialism is a political and economic ideology within the socialist movement that advocates state ownership of the means of production. This is intended either as a temporary measure, or as a characteristic of socialism in the transition from the capitalist to the socialist mode of production or to a communist society. State socialism was first theorised by Ferdinand Lassalle. It advocates a planned economy controlled by the state in which all industries and natural resources are state-owned. Aside from anarchists and other libertarian socialists, there was, in the past, confidence amongst socialists in the concept of state socialism as being the most effective form of socialism. Some early social democrats in the late 19th century and early 20th century, such as the Fabians, claimed that British society was already mostly socialist and that the economy was significantly socialist through government-run enterprises created by conservative and liberal governments which cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
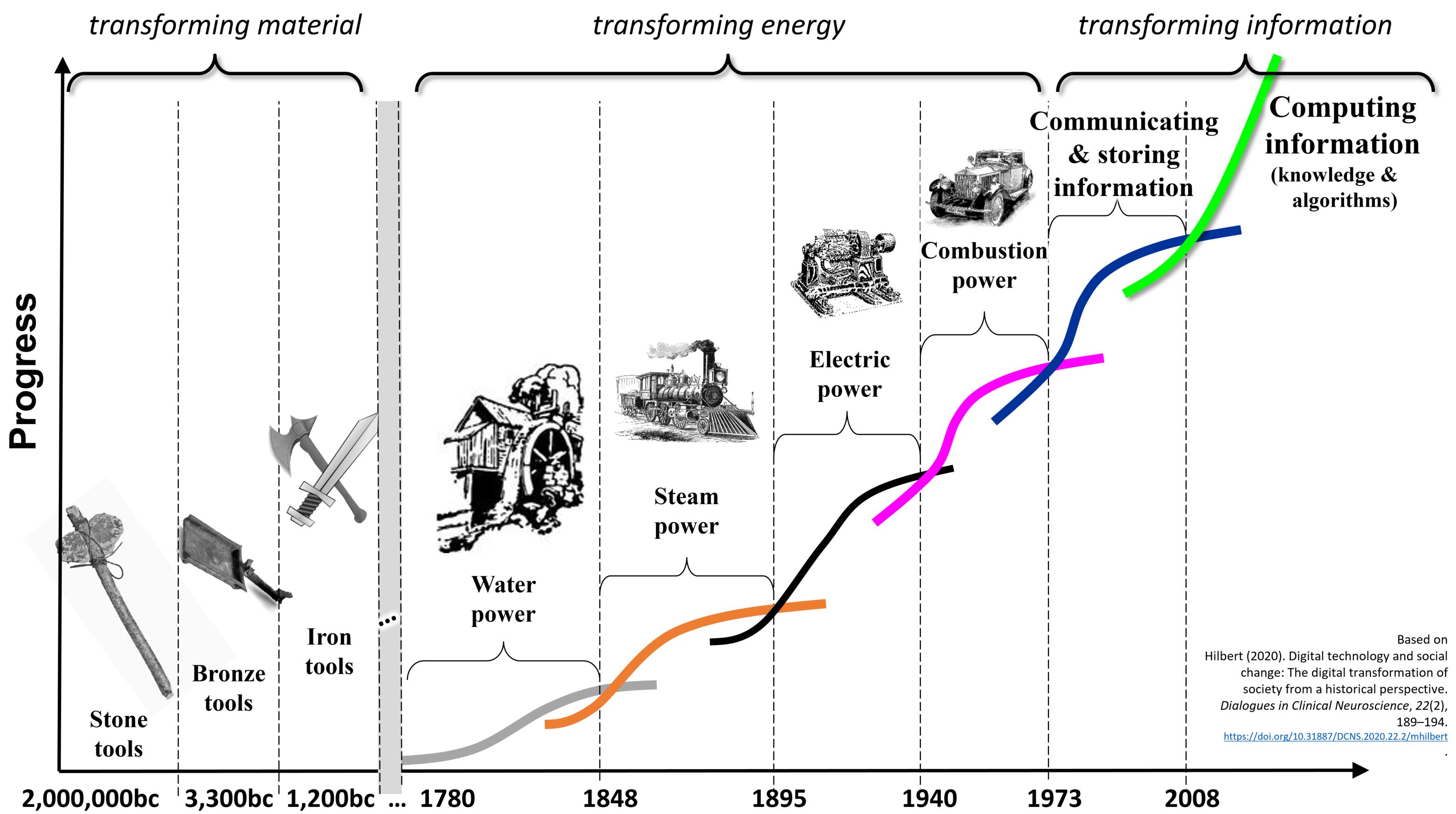
Kondratiev Wave
In economics, Kondratiev waves (also called supercycles, great surges, long waves, K-waves or the long economic cycle) are hypothesized cycle-like phenomena in the modern world economy. The phenomenon is closely connected with the technology life cycle. It is stated that the period of a wave ranges from forty to sixty years, the cycles consist of alternating intervals of high sectoral growth and intervals of relatively slow growth.See, e.g. Long wave theory is not accepted by most academic economists. Among economists who accept it, there is a lack of agreement about both the cause of the waves and the start and end years of particular waves. Among critics of the theory, the consensus is that it involves recognizing patterns that may not exist (apophenia). History of concept The Soviet economist Nikolai Kondratiev (also written Kondratieff or Kondratyev) was the first to bring these observations to international attention in his book ''The Major Economic Cycles'' (1925) al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)