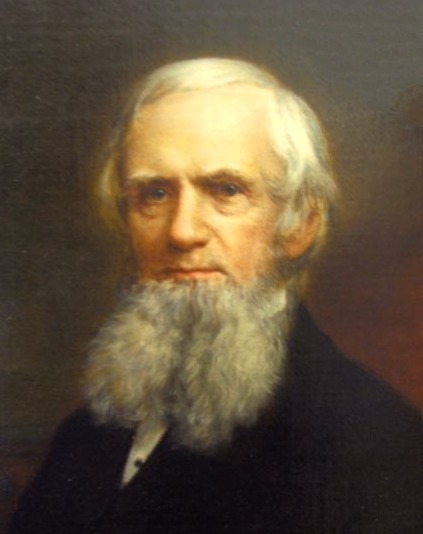|
Indian Giver
"Indian giver" is a pejorative expression used to describe a person who gives a "gift" and later wants it back or who expects something of equivalent worth in return for the item. It is based on cultural misunderstandings that took place between the early European colonists and the Indigenous people with whom they traded. Often, the Europeans viewed an exchange of items as gifts and believed that they owed nothing in return to the Indigenous people. On the other hand, the Indigenous people saw the exchange as a form of trade or equal exchange and so they had differing expectations of their guests. The phrase is used to describe a negative act or shady business dealings. It is considered disrespectful, and its use is offensive to many Indigenous people. Etymology The phrase originated, according to the researcher David Wilton, in a cultural misunderstanding that arose when European settlers first encountered Native Americans after the former had arrived in North America in the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pejorative
A pejorative or slur is a word or grammatical form expressing a negative or a disrespectful connotation, a low opinion, or a lack of respect toward someone or something. It is also used to express criticism, hostility, or disregard. Sometimes, a term is regarded as pejorative in some social or ethnic groups but not in others, or may be originally pejorative but later adopt a non-pejorative sense (or vice versa) in some or all contexts. Etymology The word ''pejorative'' is derived from a Late Latin past participle stem of ''peiorare'', meaning "to make worse", from ''peior'' "worse". Pejoration and melioration In historical linguistics, the process of an inoffensive word becoming pejorative is a form of semantic drift known as pejoration. An example of pejoration is the shift in meaning of the word ''silly'' from meaning that a person was happy and fortunate to meaning that they are foolish and unsophisticated. The process of pejoration can repeat itself around a single concept, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1910 Fruitgum Company
The 1910 Fruitgum Company is an American bubblegum pop band of the 1960s. The group's ''Billboard'' Hot 100 hits were "Simon Says", "May I Take a Giant Step", " 1, 2, 3, Red Light", "Goody Goody Gumdrops", "Indian Giver", "Special Delivery", and "The Train". Career The band began as Jeckell and The Hydes in New Jersey in 1966. The original members were Frank Jeckell, Mark Gutkowski, Floyd Marcus, Pat Karwan and Steve Mortkowitz - all from Linden, New Jersey. During 1967, they were signed to Buddah Records, where they released five LPs under their own name and a variety of singles, as well as appearing on the LP ''The Kasenetz-Katz Singing Orchestral Circus'', which sounded like the usual Buddah studio band in spite of its promotion as a "bubblegum superjam". Their first hit single, "Simon Says", was written by Elliot Chiprut. During the recording process, the band changed the beat and patterned the song after "Wooly Bully" by Sam the Sham and the Pharaohs. "Simon Says" soon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American English Idioms
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams Soccer * Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reciprocity (social And Political Philosophy)
The social norm of reciprocity is the expectation that people will respond to each other in similar ways—responding to gifts and kindnesses from others with similar benevolence of their own, and responding to harmful, hurtful acts from others with either indifference or some form of retaliation. Such norms can be crude and mechanical, such as a literal reading of the eye-for-an-eye rule lex talionis, or they can be complex and sophisticated, such as a subtle understanding of how anonymous donations to an international organization can be a form of reciprocity for the receipt of very personal benefits, such as the love of a parent. The norm of reciprocity varies widely in its details from situation to situation, and from society to society. Anthropologists and sociologists have often claimed, however, that having some version of the norm appears to be a social inevitability. Reciprocity figures prominently in social exchange theory, evolutionary psychology, social psychology, cul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potlatch
A potlatch is a gift-giving feast practiced by Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast of Canada and the United States,Harkin, Michael E., 2001, Potlatch in Anthropology, International Encyclopedia of the Social and Behavioral Sciences, Neil J. Smelser and Paul B. Baltes, eds., vol 17, pp. 11885-11889. Oxford: Pergamon Press. among whom it is traditionally the primary governmental institution, legislative body, and economic system.Aldona Jonaitis. ''Chiefly Feasts: The Enduring Kwakiutl Potlatch''. University of Washington Press 1991. . This includes the Heiltsuk, Haida, Nuxalk, Tlingit, Makah, Tsimshian, Nuu-chah-nulth, Kwakwaka'wakw, and Coast Salish cultures. Potlatches are also a common feature of the peoples of the Interior and of the Subarctic adjoining the Northwest Coast, although mostly without the elaborate ritual and gift-giving economy of the coastal peoples (see Athabaskan potlatch). A potlatch involves giving away or destroying wealth or valuable items ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Summer
An Indian summer is a period of unseasonably warm, dry weather that sometimes occurs in autumn in temperate regions of the northern hemisphere. Several sources describe a true Indian summer as not occurring until after the first frost, or more specifically the first "killing" frost. Etymology The late 19th-century lexicographer Albert Matthews made an exhaustive search of early American literature in an attempt to discover who coined the expression. The earliest reference he found dated to 1851. He also found the phrase in a letter written in England in 1778, but discounted that as a coincidental use of the phrase. Later research showed that the earliest known reference to Indian summer in its current sense occurs in an essay written in the United States circa 1778 by J. Hector St. John de Crevecoeur. The letter was first published in French. The essay remained unavailable in the United States until the 1920s. Although the exact origins of the term are uncertain, it was perhaps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Slurs
