|
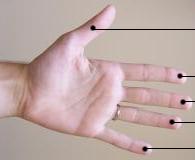
Interdigital Webbing
Interdigital webbing is the presence of membranes of skin between the digits. Normally in mammals, webbing is present in the embryo but resorbed later in development, but in various mammal species it occasionally persists in adulthood. In humans, it can be found in those suffering from LEOPARD syndrome and from Aarskog–Scott syndrome. Webbing between the digits of the hindfoot is also present in several mammals that spend part of their time in the water.Voss, 1988, p. 455 Webbing accommodates movement in the water.Voss, 1988, p. 458 Interdigital webbing is not to be confused with syndactyly, which is a fusing of digits and occurs rarely in humans. Syndactyly specifically affecting feet occurs in birds (such as ducks), amphibians (such as frogs), and mammals (such as the kangaroo). Mammals with interdigital webbing Rodents In oryzomyines, a mainly South American rodent group, the marsh rice rat, '' Pseudoryzomys simplex'', and ''Sigmodontomys alfari'' all have small webs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digit (anatomy)
A digit is one of several most distal parts of a limb, such as fingers or toes, present in many vertebrates. Names Some languages have different names for hand and foot digits (English: respectively "finger" and "toe", German: "Finger" and "Zeh", French: "doigt" and "orteil"). In other languages, e.g. Arabic, Russian, Polish, Spanish, Portuguese, Italian, Czech, Tagalog, Turkish, Bulgarian, and Persian, there are no specific one-word names for fingers and toes; these are called "digit of the hand" or "digit of the foot" instead. In Japanese, yubi (指) can mean either, depending on context. Human digits Humans normally have five digits on each extremity. Each digit is formed by several bones called phalanges, surrounded by soft tissue. Human fingers normally have a nail at the distal phalanx. The phenomenon of polydactyly occurs when extra digits are present; fewer digits than normal are also possible, for instance in ectrodactyly. Whether such a mutation can be surgica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphinectomys
''Amphinectomys savamis'', also known as the Ucayali water ratMusser and Carleton, 2005 or amphibious rat,Duff and Lawson, 2004 is a rodent from the Peruvian Amazon. It is placed as the only member of genus ''Amphinectomys'' in the tribe Oryzomyini of family Cricetidae. It is similar to ''Nectomys ''Nectomys'' is a genus of rodent in the tribe Oryzomyini of family Cricetidae. Musser and Carleton, 2005. It is closely related to '' Amphinectomys'' and was formerly considered congeneric with ''Sigmodontomys''. It consists of five species, whic ...'', but its discoverers considered it to be different enough (with more expansive interdigital webbing and a significantly broader interorbital region) to require its own genus. When it was described as a new genus in 1994, knowledge of the variation within ''Nectomys'' was much more limited than it is now, and it has been suggested that the status of the taxon be re-examined considering this new information. The species's karyotype, 2n = 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nilopegamys
The Ethiopian amphibious rat also known as the Ethiopian water mouse (''Nilopegamys plumbeus'') is an insectivorous and semiaquatic species of rodent in the monotypic genus ''Nilopegamys'' of the family Muridae. There has only been one known specimen. It was found along the Lesser Abay River near its source at an altitude of 2600 m in the highlands of northwestern Ethiopia in 1928. ''N. plumbeus'' is considered to be the most aquatically adapted African murid; its unusually large brain is thought to be one consequence of this lifestyle. The species is considered to be critically endangered or possibly extinct, since its habitat has been severely damaged by overgrazing and monoculture. Distribution and discovery In late March of 1928 the Ethiopian amphibious rat was cataloged for the first time. The specimen was discovered in a trap set by Wilfred H. Osgood, and was unlike any African rat he had seen before. The rat showed multiple adaptations to aquatic life which is uncommon f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colomys
The African wading rat or African water rat (''Colomys goslingi'') is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is native to Africa, where it occurs in Angola, Burundi, Cameroon, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Kenya, Liberia, Rwanda, South Sudan, Uganda, and Zambia.Kerbis Peterhans, J., et al. 2008''Colomys goslingi''.The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2014.3. Downloaded on 11 April 2015. An aquatic species, this rat is found in and around streams and pools in rainforest habitat, and sometimes in grassland and savanna regions. In 2020, a team of researchers from Siena College established that it is actually four separate species: the other three species have been named ''Colomys wologizi'', ''C. lumumbai'', and ''C. eisentrauti''. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area and 20% of its land area.Sayre, April Pulley (1999), ''Africa'', Twenty-First Century Books. . With billion people as of , it accounts for about of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest amongst all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Despite a wide range of natural resources, Africa is the least wealthy continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, behind Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, tribalism, colonialism, the Cold War, neocolonialism, lack of democracy, and corruption. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and the large and young population make Afr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydromys
''Hydromys'' is a genus of semiaquatic rodents in the subfamily Murinae. Three species are endemic to New Guinea and nearby islands. The fourth species, the rakali, is also found on Australia. The most recently discovered member of this genus was described in 2005. List of species Genus ''Hydromys'' - water rats *Rakali, ''Hydromys chrysogaster'' E. Geoffroy, 1804 *Western water rat, ''Hydromys hussoni'' Musser and Piik, 1982 * New Britain water rat, ''Hydromys neobritannicus'' Tate and Archbold, 1935 * Ziegler's water rat, ''Hydromys ziegleri'' Helgen, 2005 Note: ''Hydromys habbema'' Tate and Archbold, 1941 and ''Hydromys shawmayeri'' (Hinton, 1943) are placed within ''Baiyankamys '' Baiyankamys'' is a genus of amphibious murid rodents. It was originally described, along with the species '' Baiyankamys shawmayeri'' by Hinton in 1943 after he found the remains of a single individual in south east of the Bismarck Mountain ...'' after Helgen, 2005. References * * * Exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baiyankamys
'' Baiyankamys'' is a genus of amphibious murid rodents. It was originally described, along with the species ''Baiyankamys shawmayeri'' by Hinton in 1943 after he found the remains of a single individual in south east of the Bismarck Mountain Range, north east New Guinea. Tate, in 1951 and, Laurie and Hill in 1954, confirmed the existence of both the species and genus. Classification Hinton described '' Baiyankamys'' as similar in appearance to the species ''Hydromys habbema'' but differed due to its unreduced pinnae and its lower teeth. It was described as having three lower molars on both sides of the lower jaw, whereas other genera of amphibious murines in New Guinea have only two. In 1968 Mahoney discovered that the specimen of ''B. shawmayeri'' was a composite resulting from an incorrectly associated mandible of the species '' Rattus niobe'' and the skull of a small water rat. When the correct mandible was found in the BMNH collections Mahoney proposed that, based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murinae
The Old World rats and mice, part of the subfamily Murinae in the family Muridae, comprise at least 519 species. Members of this subfamily are called murines. In terms of species richness, this subfamily is larger than all mammal families except the Cricetidae and Muridae, and is larger than all mammal orders except the bats and the remainder of the rodents. Description The Murinae are native to Africa, Europe, Asia, and Australia. They are terrestrial placental mammals. They have also been introduced to all continents except Antarctica, and are serious pest animals. This is particularly true in island communities where they have contributed to the endangerment and extinction of many native animals. Two prominent murine species have become vital laboratory animals: the brown rat and house mouse are both used as medical subjects. The murines have a distinctive molar pattern that involves three rows of cusps instead of two, the primitive pattern seen most frequently in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheomys
''Rheomys'' is a genus of Mexican and Central American semiaquatic rodents in the family Cricetidae. It contains the following species: * Mexican water mouse, ''Rheomys mexicanus The Mexican water mouse, Mexican fishing mouse or Goodwin's water mouse (''Rheomys mexicanus''), is a species of semiaquatic rodent in the family Cricetidae. It has a restricted range in the state of Oaxaca in southern Mexico, Threatened by defo ...'' * Goldman's water mouse, '' Rheomys raptor'' * Thomas's water mouse, '' Rheomys thomasi'' * Underwood's water mouse, '' Rheomys underwoodi'' References Rodent genera Taxa named by Oldfield Thomas Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Sigmodontinae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyomyini
Ichthyomyini is a tribe of New World rats and mice in the subfamily Sigmodontinae. The species within this tribe share the characteristics of all being carnivorous semiaquatic rodents. *'' Anotomys'' - aquatic rat *'' Chibchanomys'' *''Ichthyomys'' - crab-eating rats *''Neusticomys'' - fish-eating rats *''Rheomys ''Rheomys'' is a genus of Mexican and Central American semiaquatic rodents in the family Cricetidae. It contains the following species: * Mexican water mouse, ''Rheomys mexicanus'' * Goldman's water mouse, ''Rheomys raptor'' * Thomas's water mou ...'' {{Taxonbar, from=Q1420397 Mammal tribes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |