|
Indigenous Decolonization
Indigenous decolonization describes ongoing theoretical and political processes whose goal is to contest and reframe narratives about indigenous community histories and the effects of colonial expansion, cultural assimilation, exploitative Western research, and often though not inherent, genocide.Smith, L. T. (1999). ''Decolonizing Methodologies: Research and Indigenous Peoples''. Zed Books. Indigenous people engaged in decolonization work adopt a critical stance towards western-centric research practices and discourse and seek to reposition knowledge within indigenous cultural practices. The decolonial work that relies on structures of western political thought has been characterized as paradoxically furthering cultural dispossession. In this context, there has been a call for the use of independent intellectual, spiritual, social, and physical reclamation and rejuvenation even if these practices don't translate readily into political recognition. Scholars may also characteriz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
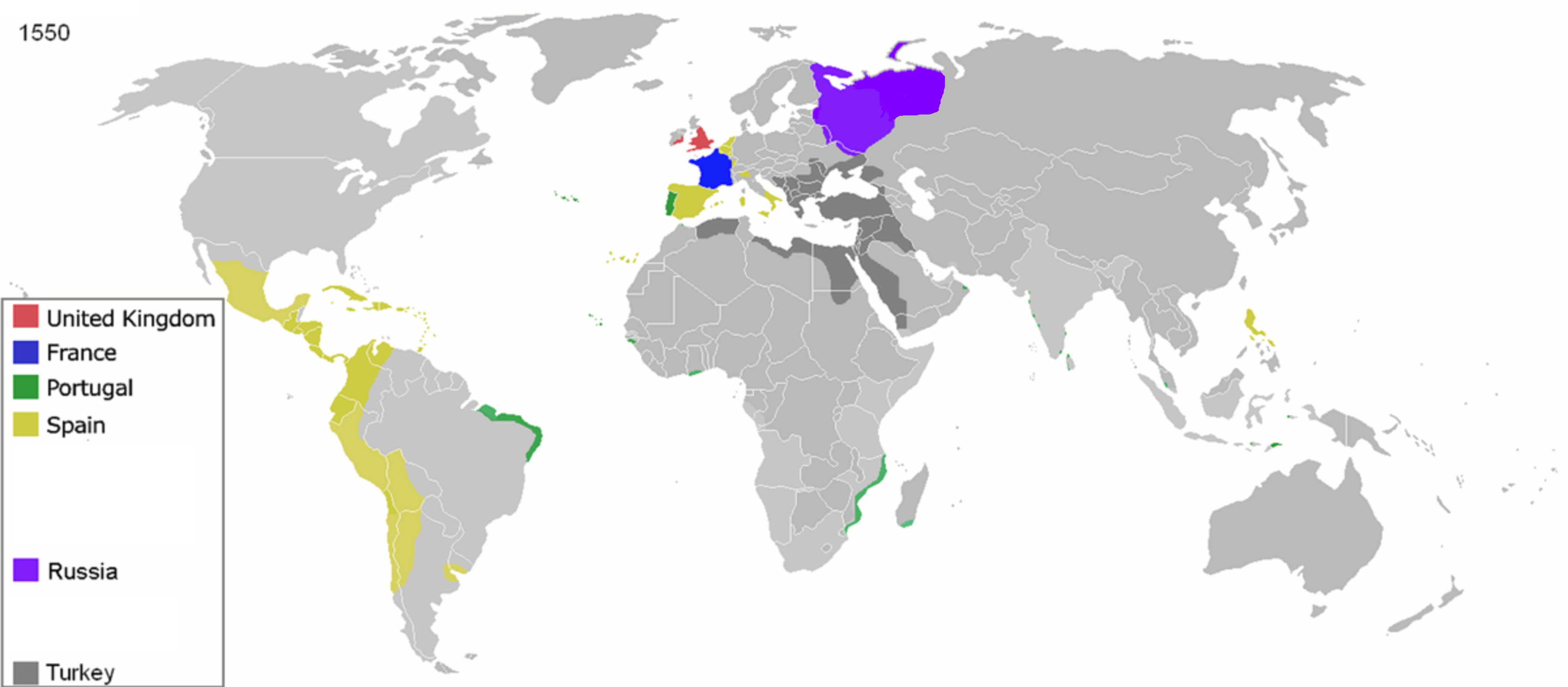
Colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colony, colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their religion, language, economics, and other cultural practices. The foreign administrators rule the territory in pursuit of their interests, seeking to benefit from the colonised region's people and resources. It is associated with but distinct from imperialism. Though colonialism Colonies in antiquity, has existed since ancient times, the concept is most strongly associated with the History of colonialism, European colonial period starting with the 15th century when some European colonial empires, European states established colonising empires. At first, European colonising countries followed policies of mercantilism, aiming to strengthen the home-country economy, so agreements usually restricted the colony to trading only with the metro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decolonization Of Asia
The decolonisation of Asia was the gradual growth of independence movements in Asia, leading ultimately to the retreat of foreign powers and the creation of several nation-states in the region. Background The decline of Spain and Portugal in the 17th century paved the way for other European powers, namely the Netherlands, France and England. Portugal would lose influence in all but three of its colonies, Portuguese India, Macau and Timor. By the end of the 17th century, the Dutch had taken over much of the old Portuguese colonies, and had established a strong presence in present-day Indonesia, with colonies in Aceh, Bantam, Makassar and Jakarta. The Dutch also had trade links with Siam, Japan, China and Bengal. The British had competed with Portuguese, Spanish and Dutch for their interests in Asia since the early 17th century and by the mid-19th century held much of India (via the British East India Company), as well as Burma, Ceylon, Malaya and Singapore. After Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genocide Of Native Americans
The genocide of indigenous peoples, colonial genocide, or settler genocide is elimination of entire communities of indigenous peoples as part of colonialism. Genocide of the native population is especially likely in cases of settler colonialism, with some scholars arguing that settler colonialism is inherently genocidal. While the concept of genocide was formulated by Raphael Lemkin in the mid-20th century, the expansion of various European colonial powers such as the British and Spanish empires and the subsequent establishment of colonies on indigenous territories frequently involved acts of genocidal violence against indigenous groups in the Americas, Australia, Africa, and Asia. According to Lemkin, colonization was in itself "intrinsically genocidal". He saw this genocide as a two-stage process, the first being the destruction of the indigenous population's way of life. In the second stage, the newcomers impose their way of life on the indigenous group. According to Davi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Survivance
Survivance is a critical term in Native American studies. History Survivance was originally a legal term, but fell out of use in the 18th century. It was also borrowed from the French term 'suvivance' in other contexts. Usage It was first employed in the context of Native American Studies by the Anishinaabe cultural theorist Gerald Vizenor, in his 1999 book '' Manifest Manners: Narratives on Postindian Survivance''.Gerald Vizenor, Manifest Manners: Narratives on Postindian Survivance' (Lincoln: Nebraska, 1999) There he explains that "Survivance is an active sense of presence, the continuance of native stories, not a mere reaction, or a survivable name. Native survivance stories are renunciations of dominance, tragedy and victimry".Vizenor (1999), p. vii Vizeno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerald Vizenor
Gerald is a male Germanic given name meaning "rule of the spear" from the prefix ''ger-'' ("spear") and suffix ''-wald'' ("rule"). Variants include the English given name Jerrold, the feminine nickname Jeri and the Welsh language Gerallt and Irish language Gearalt. Gerald is less common as a surname. The name is also found in French as Gérald. Geraldine is the feminine equivalent. Given name People with the name Gerald include: Politicians * Gerald Boland, Ireland's longest-serving Minister for Justice * Gerald Ford, 38th President of the United States * Gerald Gardiner, Baron Gardiner, Lord Chancellor from 1964 to 1970 * Gerald Häfner, German MEP * Gerald Klug, Austrian politician * Gerald Lascelles (other), several people * Gerald Nabarro, British Conservative politician * Gerald S. McGowan, US Ambassador to Portugal * Gerald Wellesley, 7th Duke of Wellington, British diplomat, soldier, and architect Sports * Gerald Asamoah, Ghanaian-born German footb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marie Battiste
Marie Ann Battiste (born 1949) is an author and educator working as a professor in Canada at the University of Saskatchewan in the Department of Educational Foundations. From the Potlotek First Nation in Nova Scotia, Battiste is the daughter of Mi'kmaq parents John and Annie Battiste and is one of four children. Battiste was raised in Houlton, Maine, where she attended high school graduating in 1967. From there she went on to the University of Maine graduating from the Farmington campus in 1971 with her teaching certificate and a bachelor of science in both elementary and junior high education. She went on to attend Harvard University graduating in 1974 with a master of education in administration and social policy as well as Stanford University, where in 1984 she graduated with a doctor of education in curriculum and teacher education. Work After graduating from the University of Maine in 1971 Battiste went on to work at the Maine Indian Education Council where she introduced an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Knowledge
Traditional knowledge (TK), indigenous knowledge (IK) and local knowledge generally refer to knowledge systems embedded in the cultural traditions of regional, indigenous, or local communities. According to the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) and the United Nations (UN), traditional knowledge and traditional cultural expressions (TCE) are both types of indigenous knowledge. Traditional knowledge includes types of knowledge about traditional technologies of subsistence (e.g. tools and techniques for hunting or agriculture), midwifery, ethnobotany and ecological knowledge, traditional medicine, celestial navigation, craft skills, ethnoastronomy, climate, and others. These kinds of knowledge, crucial for subsistence and survival, are generally based on accumulations of empirical observation and on interaction with the environment. In many cases, traditional knowledge has been passed for generations from person to person, as an oral tradition. Some forms of trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereotypes Of Indigenous Peoples Of Canada And The United States
Stereotypes of Indigenous peoples of Canada and the United States of America include many ethnic stereotypes found worldwide which include historical misrepresentations and the oversimplification of hundreds of Indigenous cultures. Negative stereotypes are associated with prejudice and discrimination that continue to affect the lives of Indigenous peoples. Indigenous peoples of the Americas are commonly called Native Americans in the United States (excluding Alaskan and Hawaiian Natives) or First Nations people (in Canada). The Circumpolar peoples of the Americas, often referred to by the English term Eskimo, have a distinct set of stereotypes. Eskimo itself is an exonym, deriving from phrases that Algonquin tribes used for their northern neighbors, in Canada the term Inuit is generally preferred, while Alaska Natives is used in the United States. It is believed that some portrayals of Natives, such as their depiction as bloodthirsty savages have disappeared. However, most po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Assimilation Of Native Americans
The cultural assimilation of Native Americans refers to a series of efforts by the United States to assimilate Native Americans into mainstream European–American culture between the years of 1790 and 1920. George Washington and Henry Knox were first to propose, in the American context, the cultural assimilation of Native Americans. They formulated a policy to encourage the so-called " civilizing process". With increased waves of immigration from Europe, there was growing public support for education to encourage a standard set of cultural values and practices to be held in common by the majority of citizens. Education was viewed as the primary method in the acculturation process for minorities. Americanization policies were based on the idea that when indigenous people learned customs and values of the United States, they would be able to merge tribal traditions with American culture and peacefully join the majority of the society. After the end of the Indian Wars, in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonization
Colonization, or colonisation, constitutes large-scale population movements wherein migrants maintain strong links with their, or their ancestors', former country – by such links, gain advantage over other inhabitants of the territory. When colonization takes place under the protection of colonial structures, it may be termed settler colonialism. This often involves the settlers dispossessing indigenous inhabitants, or instituting legal and other structures which disadvantage them. Colonization can be defined as a process of establishing foreign control over target territories or peoples for the purpose of cultivation, often by establishing colonies and possibly by settling them. In colonies established by Western European countries in the Americas, Australia, and New Zealand, settlers (supplemented by Central European, Eastern European, Asian, and African people) eventually formed a large majority of the population after assimilating, warring with, or driving away ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oppression
Oppression is malicious or unjust treatment or exercise of power, often under the guise of governmental authority or cultural opprobrium. Oppression may be overt or covert, depending on how it is practiced. Oppression refers to discrimination when the injustice does not target and may not directly afflict everyone in society but instead targets or disproportionately impacts specific groups of people. No universally accepted model or terminology has yet emerged to describe oppression in its entirety, although some scholars cite evidence of different types of oppression, such as social oppression, cultural, political, religious/belief, institutional oppression, and economic oppression. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights offers a benchmark from which to assess both individual and structural models of oppression. The concept, popularized in Marx and Engels' Communist Manifesto of 1848, is often used to justify state persecution. Authoritarian oppression The word '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Discrimination
Structural discrimination is a form of institutional discrimination against individuals of a given protected characteristic such as race or gender which has the effect of restricting their opportunities. It may be either intentional or unintentional, and it may involve either public or private institutional policies. Such discrimination occurs when these policies have disproportionately negative effects on the opportunities of certain social groups. Some conceptualizations of structural discrimination focus on past forms of discrimination that have resulted in present-day inequality, while others focus on policies that still exist today and can have disproportionately negative effects on minority groups. One overt past example of structural discrimination was Jim Crow laws in the Southern United States, which were explicitly aimed at limiting the rights of black Americans African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)