|
Inishbofin, Galway
Inishbofin (derived from the Irish ''Inis Bó Finne'' meaning 'Island of the White Cow') is a small island off the coast of Connemara, County Galway, Ireland. Inishbofin has around 180 inhabitants and is a tourist destination. Name The island's English name Inishbofin is derived from the Irish name ''Inis Bó Finne'' ('Island of the White Cow'). There are several legends concerning the origins of the island's name. According to one legend, the island was actually a floating place until some fishermen landed on it in a fog. By bringing fire onto the island, they dispelled the magic, fixing it in place. They then saw an old woman driving a white cow, which turned into a rock when the woman struck it with a stick. The Irish name has also been anglicised as 'Innisboffin' and 'Boffin' or 'Bophin' island. Geology and topography Inishbofin lies around off the Connemara coast opposite of Ballinakill Harbour and Cleggan Bay. It is separated by a narrow channel from Inishark (Shark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N. Scientific explorations of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern history, modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Middle Ages, Early, High Middle Ages, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
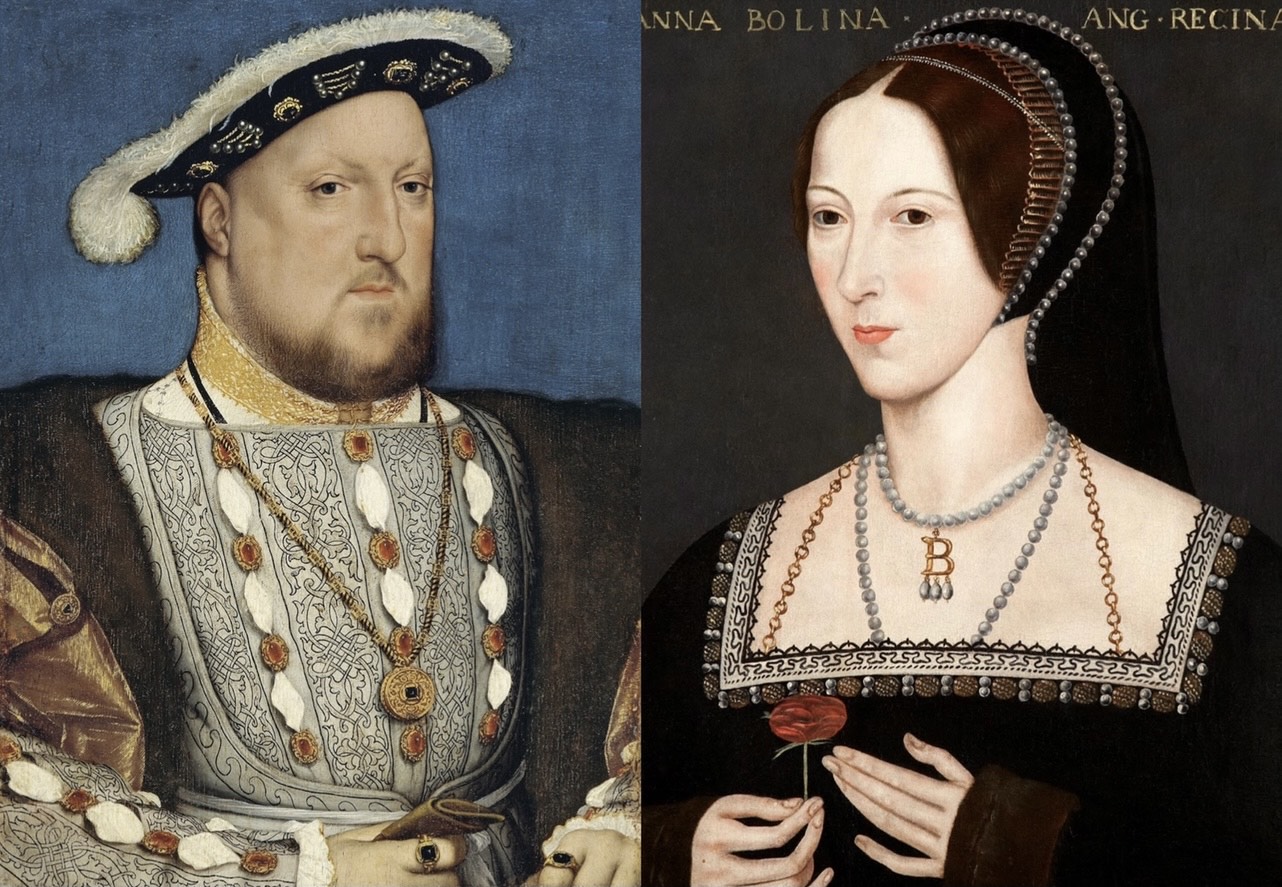
Elizabeth I Of England
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen". Elizabeth was the daughter of Henry VIII and Anne Boleyn, his second wife, who was executed when Elizabeth was two years old. Anne's marriage to Henry was annulled, and Elizabeth was for a time declared Royal bastard, illegitimate. Her half-brother Edward VI ruled until his death in 1553, bequeathing the crown to Lady Jane Grey and ignoring the claims of his two half-sisters, the Catholic Church, Catholic Mary I of England, Mary and the younger Elizabeth, in spite of Third Succession Act, statute law to the contrary. Edward's will was set aside and Mary became queen, deposing Lady Jane Grey. During Mary's reign, Elizabeth was imprisoned for nearly a year on suspicion of supporting Protestant reb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
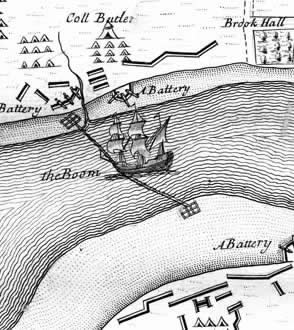
Boom (navigational Barrier)
A boom or a chain (also boom defence, harbour chain, river chain, chain boom, boom chain or variants) is an obstacle strung across a navigable stretch of water to control or block navigation. In modern times they usually have civil uses, such as to prevent access to a dangerous river channel. But, especially historically, they have been used militarily, with the goal of denying access to an enemy's ships: a modern example is the anti-submarine net. Booms have also been used to force passing vessels to pay a toll. Description A boom generally floats on the surface, while a chain can be on the surface or below the water. A chain could be made to float with rafts, logs, ships or other wood, making the chain a boom as well. Historical uses Especially in medieval times, the end of a chain could be attached to a chain tower or boom tower. This allowed safe raising or lowering of the chain, as they were often heavily fortified. By raising or lowering a chain or boom, access could be s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gráinne O'Malley
Grace O'Malley ( – c. 1603), also known as Gráinne O'Malley ( ga, Gráinne Ní Mháille, ), was the head of the Ó Máille dynasty in the west of Ireland, and the daughter of Eóghan Dubhdara Ó Máille. In Irish folklore she is commonly known as ''Gráinne Mhaol'' (anglicised as Granuaile) and is a well-known historical figure in sixteenth-century Irish history. Her name also was rendered in contemporaneous English documents in various ways, including Gráinne O'Maly, Graney O'Mally, Granny ni Maille, Grany O'Mally, Grayn Ny Mayle, Grane ne Male, Grainy O'Maly, and Granee O'Maillie, rarely as Grace O'MalleyIn popular culture she is often referred to as "The Pirate Queen". O'Malley is not mentioned in the Irish annals, so documentary evidence for her life comes mostly from English sources, especially the eighteen "Articles of Interrogatory", questions put to her in writing on behalf of Elizabeth I.See the supplement to Chambers, 2003. She is mentioned in the English State P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alonzo Bosco
Don Alonzo Bosco was a 16th-century Barbary corsair or Spanish pirate who, according to folk tradition on Inishbofin, Galway, settled on the island in the 16th century and built a castle where a Cromwellian-era ruined castle now stands. From there, he raided the mainland and passing ships. He became an ally of Grace O'Malley. Together they prevented unwanted intruders from entering the surrounding waters, or they used the natural harbour as a trap to attack and loot those ships with valuable cargo on board. They succeeded by stretching a chain boom across the harbour entrance from the castle at the harbour to Scealp na gCat at the opposite end. His ultimate fate is unknown. References * ''A Guide to Connemara's Early Christian Sites'', Anthony Previté, Oughterard Oughterard () is a small town on the banks of the Owenriff River close to the western shore of Lough Corrib in Connemara, County Galway, Ireland. The population of the town in 2016 was 1,318. It is located a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbary Pirates
The Barbary pirates, or Barbary corsairs or Ottoman corsairs, were Muslim pirates and privateers who operated from North Africa, based primarily in the ports of Salé, Rabat, Algiers, Tunis and Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli. This area was known in Europe as the Barbary Coast, in reference to the Berbers. Their predation extended throughout the Mediterranean, south along West Africa's Atlantic seaboard and into the North Atlantic as far north as Turkish Abductions, Iceland, but they primarily operated in the western Mediterranean. In addition to seizing merchant ships, they engaged in ''Razzia (military), Razzias'', raids on European coastal towns and villages, mainly in Italy, France, Spain and Portugal, but also in the British Isles, the Netherlands and Iceland. The main purpose of their attacks was to capture slaves for the Slavery in the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman slave trade as well as the general Arab slavery market in North Africa and the Middle East. Slaves in Barbary could be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pirate
