|
Information Processing Technology And Aging
An important factor to be considered with old age is cognitive decline. These information technologies need to be centered on factors that define cognition. This article highlights some of the important conceptual models and theories that govern the design of such systems. The main focus is to look at the different information processing technologies that are presently used for enabling better functional performance. As baby boomers grow older, there exists a growing demand for a good support system that can ease their burden. Technology is ubiquitous in most social contexts in industrialized countries, and has become an important part of everyday life as an integral component of most activities. The advent of technology has shown promising results in various fields such as the delivery of care and in-vehicle driving technology by focusing on the needs of older adults and placing them at the center of this transformation. Such systems would work in favor of improving and empoweri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dementia
Dementia is a disorder which manifests as a set of related symptoms, which usually surfaces when the brain is damaged by injury or disease. The symptoms involve progressive impairments in memory, thinking, and behavior, which negatively affects a person's ability to function and carry out everyday activities. Aside from memory impairment and a disruption in thought patterns, the most common symptoms include emotional problems, difficulties with language, and decreased motivation. The symptoms may be described as occurring in a continuum over several stages. Consciousness is not affected. Dementia ultimately has a significant effect on the individual, caregivers, and on social relationships in general. A diagnosis of dementia requires the observation of a change from a person's usual mental functioning, and a greater cognitive decline than what is caused by normal aging. Several diseases and injuries to the brain, such as a stroke, can give rise to dementia. However, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Processing Theory
Information processing theory is the approach to the study of cognitive development evolved out of the American experimental tradition in psychology. Developmental psychologists who adopt the information processing perspective account for mental development in terms of maturational changes in basic components of a child's mind. The theory is based on the idea that humans process the information they receive, rather than merely responding to stimuli. This perspective uses an analogy to consider how the mind works like a computer. In this way, the mind functions like a biological computer responsible for analyzing information from the environment. According to the standard information-processing model for mental development, the mind's machinery includes attention mechanisms for bringing information in, working memory for actively manipulating information, and long-term memory for passively holding information so that it can be used in the future. This theory addresses how as chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schema (psychology)
In psychology and cognitive science, a schema (plural ''schemata'' or ''schemas'') describes a pattern of thought or behavior that organizes categories of information and the relationships among them. It can also be described as a mental structure of preconceived ideas, a framework representing some aspect of the world, or a system of organizing and perceiving new information, such as a mental schema or conceptual model. Schemata influence attention and the absorption of new knowledge: people are more likely to notice things that fit into their schema, while re-interpreting contradictions to the schema as exceptions or distorting them to fit. Schemata have a tendency to remain unchanged, even in the face of contradictory information. Schemata can help in understanding the world and the rapidly changing environment. People can organize new perceptions into schemata quickly as most situations do not require complex thought when using schema, since automatic thought is all that is r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual-coding Theory
Dual-coding theory, a theory of cognition, was hypothesized by Allan Paivio of the University of Western Ontario in 1971. In developing this theory, Paivio used the idea that the formation of mental images aids learning. According to Paivio, there are two ways a person could expand on learned material: verbal associations and imagery. Dual-coding theory postulates that both sensory imagery and verbal information is used to represent information. Imagery and verbal information are processed differently and along distinct channels in the human mind, creating separate representations for information processed in each channel. The mental codes corresponding to these representations are used to organize incoming information that can be acted upon, stored, and retrieved for subsequent use. Both imagery and verbal codes can be used when recalling information. For example, say a person has stored the stimulus concept "dog" as both the word 'dog' and as the image (appearance, sound, smell, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levels-of-processing Effect
The Levels of Processing model, created by Fergus I. M. Craik and Robert S. Lockhart in 1972, describes memory recall of stimuli as a function of the depth of mental processing. Deeper levels of analysis produce more elaborate, longer-lasting, and stronger memory traces than shallow levels of analysis. Depth of processing falls on a shallow to deep continuum. Shallow processing (e.g., processing based on phonemic and orthographic components) leads to a fragile memory trace that is susceptible to rapid decay. Conversely, deep processing (e.g., semantic processing) results in a more durable memory trace. This theory contradicts the multi-store Atkinson-Shiffrin memory model which represents memory strength as being continuously variable, the assumption being that rehearsal always improves long-term memory. They argued that rehearsal that consists simply of repeating previous analyses (maintenance rehearsal) doesn't enhance long-term memory. In a study from 1975 (Craik and Tulvi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive psychology is the scientific study of mental processes such as attention, language use, memory, perception, problem solving, creativity, and reasoning. Cognitive psychology originated in the 1960s in a break from behaviorism, which held from the 1920s to 1950s that unobservable mental processes were outside the realm of empirical science. This break came as researchers in linguistics and cybernetics, as well as applied psychology, used models of mental processing to explain human behavior. Work derived from cognitive psychology was integrated into other branches of psychology and various other modern disciplines like cognitive science, linguistics, and economics. The domain of cognitive psychology overlaps with that of cognitive science, which takes a more interdisciplinary approach and includes studies of non-human subjects and artificial intelligence. History Philosophically, ruminations on the human mind and its processes have been around since the times of the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
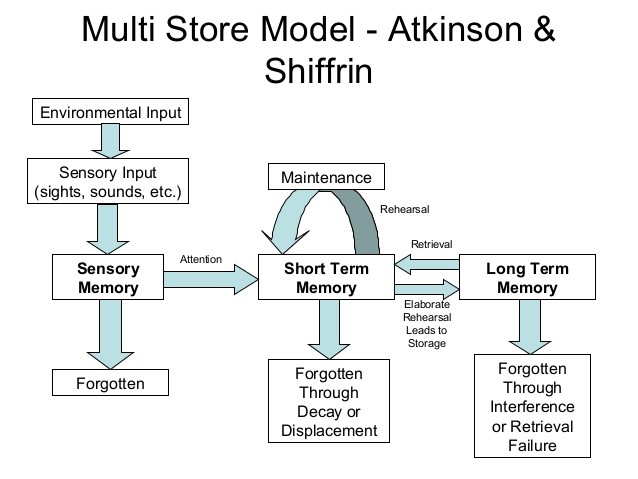
Atkinson–Shiffrin Memory Model
The Atkinson–Shiffrin model (also known as the multi-store model or modal model) is a model of memory proposed in 1968 by Richard Atkinson and Richard Shiffrin. The model asserts that human memory has three separate components: # a '' sensory register'', where sensory information enters memory, # a '' short-term store'', also called ''working memory'' or ''short-term memory'', which receives and holds input from both the sensory register and the long-term store, and # a '' long-term store'', where information which has been rehearsed (explained below) in the short-term store is held indefinitely. Since its first publication, this model has come under much scrutiny and has been criticized for various reasons (described below). However, it is notable for the significant influence it had in stimulating subsequent memory research. Summary The model of memories is an explanation of how memory processes work. The three-part, multi-store model was first described by Atkinson and Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Processing Theory
Information processing theory is the approach to the study of cognitive development evolved out of the American experimental tradition in psychology. Developmental psychologists who adopt the information processing perspective account for mental development in terms of maturational changes in basic components of a child's mind. The theory is based on the idea that humans process the information they receive, rather than merely responding to stimuli. This perspective uses an analogy to consider how the mind works like a computer. In this way, the mind functions like a biological computer responsible for analyzing information from the environment. According to the standard information-processing model for mental development, the mind's machinery includes attention mechanisms for bringing information in, working memory for actively manipulating information, and long-term memory for passively holding information so that it can be used in the future. This theory addresses how as chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Cues
''Social Cues'' is the fifth studio album by American rock band Cage the Elephant. Announced on January 31, 2019, the album was released on April 19, 2019. The album is the first by the band to feature a title track. Social Cues won the award for Best Rock Album at the 62nd Annual Grammy Awards, making it the band's second album to win the award after ''Tell Me I'm Pretty''. Background On November 26, 2018, the band announced on Twitter that their new album was "Done. Mixed. Mastered." On January 31, 2019, the band officially released "Ready to Let Go", the first single from ''Social Cues''. On March 8, 2019, "House of Glass", the second advance track from the album was released. A collaboration with Beck, "Night Running" was released on March 28, 2019. The final song released in advance of the album was "Goodbye", released on April 8, 2019. Many of the songs (Such as "Goodbye", "Ready to Let Go", and "Love's the Only Way") were based on the divorce that Matt Shultz went through wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinicians
A clinician is a health care professional typically employed at a skilled nursing facility or clinic. Clinicians work directly with patients rather than in a laboratory or as a researcher. A clinician may diagnose, treat, and otherwise care for patients. For example, psychologists, clinical pharmacists, clinical scientists, nurses, physiotherapists, dentists, optometrists, physician assistants and physicians can be considered clinicians. Many clinicians take comprehensive exams to be licensed and some complete graduate degrees (master's or doctorates) in their field of expertise. A main function of a clinician is to manage a sick person in order to cure the effects of their illness. The clinician can also consider the impact of illness upon the patient and his or her family, as well as other social factors. See also * List of healthcare occupations A listing of health care professions by medical discipline. Anesthesiology * Anesthesiologist * Anesthesiology Fellow * Certifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schedules
A schedule or a timetable, as a basic time-management tool, consists of a list of times at which possible tasks, events, or actions are intended to take place, or of a sequence of events in the chronological order in which such things are intended to take place. The process of creating a schedule — deciding how to order these tasks and how to commit resources between the variety of possible tasks — is called scheduling,Ofer Zwikael, John Smyrk, ''Project Management for the Creation of Organisational Value'' (2011), p. 196: "The process is called scheduling, the output from which is a timetable of some form". and a person responsible for making a particular schedule may be called a scheduler. Making and following schedules is an ancient human activity. Some scenarios associate this kind of planning with learning life skills. Schedules are necessary, or at least useful, in situations where individuals need to know what time they must be at a specific location to receive a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Information
Medical information may refer to: *Medical record, individual *Health information, general See also *Medical information on Wikipedia The Wikipedia online encyclopedia has, since the late 2000s, served as a popular source for health information for both laypersons and, in many cases, health care practitioners. Health-related articles on Wikipedia are popularly accessed as resul ... * Medical Information Bureau, a membership corporation owned by insurance companies in the United States and Canada * Medical Information Technology (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |