|
Instrumental Idiom
In music, an instrumental idiom refers to writing, parts, and performance, those being ''idiomatic'' or ''nonidiomatic'' depending on how well each is suited to the specific instrument intended, in terms of both ease of playing and quality of music and the inherent tendencies and limitations of specific instruments. The analogy is with linguistic idiomaticness, that is, form or structure peculiar to one language but not another. For example, the trombone is played with a slide, making it one of the few wind instruments capable of glissando or sliding. However, pitches are different harmonics from the harmonic series on different slide positions. Thus, in the lower range, significant movement of the slide is required between positions, but for higher notes the player need only use the first four positions of the slide since the partials are closer together, allowing higher notes to be played in alternate positions. As an example, F4 (at the bottom of the treble clef) may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maurice Ravel
Joseph Maurice Ravel (7 March 1875 – 28 December 1937) was a French composer, pianist and conductor. He is often associated with Impressionism along with his elder contemporary Claude Debussy, although both composers rejected the term. In the 1920s and 1930s Ravel was internationally regarded as France's greatest living composer. Born to a music-loving family, Ravel attended France's premier music college, the Paris Conservatoire; he was not well regarded by its conservative establishment, whose biased treatment of him caused a scandal. After leaving the conservatoire, Ravel found his own way as a composer, developing a style of great clarity and incorporating elements of modernism, baroque, neoclassicism and, in his later works, jazz. He liked to experiment with musical form, as in his best-known work, ''Boléro'' (1928), in which repetition takes the place of development. Renowned for his abilities in orchestration, Ravel made some orchestral arrangements of other compose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Tuning
In music, there are two common meanings for tuning: * Tuning practice, the act of tuning an instrument or voice. * Tuning systems, the various systems of pitches used to tune an instrument, and their theoretical bases. Tuning practice Tuning is the process of adjusting the pitch of one or many tones from musical instruments to establish typical intervals between these tones. Tuning is usually based on a fixed reference, such as A = 440 Hz. The term "''out of tune''" refers to a pitch/tone that is either too high (sharp) or too low (flat) in relation to a given reference pitch. While an instrument might be in tune relative to its own range of notes, it may not be considered 'in tune' if it does not match the chosen reference pitch. Some instruments become 'out of tune' with temperature, humidity, damage, or simply time, and must be readjusted or repaired. Different methods of sound production require different methods of adjustment: * Tuning to a pitch with one's voic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empirical Musicology Review
The Ohio State University Libraries are the collective libraries of the Ohio State University and its satellite campuses. This system welcomes Ohio State faculty, students, visiting scholars and the general public to study and research. It includes ten libraries located on the Columbus campus, six libraries on the regional campus of the university and nine special collections. The Ohio State University Libraries offer educational resources and services to support readers to research, learn and teach. They can help researchers find and borrow physical and digital materials from articles, journals, databases, books, dissertations, theses, newspapers, streaming videos and images, etc. The Ohio State University libraries hold over six million volumes in traditional library formats and more in electronic information resources. History In 1893, the Ohio State University built the Orton Hall Library, the first library at this university. It holds over 200,000 geologic and topographic map ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camille Saint-Saëns
Charles-Camille Saint-Saëns (; 9 October 183516 December 1921) was a French composer, organist, conductor and pianist of the Romantic music, Romantic era. His best-known works include Introduction and Rondo Capriccioso (1863), the Piano Concerto No. 2 (Saint-Saëns), Second Piano Concerto (1868), the Cello Concerto No. 1 (Saint-Saëns), First Cello Concerto (1872), ''Danse macabre (Saint-Saëns), Danse macabre'' (1874), the opera ''Samson and Delilah (opera), Samson and Delilah'' (1877), the Violin Concerto No. 3 (Saint-Saëns), Third Violin Concerto (1880), the Symphony No. 3 (Saint-Saëns), Third ("Organ") Symphony (1886) and ''The Carnival of the Animals'' (1886). Saint-Saëns was a musical prodigy; he made his concert debut at the age of ten. After studying at the Paris Conservatoire he followed a conventional career as a church organist, first at Saint-Merri, Paris and, from 1858, La Madeleine, Paris, La Madeleine, the official church of the Second French Empire, Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viola
The viola ( , also , ) is a string instrument that is bow (music), bowed, plucked, or played with varying techniques. Slightly larger than a violin, it has a lower and deeper sound. Since the 18th century, it has been the middle or alto voice of the violin family, between the violin (which is tuned a perfect fifth above) and the cello (which is tuned an octave below). The strings from low to high are typically tuned to scientific pitch notation, C3, G3, D4, and A4. In the past, the viola varied in size and style, as did its names. The word viola originates from the Italian language. The Italians often used the term viola da braccio meaning literally: 'of the arm'. "Brazzo" was another Italian word for the viola, which the Germans adopted as ''Bratsche''. The French had their own names: ''cinquiesme'' was a small viola, ''haute contre'' was a large viola, and ''taile'' was a tenor. Today, the French use the term ''alto'', a reference to its range. The viola was popular in the heyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky
Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky , group=n ( ; 7 May 1840 – 6 November 1893) was a Russian composer of the Romantic period. He was the first Russian composer whose music would make a lasting impression internationally. He wrote some of the most popular concert and theatrical music in the current classical repertoire, including the ballets '' Swan Lake'' and ''The Nutcracker'', the ''1812 Overture'', his First Piano Concerto, Violin Concerto, the ''Romeo and Juliet'' Overture-Fantasy, several symphonies, and the opera ''Eugene Onegin''. Although musically precocious, Tchaikovsky was educated for a career as a civil servant as there was little opportunity for a musical career in Russia at the time and no system of public music education. When an opportunity for such an education arose, he entered the nascent Saint Petersburg Conservatory, from which he graduated in 1865. The formal Western-oriented teaching that he received there set him apart from composers of the contemporary nati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octave
In music, an octave ( la, octavus: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is the interval between one musical pitch and another with double its frequency. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referred to as the "basic miracle of music," the use of which is "common in most musical systems." The interval between the first and second harmonics of the harmonic series is an octave. In Western music notation, notes separated by an octave (or multiple octaves) have the same name and are of the same pitch class. To emphasize that it is one of the perfect intervals (including unison, perfect fourth, and perfect fifth), the octave is designated P8. Other interval qualities are also possible, though rare. The octave above or below an indicated note is sometimes abbreviated ''8a'' or ''8va'' ( it, all'ottava), ''8va bassa'' ( it, all'ottava bassa, sometimes also ''8vb''), or simply ''8'' for the octave in the direction indicated by placing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
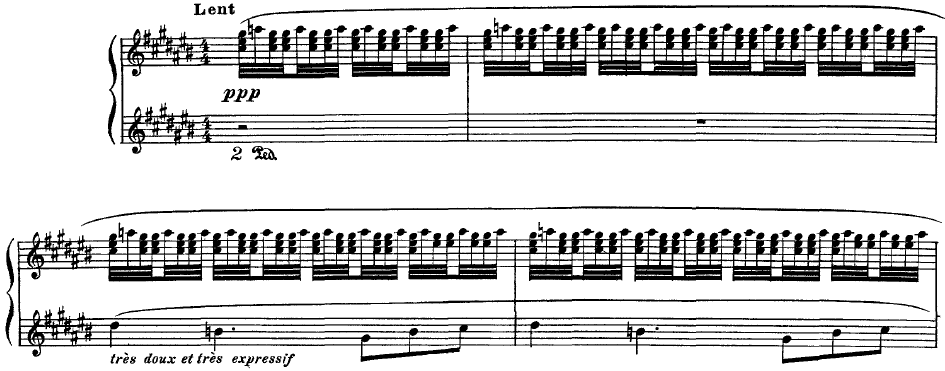
Gaspard De La Nuit
''Gaspard de la nuit'' (subtitled ''Trois poèmes pour piano d'après Aloysius Bertrand''), M. 55 is a suite of piano pieces by Maurice Ravel, written in 1908. It has three movements, each based on a poem or ''fantaisie'' from the collection '' Gaspard de la Nuit – Fantaisies à la manière de Rembrandt et de Callot'' completed in 1836 by Aloysius Bertrand. The work was premiered in Paris, on January 9, 1909, by Ricardo Viñes. The piece is famous for its difficulty, partly because Ravel intended the Scarbo movement to be more difficult than Balakirev's ''Islamey''. Because of its technical challenges and profound musical structure, Scarbo is considered one of the most difficult solo piano pieces in the standard repertoire. The manuscript currently resides in the Harry Ransom Center of the University of Texas at Austin. Etymology The name " Gaspard" is derived from its original Persian form, denoting "the man in charge of the royal treasures": "Gaspard of the Night" or th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeux D'eau (Ravel)
''Jeux d'eau'' () is a piece for solo piano by Maurice Ravel, composed in 1901 and given its first public performance the following year. The title is variously translated as "Fountains", "Playing Water" or literally "Water Games". At the time of writing ''Jeux d'eau'', Ravel was a student of Gabriel Fauré, to whom the piece is dedicated. The work is in a single movement, typically lasting between four and half and six minutes in performance. Background and first performances In 1901 Maurice Ravel was aged 26 and had yet to make an impression on the French musical scene. He had failed to win any prizes as a student at the Paris Conservatoire and was expelled on that account. As a former student he was permitted to attend the classes of his teacher Gabriel Fauré, who thought highly of him and encouraged him. Ravel dedicated ''Jeux d'eau'' and his String Quartet "à mon cher maître Gabriel Fauré". ''Jeux d'eau'' represented what Ravel's biographer Gerald Larner calls "a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piano
The piano is a stringed keyboard instrument in which the strings are struck by wooden hammers that are coated with a softer material (modern hammers are covered with dense wool felt; some early pianos used leather). It is played using a keyboard, which is a row of keys (small levers) that the performer presses down or strikes with the fingers and thumbs of both hands to cause the hammers to strike the strings. It was invented in Italy by Bartolomeo Cristofori around the year 1700. Description The word "piano" is a shortened form of ''pianoforte'', the Italian term for the early 1700s versions of the instrument, which in turn derives from ''clavicembalo col piano e forte'' (key cimbalom with quiet and loud)Pollens (1995, 238) and ''fortepiano''. The Italian musical terms ''piano'' and ''forte'' indicate "soft" and "loud" respectively, in this context referring to the variations in volume (i.e., loudness) produced in response to a pianist's touch or pressure on the keys: the grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piano Concerto (Ravel)
Maurice Ravel's Piano Concerto in G major, was composed between 1929 and 1931. The concerto is in three movements, with a total playing time of a little over 20 minutes. Ravel said that in this piece he was not aiming to be profound but to entertain, in the manner of Mozart and Saint-Saëns. Among its other influences are jazz and Basque folk music. The first performance was given in Paris in 1932 by the pianist Marguerite Long, with the Orchestre Lamoureux conducted by the composer. Within months the work was heard in the major cities of Europe and in the US. It has been recorded many times by pianists, orchestras and conductors from all over the world. Background and first performance The concerto was Ravel's penultimate composition. He had contemplated a piano concerto, based on Basque themes, in 1906; he returned to the idea in 1913, but abandoned work on the piece in 1914.Orledge, p. 34 Fifteen years elapsed before he turned once more to the idea of writing a concerto. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)