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, vessels used for piracy are pirate ships. The earliest documented instances of piracy were in the 14th century BC, when the Sea Peoples, a group of ocean raiders, attacked the ships of the Aegean and Mediterranean civilisations. Narrow channels which funnel shipping into predictable routes have long created opportunities for piracy, as well as for privateering and commerce raiding. Historic examples include the waters of Gibraltar, the Strait of Malacca, Madagascar, the Gulf of Aden, and the English Channel, whose geographic structures facilitated pirate attacks. The term ''piracy'' generally refers to maritime piracy, although the term has been generalized to refer to acts committed on land, in the air, on computer networks, and (in scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kings Of Umaill
The Kings of Umaill were rulers of Umaill, a kingdom or territory located in the west of what is now County Mayo, Ireland. Its earliest rulers were the semi-historical Tuath mhac nUmhoir. The Umaill, its early historical rulers, were renamed the Uí Briúin Umaill to claim a fictitious relationship with the Uí Briúin. By the 12th century the ruling family adopted the surname Ó Máille, and were reckoned with the Ó Dubhda, Ó Flaithbheartaigh and Mac Conraoi as supreme seafaring clans of Connacht. Kings of Umaill * Flannabhra, died 773 * Dunghal mac Flaithniadh, died 776 * Aedhghal, died 779 * Flathghal mac Flannbhrath, died 782 * Cosgrach mac Flannbhrath, died 812 * Cairbre mac Cinaedh, died 847 * Gilla na nInghen Ua Cobhthaigh, died 1004 * Domhnall Ua Máille, died 1176 * Domnall Ruadh Ó Máille, died 11 November 1337 * Owen Ó Máille, died 1362 * Diarmuid mac Owen Ó Máille, died 1362 * Donell Ó Máille, 1401 (''Donnell O'Malley, Lord of Umallia, died, after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guairim Of Inisbofin
Guairim of Inisbofin () was chief of Inishbofin, Galway. Biography Little is known of Guairim. He is said to have been a contemporary of Colmán of Lindisfarne who founded a monastery on the island in 665. A site adjacent to the harbour on some old maps was called 'Guairim's Castle'; the presbytery is now located there. Another site, listed on the Ordnance Survey maps as Áit Tigh Ghuairim was located in the townland of Bunamullen. Stones from it were taken to build the parochial house. Guairim is supposed to have murdered six of Colmán's monks at Clossy Road, "over a question of tithes." ''Traditional lore, used to tell of blood flowing from the earth at this site. Guairim was taken to Renvyle and tried, then chained to a rock at low tide and left to drown.'' See also * Seven Sisters of Renvyle The Seven Sisters of Renvyle were Medieval Irish people, said to be the daughters of a King of Leinster, or a chief of Omey Island. They preached along the coast of Conmhaícn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden), who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9–22. They also voyaged as far as the Mediterranean, North Africa, Volga Bulgaria, the Middle East, and North America. In some of the countries they raided and settled in, this period is popularly known as the Viking Age, and the term "Viking" also commonly includes the inhabitants of the Scandinavian homelands as a collective whole. The Vikings had a profound impact on the early medieval history of Scandinavia, the British Isles, France, Estonia, and Kievan Rus'. Expert sailors and navigators aboard their characteristic longships, Vikings established Norse settlements and governments in the Viking activity in the British Isles, British Isles, the Faroe Islands, Settlement of Iceland, Icela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |