|
International Prognostic Scoring System
The International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS), published in 1997, is used by many doctors to help assess the severity of a patient's myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). Based on the IPSS score, the patient's history, and his/her personal observations, the physician will design a treatment plan to address the MDS. Process The IPSS uses three "prognostic indicators" to develop a "score" which may be useful in understanding how the MDS may progress: :* the proportion of blast cells in the bonemarrow :* the type of chromosomal changes, if any, in the marrow cells :* the presence of one or more low blood cell counts (cytopenias Cytopenia is a reduction in the number of mature blood cells. It is common in cancer patients being treated with radiation and/or chemotherapy. Types Anemia – a reduction of the red blood cells in the body. Leukopenia – a deficiency of whit ...) Each indicator is rated according to its severity and the ratings are combined into a "score." Scores ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
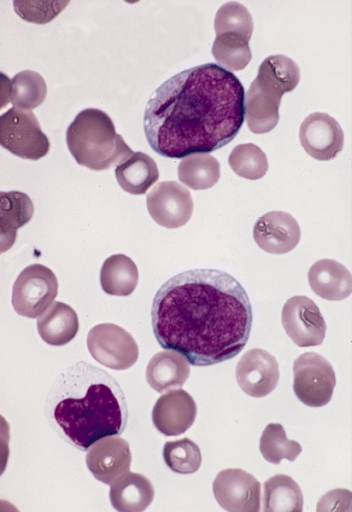
Myelodysplastic Syndrome
A myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is one of a group of cancers in which immature blood cells in the bone marrow do not mature, and as a result, do not develop into healthy blood cells. Early on, no symptoms typically are seen. Later, symptoms may include feeling tired, shortness of breath, bleeding disorders, anemia, or frequent infections. Some types may develop into acute myeloid leukemia. Risk factors include previous chemotherapy or radiation therapy, exposure to certain chemicals such as tobacco smoke, pesticides, and benzene, and exposure to heavy metals such as mercury or lead. Problems with blood cell formation result in some combination of low red blood cell, platelet, and white blood cell counts. Some types have an increase in immature blood cells, called blasts, in the bone marrow or blood. The types of MDS are based on specific changes in the blood cells and bone marrow. Treatments may include supportive care, drug therapy, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blast Cells
In cell biology, a precursor cell, also called a blast cell or simply blast, is a partially differentiated cell, usually referred to as a unipotent cell that has lost most of its stem cell properties. A precursor cell is also known as a progenitor cell but progenitor cells are multipotent. Precursor cells are known as the intermediate cell before they become differentiated after being a stem cell. Usually, a precursor cell is a stem cell with the capacity to differentiate into only one cell type. Sometimes, ''precursor cell'' is used as an alternative term for unipotent stem cells. In embryology, precursor cells are a group of cells that later differentiate into one organ. A blastoma is any cancer created by malignancies of precursor cells. Precursor cells, and progenitor cells, have many potential uses in medicine. , there is research being done to use these cells to build heart valves, blood vessels and other tissues, by using blood and muscle precursor, or progenitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome Abnormality
A chromosomal abnormality, chromosomal anomaly, chromosomal aberration, chromosomal mutation, or chromosomal disorder, is a missing, extra, or irregular portion of chromosomal DNA. These can occur in the form of numerical abnormalities, where there is an atypical number of chromosomes, or as structural abnormalities, where one or more individual chromosomes are altered. Chromosome mutation was formerly used in a strict sense to mean a change in a chromosomal segment, involving more than one gene. Chromosome anomalies usually occur when there is an error in cell division following meiosis or mitosis. Chromosome abnormalities may be detected or confirmed by comparing an individual's karyotype, or full set of chromosomes, to a typical karyotype for the species via genetic testing. Numerical abnormality An abnormal number of chromosomes is called aneuploidy, and occurs when an individual is either missing a chromosome from a pair (resulting in monosomy) or has more than two chromosome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
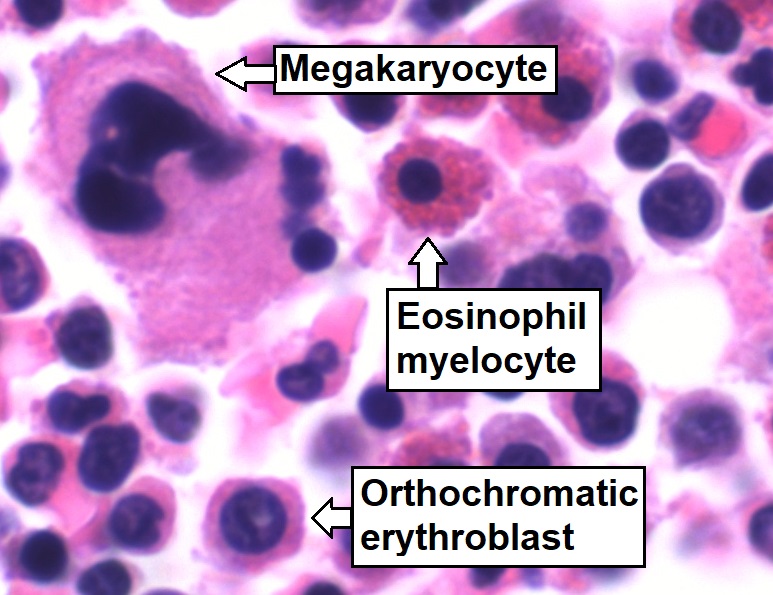
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a man weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of hematopoietic cells, including both myeloid and lymphoid lineages, are created in bone marrow; however, lymphoid cells must migrate to other lymphoid organs (e.g. thymus) in order to complete maturation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytopenias
Cytopenia is a reduction in the number of mature blood cells. It is common in cancer patients being treated with radiation and/or chemotherapy. Types Anemia – a reduction of the red blood cells in the body. Leukopenia – a deficiency of white blood cells, or leukocytes Neutropenia – a type of leukopenia, with a specific deficiency in neutrophils Thrombocytopenia – a deficiency of platelets Pancytopenia – when all three types of blood cells; red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, are all deficient. This is a life-threatening disorder that is a characteristic of aplastic anemia. There are also two general types of cytopenia: autoimmune and refractory. Autoimmune cytopenia – caused by an autoimmune disease when your body produces antibodies to destroy the healthy blood cells. Refractory cytopenia – caused by bone marrow not producing healthy blood cells, and can be a result of cancer. Symptoms and signs The symptoms of cytopenia vary depending on w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |