|
Inequality Within Immigrant Families In The United States
Inequality within immigrant families refers to instances in which members of the same family have differing access to resources. Much literature focuses on inequality between families, but inequality often exists within families as well. Though within-family inequality is not unique to immigrant families, the processes of migration and assimilation into American society provide new channels through which such inequality may emerge. Legal status Immigrants to the United States vary widely in terms of their citizenship status. Some immigrants may lack documentation altogether. An individual's legal status in the United States determines many of the resources available to him or her. Legal status can thus provide the basis for many inequalities in the home. Mixed-status families The Citizenship Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution guarantees citizenship status to anyone born on United States soil "and subject to the jurisdiction thereof". This means t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citizenship Clause
The Citizenship Clause is the first sentence of the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which was adopted on July 9, 1868, which states: This clause reversed a portion of the ''Dred Scott v. Sandford'' decision, which had declared that African Americans were not and could not become citizens of the United States or enjoy any of the privileges and immunities of citizenship. The concepts of state and national citizenship were already mentioned in the original U.S. Constitution adopted in 1789, but the details were unclear. Prior to the Civil War, only some persons born or naturalized in the United States, and subject to the jurisdiction thereof, were citizens of the United States and of the state wherein they reside, according to the various applicable state and federal laws and court decisions. The Civil Rights Act of 1866 granted U.S. citizenship to all persons born in the United States "not subject to any foreign power". The 39th Congress proposed the prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immigrant Health Care In The United States
Immigrant health care in the United States refers to the collective systems in the United States that deliver health care services to immigrants. The term "immigrant" is often used to encompass non-citizens of varying status; this includes permanent legal residents, refugees, and undocumented residents. Immigrant health care is considered distinct from citizen health care, due to intersecting socioeconomic factors and health policies associated with immigration status. Disparities in health care usage, coverage, and quality are also observed, not only between immigrants and citizens but also among immigrant groups as well. Existing studies have revealed strong correlation of these disparities with a combination of structural and social factors, including lack of insurance, high costs of care, restrictions associated with undocumented status, perceptions of discrimination, and language barriers. Intersections of health and immigration policies also create distinctive outcomes for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Assimilation
Cultural assimilation is the process in which a minority group or culture comes to resemble a society's majority group or assume the values, behaviors, and beliefs of another group whether fully or partially. The different types of cultural assimilation include full assimilation and forced assimilation; full assimilation being the most prevalent of the two, as it occurs spontaneously. During cultural assimilation, minority groups are expected to adapt to the everyday practices of the dominant culture through language and appearance as well as via more significant socioeconomic factors such as absorption into the local cultural and employment community. Some types of cultural assimilation resemble acculturation in which a minority group or culture completely assimilates into the dominant culture in which defining characteristics of the minority culture are less obverse or outright disappear; while in other types of cultural assimilation such as cultural integration mostly found i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Work–family Balance In The United States
Work–family balance in the United States refers to the specific issues that arise when men and women in the United States attempt to balance their occupational lives with their family lives. This differs from work–life balance in the United States: while work–life balance may refer to the health and living issues that arise from work, work–family balance refers specifically to how work and families intersect and influence each other. Work–family balance in the U.S. differs significantly for families of different social class. Middle-class family issues center on dual-earner spouses and parents while lower class issues center on problems that arise due to single parenting. Work–family balance issues also differ by class, since middle class occupations provide more benefits and family support while low-wage jobs are less flexible with benefits. Solutions for helping individuals manage work–family balance in the U.S. include legislation, workplace policies, and the marke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transnational Marriage
A transnational marriage or international marriage is a marriage between two people from different countries. History Transnational marriage has been attested since ancient times, often in instances where royal families sought to form alliances with one another. For example, Hermodike I (c. 800 BC) and Hermodike II (c. 600BC), Greek princesses from the house of Agamemnon, transnationally married kings from what is now central Turkey. These unions resulted in the introduction of ground-breaking technology to Ancient Greeks. Hermodike the First's marriage introduced Greece to the Phoenecian written script while Hermodike the Second's marriage introduced Greece to the use of coinage (to use a token currency, where the value is guaranteed by the state). Both inventions were rapidly adopted by surrounding nations through trade and cooperation and have been of fundamental benefit to the progress of civilization. More recently, transnational marriages have resulted from increasing glob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sociology Of The Family
Sociology of the family is a subfield of the subject of sociology, in which researchers and academics study family structure as a social institution and unit of socialization from various sociological perspectives. It can be seen as an example of patterned social relations and group dynamics. Main areas of focus Methodology Quantitative One of the best known sources for gathering both historical and contemporary data on families is the national census survey. In the United States, the national census occurs in every household every 10 years. There are smaller surveys taken in between called the American Community Survey. Both are held by the larger U.S. Census Bureau and its related subsidiaries in each state. The Census Bureau collects data about American families for the nation, states and communities. Their data provides statistics on trends in household and family composition, and show the number of children, young adults and couples living in the United States. Their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Mobility
Social mobility is the movement of individuals, families, households or other categories of people within or between social strata in a society. It is a change in social status relative to one's current social location within a given society. This movement occurs between layers or tiers in an open system of social stratification. Open stratification systems are those in which at least some value is given to achieved status characteristics in a society. The movement can be in a ''downward'' or ''upward'' direction. Markers for social mobility such as education and class, are used to predict, discuss and learn more about an individual or a group's mobility in society. Typology Mobility is most often quantitatively measured in terms of change in economic mobility such as changes in income or wealth. Occupation is another measure used in researching mobility which usually involves both quantitative and qualitative analysis of data, but other studies may concentrate on social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Inequality
Social inequality occurs when resources in a given society are distributed unevenly, typically through norms of allocation, that engender specific patterns along lines of socially defined categories of persons. It posses and creates gender cap between individuals that limits the accessibility that women have within society. the differentiation preference of access of social goods in the society brought about by power, religion, kinship, prestige, race, ethnicity, gender, age, sexual orientation, and class. Social inequality usually implies the lack of equality of outcome, but may alternatively be conceptualized in terms of the lack of equality of access to opportunity. This accompanies the way that inequality is presented throughout social economies and the rights that are skilled within this basis. The social rights include labor market, the source of income, health care, and freedom of speech, education, political representation, and participation. Social inequality is link ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second-generation Immigrants In The United States
Second-generation immigrants in the United States are individuals born and raised in the United States who have at least one foreign born parent.Suro, Roberto, and Jeffrey Passel. "The Rise of the Second Generation: Changing Patterns in Hispanic Population Growth." Pew Hispanic Center, October 14, 2003. http://pewhispanic.org/files/reports/22.pdf (accessed March 2, 2012). Although the term is an oxymoron which is often used ambiguously, this definition is cited by major research centers including the United States Census Bureau and the Pew Research Center."Nation's Foreign-Born Population Nears 37 Million". Press Release. U.S. Census Bureau. October 19, 2010. https://www.census.gov/newsroom/releases/archives/foreignborn_population/cb10-159.html (accessed March 2, 2012). As the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution guarantees citizenship to any individual born in the U.S. who is also subject to the jurisdiction of the U.S., second-generation Americans are currently g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Migrant Worker
A migrant worker is a person who Human migration, migrates within a home country or outside it to pursue work. Migrant workers usually do not have the intention to stay permanently in the country or region in which they work. Migrant workers who work outside their home country are also called foreign workers. They may also be called expatriates or guest workers, especially when they have been sent for or invited to work in the host country before leaving the home country. The International Labour Organization estimated in 2019 that there were 169 million international migrants worldwide. Some countries have millions of migrant workers. Some migrant workers are undocumented immigrants or slaves. Worldwide An estimated 14 million foreign workers live in the United States, which draws most of its immigrants from Mexico, including 4 or 5 million illegal aliens, undocumented workers. It is estimated that around 5 million foreign workers live in Northwestern Europe, half-a-millio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intra-household Bargaining
Intra-household bargaining refers to negotiations that occur between members of a household in order to arrive at decisions regarding the household unit, like whether to spend or save, whether to study or work. Bargaining is traditionally defined in economic terms of negotiating conditions of a purchase or contract and is sometimes used in place of direct monetary exchange. Bargaining process within a family is one of the important aspects of family economics. Bargaining also plays a role in the functioning and decision making of households, where agreements and decisions do not often have direct monetary values and affect various members of the household. Household dynamics The household is traditionally described as a single economic unit that "works as a group for its own good", meaning all members of the household contribute in an altruistic manner towards the benefit and functioning of the entire household. The household is "the basic residential unit in which economic producti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
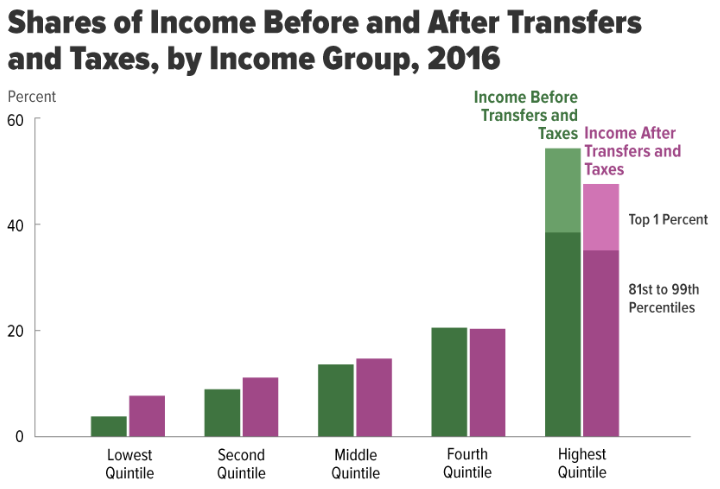
Income Inequality In The United States
Income inequality in the United States is the extent to which income is distributed in differing amounts among the American population. It has fluctuated considerably since measurements began around 1915, moving in an arc between peaks in the 1920s and 2000s, with a 30-year period of relatively lower inequality between 1950 and 1980. The U.S. has the highest level of income inequality among its (post-)industrialized peers.United Press International (UPI), June 22, 2018"U.N. Report: With 40M in Poverty, U.S. Most Unequal Developed Nation"/ref> When measured for all households, U.S. income inequality is comparable to other developed countries before taxes and transfers, but is among the highest after taxes and transfers, meaning the U.S. shifts relatively less income from higher income households to lower income households. In 2016, average market income was $15,600 for the lowest quintile and $280,300 for the highest quintile. The degree of inequality accelerated within the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |