|
Inner Labia
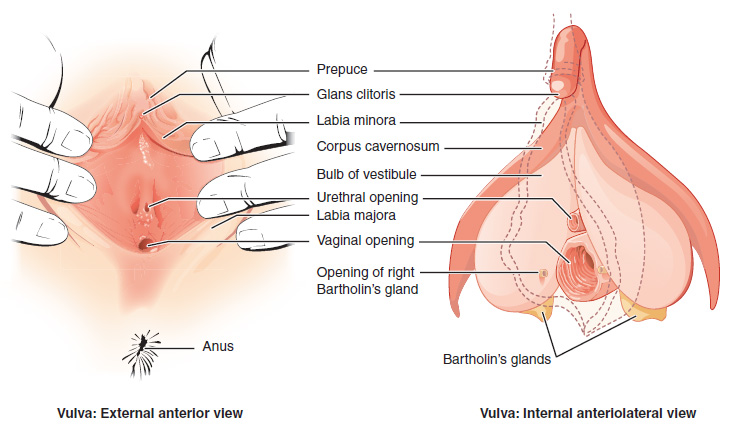
The labia minora (Latin for 'smaller lips', singular: ''labium minus'', 'smaller lip'), also known as the inner labia, inner lips, vaginal lips or nymphae are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginal opening in the vulva, situated between the labia majora (Latin for 'larger lips'; also called outer labia, or outer lips). The labia minora vary widely in size, color and shape from individual to individual. The labia minora are homologous to the male urethral surface of the penis. Structure and functioning The labia minora extend from the clitoris obliquely downward, laterally, and backward on either side of the vulval vestibule, ending between the bottom of the vulval vestibule and the labia majora. The posterior ends (bottom) of the labia minora are usually joined across the middle line by a flap of skin, named the frenulum of labia minora or fourchette. On the front, each lip forks dividing into two portions surrounding the clitoris. The upper part of each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urogenital Folds
The development of the reproductive system is the part of embryonic growth that results in the sex organs and contributes to sexual differentiation. Due to its large overlap with development of the urinary system, the two systems are typically described together as the urogenital or genitourinary system. The reproductive organs develop from the intermediate mesoderm and are preceded by more primitive structures that are superseded before birth. These embryonic structures are the mesonephric ducts (also known as ''Wolffian ducts'') and the paramesonephric ducts, (also known as ''Müllerian ducts''). The mesonephric duct gives rise to the male seminal vesicles, epididymes and vas deferens. The paramesonephric duct gives rise to the female fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and upper part of the vagina. Mesonephric ducts The mesonephric duct originates from a part of the pronephric duct. Origin In the outer part of the intermediate mesoderm, immediately under the ectoderm, in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clitoral Hood
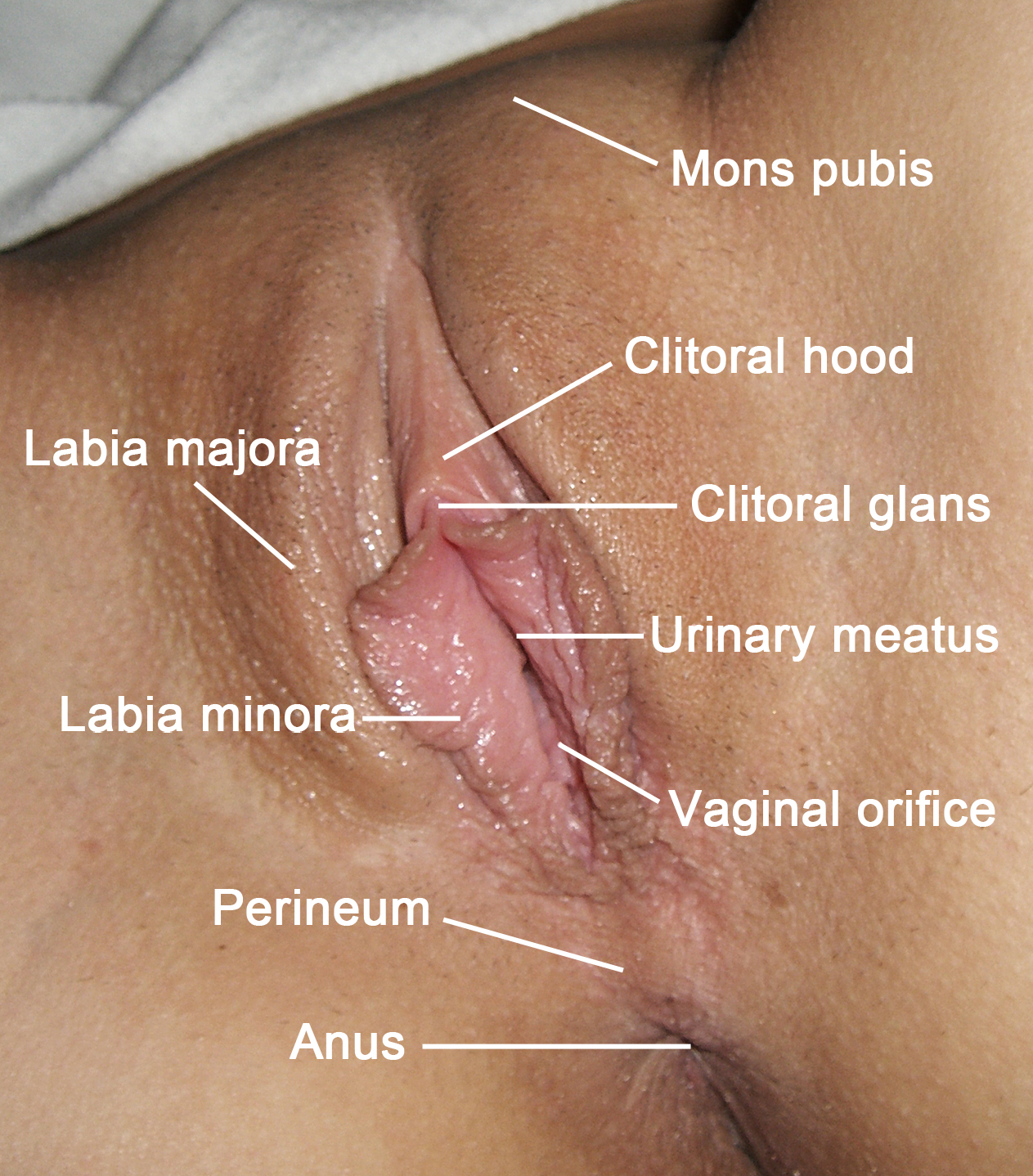
In the female human body, the clitoral hood (also called preputium clitoridis and clitoral prepuce) is a fold of skin that surrounds and protects the clitoral glans, glans of the clitoris; it also covers the external shaft of the clitoris, develops as part of the labia minora and is homology (biology), homologous with the foreskin (also called the ''prepuce'') in the male reproductive system. The clitoral hood is composed of Mucocutaneous junction, muccocutaneous tissues; these tissues are between the mucous membrane and the skin, and they may have immunological importance because they may be a point of entry of mucosal vaccines. The clitoral hood is also important not only in the protection of the clitoral glans, but also in pleasure, as its tissue forms part of the erogenous zones of the vulva. Development and variation The clitoral hood is formed during the Fetus, fetal stage by the cellular lamella. The cellular lamella grows down on the dorsal side of the clitoris and is event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labia Stretching
Labia stretching, also referred to as labia elongation or labia pulling, is the act of lengthening the ''labia minora'' (the inner lips of the female genitals) through manual manipulation (pulling) or physical equipment (such as weights).Rwandan Women View The Elongation Of Their Labia As Positive , retrieved on 18 June 2008 It is a familial in parts of and ,< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labiaplasty
Labiaplasty (also known as labioplasty, labia minora reduction, and labial reduction) is a plastic surgery procedure for altering the labia minora (inner labia) and the labia majora (outer labia), the folds of skin surrounding the human vulva. There are two main categories of women seeking cosmetic genital surgery: those with congenital conditions such as intersex, and those with no underlying condition who experience physical discomfort or wish to alter the appearance of their genitals because they believe they do not fall within a normal range. The size, colour, and shape of labia vary significantly, and may change as a result of childbirth, aging, and other events. Conditions addressed by labiaplasty include congenital defects and abnormalities such as vaginal atresia (absent vaginal passage), Müllerian agenesis (malformed uterus and fallopian tubes), intersex conditions (male and female sexual characteristics in a person); and tearing and stretching of the labia minora caus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rugosity
Rugosity, ''f''r, is a measure of small-scale variations of amplitude in the height of a surface, :f_ = A_/A_ where ''A''r is the real (true, actual) surface area and ''A''g is the geometric surface area. Utility Rugosity calculations are commonly used in materials science to characterize surfaces, amongst others, in marine science to characterize seafloor habitats. A common technique to measure seafloor rugosity is Risk's chain-and-tape method but with the advent of underwater photography less invasive quantitative methods have been developed. Some examples include measuring small-scale seafloor bottom roughness from microtopographic laser scanning (Du Preez and Tunnicliffe 2012), and deriving multi-scale measures of rugosity, slope and aspect from benthic stereo image reconstructions (Friedman et al. 2012). Inconsistency Despite the popularity of using rugosity for two- and three-dimensional surface analyses, methodological inconsistency has been problematic. Building off re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanner Scale
The Tanner scale (also known as the Tanner stages or Sexual Maturity Rating (SMR)) is a scale of physical development in children, adolescents and adults. The scale defines physical measurements of development based on external primary and secondary sex characteristics, such as the size of the breasts, genitals, testicular volume and development of pubic hair. This scale was first identified in 1969 by James Tanner, a British pediatrician, after a two-decade-long study following the physical changes in girls undergoing puberty. Due to natural variation, individuals pass through the Tanner stages at different rates, depending in particular on the timing of puberty. Among researchers who study puberty, the Tanner scale is commonly considered the "gold standard" for assessing pubertal status when it is conducted by a trained medical examiner. In HIV treatment, the Tanner scale is used to determine which regimen to follow for pediatric or adolescent patients on antiretroviral thera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen. At the deep end, the cervix (neck of the uterus) bulges into the vagina. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse and birth. It also channels menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle. Although research on the vagina is especially lacking for different animals, its location, structure and size are documented as varying among species. Female mammals usually have two external openings in the vulva; these are the urethral opening for the urinary tract and the vaginal opening for the genital tract. This is different from male mammals, who usually have a single urethral opening for both urination and reproduction. The vaginal opening is much larger than the nearby urethral opening, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perineum
The perineum in humans is the space between the anus and scrotum in the male, or between the anus and the vulva in the female. The perineum is the region of the body between the pubic symphysis (pubic arch) and the coccyx (tail bone), including the perineal body and surrounding structures. There is some variability in how the boundaries are defined. The perineal raphe is visible and pronounced to varying degrees. The perineum is an erogenous zone. The word perineum entered English from late Latin via Greek περίναιος ~ περίνεος ''perinaios, perineos'', itself from περίνεος, περίνεοι 'male genitals' and earlier περίς ''perís'' 'penis' through influence from πηρίς ''pērís'' 'scrotum'. The term was originally understood as a purely male body-part with the perineal raphe seen as a continuation of the scrotal septum since masculinization causes the development of a large anogenital distance in men, in comparison to the corresponding lack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labia Majora