The following is a list of ethnic slurs or ethnophaulisms or ethnic epithets that are, or have been, used as insinuations or allegations about members of a given ethnicity or racial group or to refer to them in a derogatory, pejorative, or otherwise insulting manner. Some of the terms listed below (such as "gringo", "yank", etc.) can be used in casual speech without any intention of causing offense. The connotation of a term and prevalence of its use as a pejorative or neutral descriptor varies over time and by geography. For the purposes of this list, an ''ethnic slur'' is a term designed to insult others on the basis of race, ethnicity, or nationality. Each term is listed followed by its country or region of usage, a definition, and a reference to that term. Ethnic slurs may also be produced as a racial epithet by combining a general-purpose insult with the name of ethnicity, such as "dirty Jew", "Russian pig", etc. Other common insulting modifiers include "dog", "filthy", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Competitive Altruism
Competitive altruism is a possible mechanism for the persistence of cooperative behaviors, specifically those that are performed unconditionally. The theory of reciprocal altruism can be used to explain behaviors that are performed by a donor who receives some sort of benefit in the future. When no such compensation is received, however, reciprocity fails to explain altruistic behavior. Characteristics To explain competitive altruism, RobertsRoberts, G. 1998. Competitive altruism: from reciprocity to the handicap principle. Proc. R. Soc. Lond., B 265: 429-430. uses the example of preening among birds. Because certain birds cannot reach parasites on all parts of their bodies, particularly their necks, they benefit from preening one another. For any given bird, there is an entire flock of potential preeners, who compete in hopes of establishing a beneficial relationship. Cheaters, or those birds that try to be preened without preening others, do not compete and thus are excluded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Giver (song)
"Indian Giver" is a song written by Bobby Bloom, Ritchie Cordell, and Bo Gentry. It was first recorded by 1910 Fruitgum Company for their 1969 album, ''Indian Giver''. The song went to #5 on The Billboard Hot 100 in 1969 and was on the charts for 13 weeks. Its B-Side, "Pow Wow", was actually a song called "Bring Back Howdy Doody" deliberately pressed backwards as a way of deterring radio stations from playing the B-Side, which was later recorded by another Buddah bubblegum music group produced by Jerry Kasenetz and Jeffry Katz called Flying Giraffe. The song went to #1 in Canada and South Africa, and #4 in Australia. It was named the #50 song of 1969 on the Cashbox charts. The song was certified as a gold disc Music recording certification is a system of certifying that a music recording has shipped, sold, or streamed a certain number of units. The threshold quantity varies by type (such as album, single, music video) and by nation or territory (see ... in March 1969. Refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Giver (album)
''Indian Giver'', the fourth studio album by American bubblegum pop group the 1910 Fruitgum Company, was released in 1969. The title song written by Bobby Bloom, Ritchie Cordell, and Bo Gentry peaked at #5 on the ''Billboard'' Hot 100. The song "Special Delivery" went to #38 on the Billboard Hot 100. The album went to 147 on the ''Billboard'' 200. Track listing All songs written by Mark Gutkowski, Ted Gutkowski, Jerry Kasenetz, Jeffry Katz Jeffry Katz (born May 20, 1943, Brooklyn, New York) is an American music producer, one of the first exponents of bubblegum pop. Music career He is one half of a hitmaking duo with Jerry Kasenetz, the two working together as the Super K Production ... except where noted. Retrieved October 4, 2011 Charts Album Singles Rel ...
|
John Russell Bartlett
John Russell Bartlett (October 23, 1805 – May 28, 1886) was an American historian and linguist. Biography Bartlett was born in Providence, Rhode Island, on October 23, 1805. In 1819 he was a student at the Lowville Academy in Lowville, New York, which he attended for two years. From 1807 to 1824 he lived in Kingston, Canada. From 1824 to 1836 he lived in Providence where he worked first as a clerk in his uncle's dry goods store (1824–1828), then as a bookkeeper and acting teller at the Bank of North America (1828–1831), and finally as the first cashier of the Globe Bank (1831–1836). In 1831, he was one of the founders of the Providence Athenaeum, and was elected its first treasurer. That year he was also elected to membership in the Rhode Island Historical Society. The following year he was ordering books for the newly founded Providence Franklin Society, an early lyceum. Over the course of his life he became involved with a number of other organizations including th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Appropriations
Native Appropriations is a blog that critically discusses the ways that Indigenous people are depicted in mainstream, Euro-American dominated, culture. Active since 2010, the website is created and maintained by Cherokee Nation scholar Adrienne Keene. Subjects Some of the most frequently discussed topics on the blog are " hipster headdresses", the Native American mascot controversy and appropriation and misrepresentations of Native American cultures in Hollywood movies. Targets of critique include the Washington Redskins use of an ethnic slur as the name for their football team, The Lone Ranger movie remake, misrepresentations of Native American spiritual beliefs in the work of author J. K. Rowling,Keene, Dr. Adrienne,Magic in North America Part 1: Ugh. at ''Native Appropriations'', 8 March 2016. Accessed 9 April 2016. "What happens when Rowling pulls this in, is we as Native people are now opened up to a barrage of questions about these beliefs and traditions…but these are no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
_a_Kwakwaka'wakw_big_house.jpg)