|
Ingeborg Of Denmark, Queen Of France
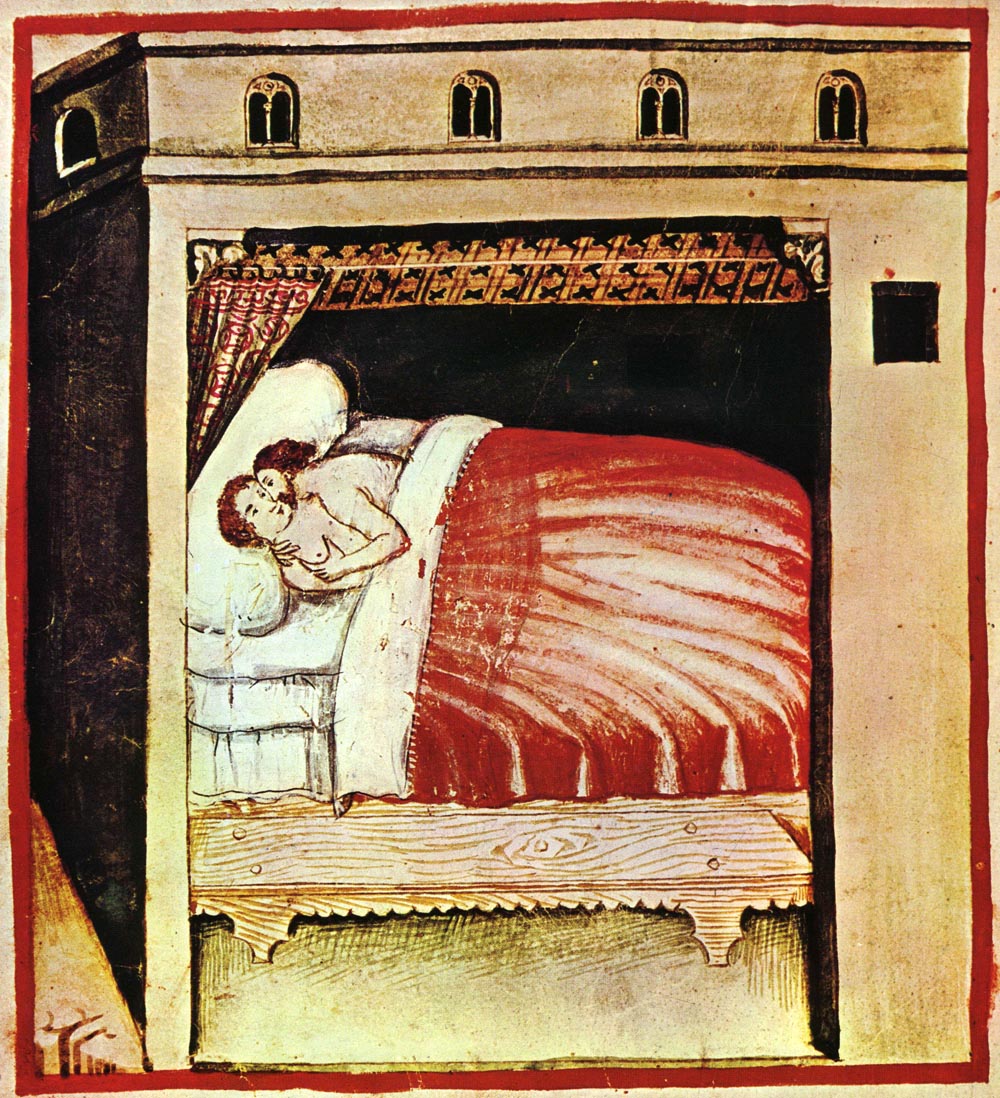
Ingeborg of Denmark (french: Ingeburge; 1174 – 29 July 1237) was Queen of France by marriage to Philip II of France. She was a daughter of Valdemar I of Denmark and Sofia of Minsk. Marriage Ingeborg was married to Philip II Augustus of France on 14 August 1193, after the death of Philip's first wife Isabelle of Hainaut (d. 1190). Her marriage brought a large dowry from her brother King Canute VI of Denmark. Stephen of Tournai described her as "''very kind, young of age but old of wisdom''." On the day after his marriage to Ingeborg, King Philip changed his mind, wished to obtain a separation and attempted to send her back to Denmark. Outraged, Ingeborg fled to a convent in Soissons, from where she protested to Pope Celestine III. Three months after the wedding, Philip summoned an ecclesiastical council in Compiègne and had it draw a false family tree to show that he and Ingeborg would have been related through Philip's first wife. Contemporary Canon law stated that a man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Consort Of France
This is a list of the women who were queen consort, queens or Emperor, empresses as wives of List of French monarchs, French monarchs from the 843 Treaty of Verdun, which gave rise to West Francia, until 1870, when the French Third Republic, Third Republic was declared. Living wives of reigning monarchs technically became queen consorts, including Margaret of Burgundy, Queen of France, Margaret of Burgundy and Blanche of Burgundy who were kept in prison during their whole queenships. Carolingian dynasty Capetian dynasty Direct Capetians House of Valois House of Lancaster Some sources refer to Margaret of Anjou as Queen of France,Mary Ann Hookham: "The life and times of Margaret of Anjou, queen of England and France ", 1872 but her right to enjoy that title is disputed. She was briefly recognized only in English-controlled territories of France. (See also: Dual monarchy of England and France) Capetian dynasty House of Valois House of Valois-Orléans House ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annulment
Annulment is a legal procedure within Law, secular and Religious law, religious legal systems for declaring a marriage Void (law), null and void. Unlike divorce, it is usually ex post facto law, retroactive, meaning that an annulled marriage is considered to be invalid from the beginning almost as if it had never taken place (though some jurisdictions provide that the marriage is only void from the date of the annulment; for example, this is the case in section 12 of the Matrimonial Causes Act 1973 in England and Wales). In legal terminology, an annulment makes a void marriage or a voidable marriage null.John L. Esposito (2002), Women in Muslim Family Law, Syracuse University Press, , pp. 33–34 Void vs voidable marriage A difference exists between a ''void marriage'' and a ''voidable marriage''. A void marriage is a marriage that was not legally valid under the laws of the jurisdiction where the marriage occurred, and is void (law), void ''ab initio''. Although the marriage i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genealogy
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kinship and pedigrees of its members. The results are often displayed in charts or written as narratives. The field of family history is broader than genealogy, and covers not just lineage but also family and community history and biography. The record of genealogical work may be presented as a "genealogy", a "family history", or a "family tree". In the narrow sense, a "genealogy" or a "family tree" traces the descendants of one person, whereas a "family history" traces the ancestors of one person, but the terms are often used interchangeably. A family history may include additional biographical information, family traditions, and the like. The pursuit of family history and origins tends to be shaped by several motives, including the desire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Of Æbelholt
William of Æbelholt (also known as Vilhelm of Æbelholt, William of Eskilsø and William of Paris) (d. Easter Sunday, 1203) was a French-born churchman of Denmark. Early life William was born of a noble French family and educated by his uncle Hugh, forty-second abbot of Saint-Germain-des-Prés at Paris, and, having been ordained subdeacon, received a prebend in the church of Sainte-Geneviève-du-Mont."St. William of Paris." The Catholic Encyclopedia Vol. 15. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1912. 18 Dec.ember 2021 William reportedly sought entry into a stricter house (either a or a |
Sweating Sickness
Sweating sickness, also known as the sweats, English sweating sickness, English sweat or ''sudor anglicus'' in Latin, was a mysterious and contagious disease that struck England and later continental Europe in a series of epidemics beginning in 1485. The last outbreak occurred in 1551, after which the disease apparently vanished. The onset of symptoms was sudden, with death often occurring within hours. Sweating sickness epidemics were unique compared with other disease outbreaks of the time: whereas other epidemics were typically urban and long-lasting, cases of sweating sickness spiked and receded very quickly, and heavily affected rural populations. Its cause remains unknown, although it has been suggested that an unknown species of hantavirus was responsible. Signs and symptoms John Caius was a physician in Shrewsbury in 1551, when an outbreak occurred, and he described the symptoms and signs of the disease in ''A Boke or Counseill Against the Disease Commonly Called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impotence
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also called impotence, is the type of sexual dysfunction in which the penis fails to become or stay erect during sexual activity. It is the most common sexual problem in men.Cunningham GR, Rosen RC. Overview of male sexual dysfunction. In: UpToDate, Martin KA (Ed), UpToDate, Waltham, MA, 2018. Through its connection to self-image and to problems in sexual relationships, erectile dysfunction can cause psychological harm. In about 80% of cases, physical causes can be identified. These include cardiovascular disease; diabetes mellitus; neurological problems, such as those following prostatectomy; hypogonadism; and drug side effects. About 10% of cases are psychological impotence, caused by thoughts or feelings; here, there is a strong response to placebo treatment. The term ''erectile dysfunction'' is not used for other disorders of erection, such as priapism. Treatment involves addressing the underlying causes, lifestyle modifications, and addr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consummate
In many traditions and statutes of civil or religious law, the consummation of a marriage, often called simply ''consummation'', is the first (or first officially credited) act of sexual intercourse between two people, following their marriage to each other. The definition of consummation usually refers to penile-vaginal sexual penetration, but some religious doctrines hold that there is an additional requirement that no contraception must be used. The religious, cultural, or legal significance of consummation may arise from theories of marriage as having the purpose of producing legally recognized descendants of the partners, or of providing sanction to their sexual acts together, or both, and its absence may amount to treating a marriage ''ceremony'' as falling short of ''completing'' the state of being married, or as creating a marriage which may later be repudiated. Thus in some legal systems a marriage may be annulled if it has not been consummated. Consummation is also relev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Æbelholt Abbey
Æbelholt Abbey ( da, Æbelholt Kloster) was an Augustinian monastery situated at Tjæreby in Hillerød municipality in North Zealand, Denmark. History William of Æbelholt The monastery was first established on Eskilsø Island in Roskilde Fjord in 1104. The stone abbey church still remains in ruins. It was 24 meters long and had a nave, choir, and apse in the Romanesque style. Bishop Absalon of Roskilde, determined to obtain a new Augustinian superior, sent for his friend, Abbot William (''Abbed Vilhelm'') of Sainte-Geneviève in Paris. When Abbot William arrived in 1165 with three French Canons Regular there were only six religious left at Eskilsø, two of whom were dismissed when they refused to submit to the new rule. In 1167 the abbey moved to Æbelholt in Tjæreby, supported by a donation of land from Absalon in Tjæreby Parish and endowed with several income-producing farms, tithes from many north Zealand churches, and several mills. The monastery on Eskilsø was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knud VI Of Denmark
Canute VI (; c. 1163 – 12 November 1202) was King of Denmark (1182–1202). Contemporary sources describe Canute as an earnest, strongly religious man. Background Canute VI was the eldest son of King Valdemar I and Sophia of Polotsk. His younger brother Valdemar was born in 1170. In 1170, at age 7, Canute was proclaimed co-regent of Denmark with his father. Reign Following his father's death in 1182, Canute became sole ruler and King of Denmark in 1182. at the Urnehoved Assembly (Danish: ''landsting'') and subsequently at the other assemblies throughout Denmark. He immediately faced a peasant uprising in Skåne. The peasants refused to pay Bishop Absalon's tithe. They met at the Skåne Assembly and chose Harald Skreng, one of Canute friends to represent them to the king to plead their case. The king refused to hear Skreng out and began to gather an army to teach the peasants their place. Before the king could muster his army, the nobles of Halland and Skåne cobb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dowry
A dowry is a payment, such as property or money, paid by the bride's family to the groom or his family at the time of marriage. Dowry contrasts with the related concepts of bride price and dower. While bride price or bride service is a payment by the Bridegroom, groom, or his family, to the bride, or her family, dowry is the wealth transferred from the bride, or her family, to the groom, or his family. Similarly, dower is the property settled on the bride herself, by the groom at the time of marriage, and which remains under her ownership and control. Dowry is an ancient custom that is already mentioned in some of the earliest writings, and its existence may well predate records of it. Dowries continue to be expected and demanded as a condition to accept a marriage proposal in some parts of the world, mainly in parts of Asia, The custom of dowry is most common in cultures that are strongly patrilineal and that expect women to reside with or near their husband's family (patriloca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angevin Kings Of England
The Angevins (; "from County of Anjou, Anjou") were a royal house of French origin that ruled England in the 12th and early 13th centuries; its monarchs were Henry II of England, Henry II, Richard I of England, Richard I and John, King of England, John. In the 10 years from 1144, two successive count of Anjou, counts of Anjou in France, Geoffrey Plantagenet, Count of Anjou, Geoffrey and his son, the future Henry II, won control of a vast assemblage of lands in western Europe that would last for 80 years and would retrospectively be referred to as the Angevin Empire. As a political entity this was structurally different from the preceding House of Normandy, Norman and subsequent House of Plantagenet, Plantagenet realms. Geoffrey became Duke of Normandy in 1144 and died in 1151. In 1152, his heir, Henry, added Duchy of Aquitaine, Aquitaine by virtue of his marriage to Eleanor of Aquitaine. Henry also inherited the claim of his mother, Empress Matilda, the daughter of Henry I of Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_-_no_watermark.jpg)
.jpg)