The labia majora (singular: ''labium majus'') are two prominent longitudinal cutaneous folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum. Together with the labia minora they form the labia of the vulva. The labia majora are homologous to the male scrotum. Etymology ''Labia majora'' is the Latin plural for big ("major") lips; the singular is ''labium majus.'' The Latin term ''labium/labia'' is used in anatomy for a number of usually paired parallel structures, but in English it is mostly applied to two pairs of parts of female external genitals (vulva)—labia majora and labia minora. Labia majora are commonly known as the outer lips, while labia minora (Latin for ''small lips''), which run alongside between them, are referred to as the inner lips. Traditionally, to avoid confusion with other lip-like structures of the body, the labia of female genitals were termed by anatomists in Latin as ''labia majora (''or ''minora) pudendi.'' Embryology Embryolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clitoral Glans
The clitoris ( or ) is a female sex organ present in mammals, ostriches and a limited number of other animals. In humans, the visible portion – the glans – is at the front junction of the labia minora (inner lips), above the opening of the urethra. Unlike the penis, the male homologue (equivalent) to the clitoris, it usually does not contain the distal portion (or opening) of the urethra and is therefore not used for urination. In most species, the clitoris lacks any reproductive function. While few animals urinate through the clitoris or use it reproductively, the spotted hyena, which has an especially large clitoris, urinates, mates, and gives birth via the organ. Some other mammals, such as lemurs and spider monkeys, also have a large clitoris. The clitoris is the human female's most sensitive erogenous zone and generally the primary anatomical source of human female sexual pleasure. In humans and other mammals, it develops from an outgrowth in the embry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clitoris
The clitoris ( or ) is a female sex organ present in mammals, ostriches and a limited number of other animals. In humans, the visible portion – the glans – is at the front junction of the labia minora (inner lips), above the opening of the urethra. Unlike the penis, the male homologue (equivalent) to the clitoris, it usually does not contain the distal portion (or opening) of the urethra and is therefore not used for urination. In most species, the clitoris lacks any reproductive function. While few animals urinate through the clitoris or use it reproductively, the spotted hyena, which has an especially large clitoris, urinates, mates, and gives birth via the organ. Some other mammals, such as lemurs and spider monkeys, also have a large clitoris. The clitoris is the human female's most sensitive erogenous zone and generally the primary anatomical source of human female sexual pleasure. In humans and other mammals, it develops from an outgrowth in the embry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pudendal Cleft
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, vulval vestibule, urinary meatus, the vaginal opening, hymen, and Bartholin's and Skene's vestibular glands. The urinary meatus is also included as it opens into the vulval vestibule. Other features of the vulva include the pudendal cleft, sebaceous glands, the urogenital triangle (anterior part of the perineum), and pubic hair. The vulva includes the entrance to the vagina, which leads to the uterus, and provides a double layer of protection for this by the folds of the outer and inner labia. Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support. Blood supply to the vulva comes from the three pudendal arteries. The internal pudendal veins give drainage. Afferent lymph vessels carr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)