|
International Phonetic Alphabet Chart For English Dialects
This chart shows the most common applications of the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) to represent English language pronunciations. See Pronunciation respelling for English for phonetic transcriptions used in different dictionaries. *AmE, American English *AuE, Australian English *BahE, Bahamian English *BarE, Barbadian English *CaE, Canadian English *CIE, Channel Island English *EnE, English English *FiE, Fiji English *InE, Indian English *IrE, Irish English *JSE, Jamaican English *NZE, New Zealand English *PaE, Palauan English *ScE, Scottish English *SIE, Solomon Islands English *SAE, South African English *SSE, Standard Singapore English *WaE, Welsh English Chart This chart gives a partial system of diaphonemes for English. The symbols for the diaphonemes are given in bold, followed by their most common phonetic values. For the vowels, a separate phonetic value is given for each major dialect, and words used to name corresponding lexical sets are also given. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish English
Scottish English ( gd, Beurla Albannach) is the set of varieties of the English language spoken in Scotland. The transregional, standardised variety is called Scottish Standard English or Standard Scottish English (SSE). Scottish Standard English may be defined as "the characteristic speech of the professional class n Scotlandand the accepted norm in schools". IETF language tag for "Scottish Standard English" is en-scotland. In addition to distinct pronunciation, grammar and expressions, Scottish English has distinctive vocabulary, particularly pertaining to Scottish institutions such as the Church of Scotland, local government and the education and legal systems. Scottish Standard English is at one end of a bipolar linguistic continuum, with focused broad Scots at the other. Scottish English may be influenced to varying degrees by Scots.Stuart-Smith J. ''Scottish English: Phonology'' in Varieties of English: The British Isles, Kortman & Upton (Eds), Mouton de Gru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
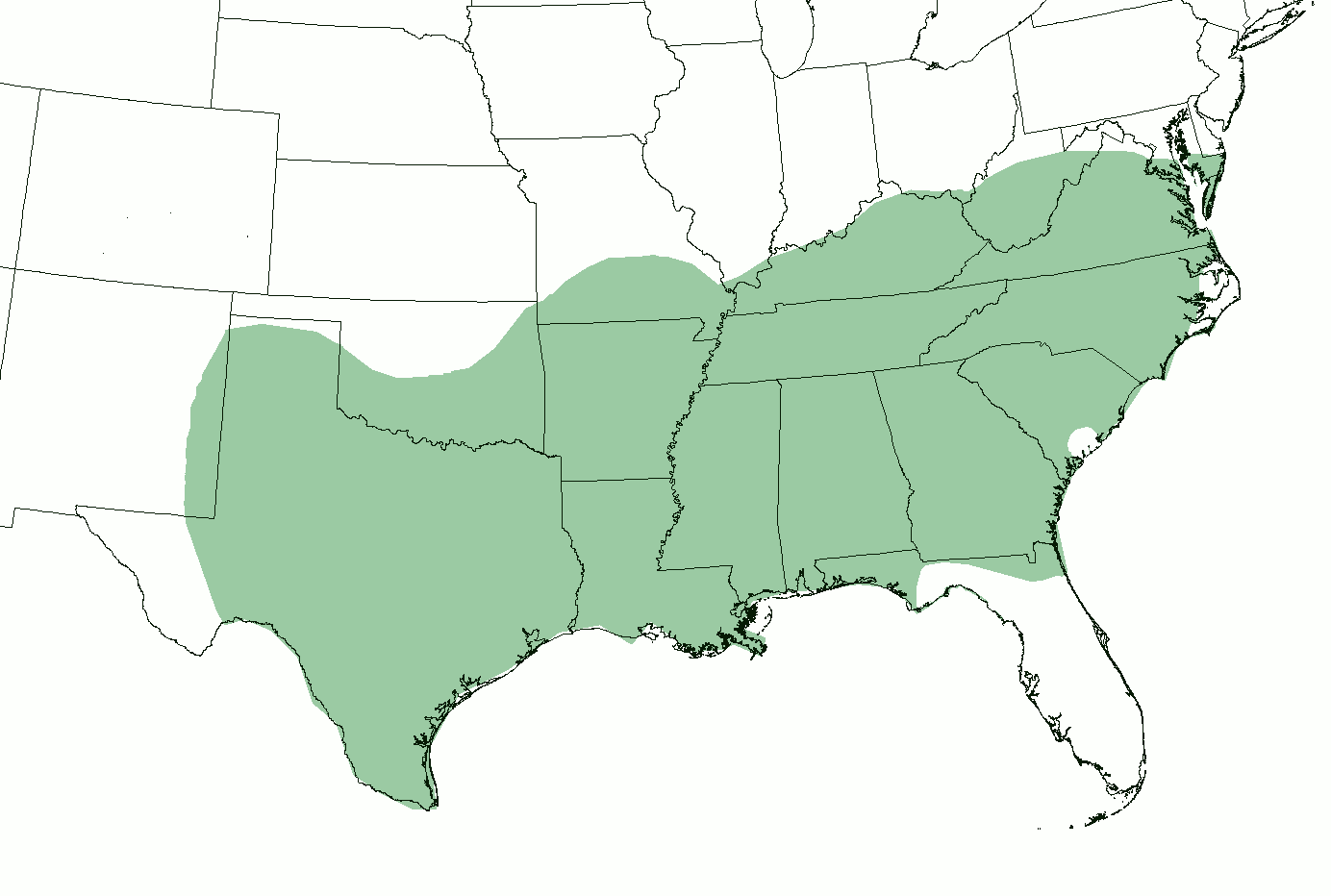
Southern American English
Southern American English or Southern U.S. English is a regional dialect or collection of dialects of American English spoken throughout the Southern United States, though concentrated increasingly in more rural areas, and spoken primarily by White Southerners. In terms of accent, its most innovative forms include southern varieties of Appalachian English and certain varieties of Texan English. Popularly known in the United States as a Southern accent or simply Southern, Southern American English now comprises the largest American regional accent group by number of speakers. Formal, much more recent terms within American linguistics include Southern White Vernacular English and Rural White Southern English. History and geography A diversity of earlier Southern dialects once existed: a consequence of the mix of English speakers from the British Isles (including largely Southern English and Scots-Irish immigrants) who migrated to the American South in the 17th and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
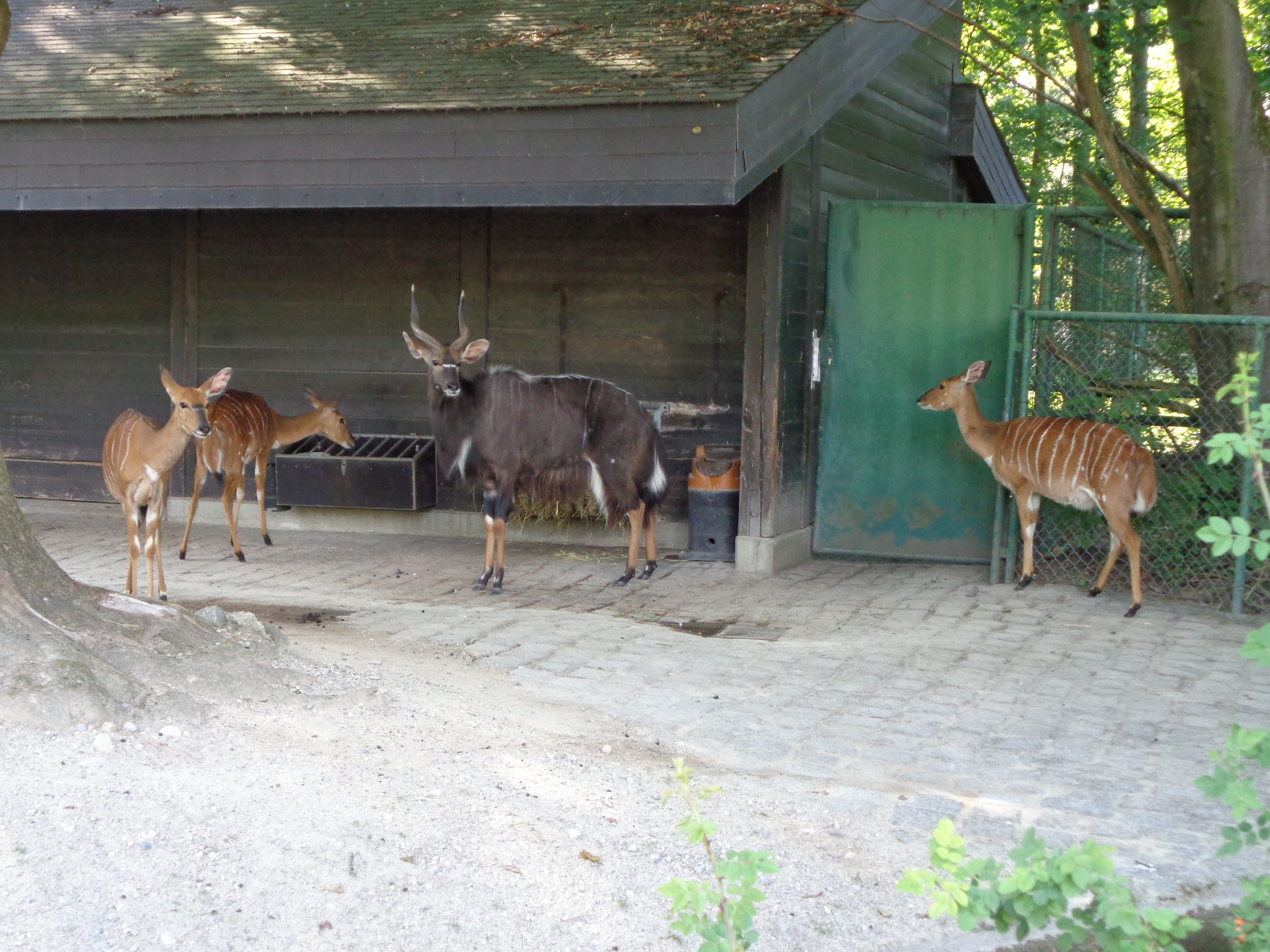
Nyala
The lowland nyala or simply nyala (''Tragelaphus angasii'') is a spiral-horned antelope native to southern Africa. It is a species of the family Bovidae and genus ''Tragelaphus'', previously placed in genus ''Nyala''. It was first described in 1849 by George French Angas. The body length is , and it weighs . The coat is maroon or rufous brown in females and juveniles, but grows a dark brown or slate grey, often tinged with blue, in adult males. Females and young males have ten or more white stripes on their sides. Only males have horns, long and yellow-tipped. It exhibits the highest sexual dimorphism among the spiral-horned antelopes. It is not to be confused with the endangered mountain nyala living in the Bale region of Ethiopia). The nyala is mainly active in the early morning and the late afternoon. It generally browses during the day if temperatures are and during the night in the rainy season. As a herbivore, the nyala feeds upon foliage, fruits and grasses, and req ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-labialization
The pronunciation of the phoneme in the English language has many variations in different dialects. Variations Depending on dialect, has at least the following allophones in varieties of English around the world: *"Standard" R: labialized postalveolar approximant (a common realization of the phoneme worldwide, Received Pronunciation and General American included) **"Bunched" or "Molar" R: labialized and pharyngealized velar bunched approximant (occurs in Southern American English and some Midwestern and Western American English most strongly); in fact, there is often a continuum of possible realizations for the postalveolar approximant within any single dialect from a more apical articulation to this more bunched articulation, which can be specified in IPA as . *"Velarized" R: velarized alveolar approximant (occurs in conservative Irish English) *"Retroflex" R: labialized retroflex approximant (occurs in West Country English, some American and Canadian English and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-vocalization
''L''-vocalization, in linguistics, is a process by which a lateral approximant sound such as , or, perhaps more often, velarized , is replaced by a vowel or a semivowel. Types There are two types of ''l''-vocalization: * A labiovelar approximant, velar approximant, or back vowel: > or > or * A front vowel or palatal approximant: > > West Germanic languages Examples of L-vocalization can be found in many West Germanic languages, including English, Scots, Dutch, and some German dialects. Early Modern English L-vocalization has occurred, since Early Modern English, in certain ''-al-'' and ''-ol-'' sequences before coronal or velar consonants, or at the end of a word or morpheme. In those sequences, became and diphthonged to , while became and diphthonged to . At the end of a word or morpheme, it produced ''all'', ''ball'', ''call'', ''control'', ''droll'', ''extol'', ''fall'', ''gall'', ''hall'', ''knoll'', ''mall'', ''pall'', ''poll'', ''roll'', ''scroll'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brummie
The Brummie dialect, or more formally the Birmingham dialect, is spoken by many people in Birmingham, England, and some of its surrounding areas. "Brummie" is also a demonym for people from Birmingham. It is often erroneously used in referring to all accents of the West Midlands, as it is markedly distinct from the traditional accent of the adjacent Black Country, but modern-day population mobility has tended to blur the distinction. For instance, Dudley-born comedian Lenny Henry, Walsall-born rock musician Noddy Holder, Smethwick-reared actress Julie Walters, Wollaston-born soap actress Jan Pearson, Solihull-born motoring journalist and TV presenter Richard Hammond, and West Bromwich-born comedian Frank Skinner are sometimes mistaken for Brummie-speakers by people outside the West Midlands county. Additionally, population mobility has meant that to a degree, the Brummie accent extends into some parts of the Metropolitan Borough of Solihull, but much of the accent within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voicelessness
In linguistics, voicelessness is the property of sounds being pronounced without the larynx vibrating. Phonologically, it is a type of phonation, which contrasts with other states of the larynx, but some object that the word phonation implies voicing and that voicelessness is the lack of phonation. The International Phonetic Alphabet has distinct letters for many voiceless and modally voiced pairs of consonants (the obstruents), such as . Also, there are diacritics for voicelessness, and , which is used for letters with a descender. Diacritics are typically used with letters for prototypically voiced sounds, such as vowels and sonorant consonants: . In Russian use of the IPA, the voicing diacritic may be turned for voicelessness, e.g. . Voiceless vowels and other sonorants Sonorants are sounds such as vowels and nasals that are voiced in most of the world's languages. However, in some languages sonorants may be voiceless, usually allophonically. For example, the Japa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are and pronounced with the lips; and pronounced with the front of the tongue; and pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; , and , pronounced by forcing air through a narrow channel (fricatives); and and , which have air flowing through the nose (nasals). Contrasting with consonants are vowels. Since the number of speech sounds in the world's languages is much greater than the number of letters in any one alphabet, linguists have devised systems such as the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) to assign a unique and unambiguous symbol to each attested consonant. The English alphabet has fewer consonant letters than the English language has consonant sounds, so digraphs like , , , and are used to extend the alphabet, though some letters and digraphs represent more than one consonant. For exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexical Set
A lexical set is a group of words that all fall under a single category based on a single shared phonological feature. A phoneme is a basic unit of sound in a language that can distinguish one word from another. Most commonly, following the work of phonetician John C. Wells, a lexical set is a class of words in a language that all share a certain vowel phoneme. As Wells himself says, lexical sets "enable one to refer concisely to large groups of words which tend to share the same vowel, and to the vowel which they share". For instance, the pronunciation of the vowel in ''cup'', ''luck'', ''sun'', ''blood'', ''glove'', and ''tough'' may vary in different English dialects, but is usually consistent within each dialect, and so this category of words forms a lexical set:Mesthrie, Rajend (2000). "Regional Dialectology". ''Introducing Sociolinguistics''. Edinburgh University Press, p. 50. what Wells, for ease, calls the set. Meanwhile, words like ''bid'', ''cliff'', ''limb'', ''miss'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphoneme
A diaphoneme is an abstract phonological unit that identifies a correspondence between related sounds of two or more varieties of a language or language cluster. For example, some English varieties contrast the vowel of ''late'' () with that of ''wait'' or ''eight'' (). Other English varieties contrast the vowel of ''late'' or ''wait'' () with that of ''eight'' (). This non-overlapping pair of phonemes from two different varieties can be reconciled by positing three different diaphonemes: A first diaphoneme for words like ''late'' (), a second diaphoneme for words like ''wait'' (), and a third diaphoneme for words like ''eight'' (). Diaphonology studies the realization of diaphones across dialects, and is important if an orthography is to be adequate for more than one dialect of a language. In historical linguistics, it is concerned with the reflexes of an ancestral phoneme as a language splits into dialects, such as the modern realizations of Old English . The concept goes ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welsh English
Welsh English ( cy, Saesneg Gymreig) comprises the dialects of English spoken by Welsh people. The dialects are significantly influenced by Welsh grammar and often include words derived from Welsh. In addition to the distinctive words and grammar, a variety of accents are found across Wales, including those of North Wales, the Cardiff dialect, the South Wales Valleys and West Wales. Accents and dialects in the west of Wales have been more heavily influenced by the Welsh language while dialects in the east have been influenced more by dialects in England. In the east and south east, it has been influenced by West Country and West Midland dialects while in north east Wales and parts of the North Wales coast, it has been influenced by Merseyside English. A colloquial portmanteau word for Welsh English is Wenglish. It has been in use since 1985. Pronunciation Vowels Short monophthongs * The vowel of ''cat'' is pronounced either as an open front unrounded vowel or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |