|
Indian Remote Sensing Satellite
India's remote sensing program was developed with the idea of applying space technologies for the benefit of humankind and the development of the country. The program involved the development of three principal capabilities. The first was to design, build and launch satellites to a Sun-synchronous orbit. The second was to establish and operate ground stations for spacecraft control, data transfer along with data processing and archival. The third was to use the data obtained for various applications on the ground. India demonstrated the ability of remote sensing for societal application by detecting coconut root-wilt disease from a helicopter mounted multispectral camera in 1970. This was followed by flying two experimental satellites, Bhaskara-1 in 1979 and Bhaskara-2 in 1981. These satellites carried optical and microwave payloads. India's remote sensing programme under the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) started off in 1988 with the IRS-1A, the first of the series o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Earth and other planets. Remote sensing is used in numerous fields, including geography, land surveying and most Earth science disciplines (e.g. hydrology, ecology, meteorology, oceanography, glaciology, geology); it also has military, intelligence, commercial, economic, planning, and humanitarian applications, among others. In current usage, the term ''remote sensing'' generally refers to the use of satellite- or aircraft-based sensor technologies to detect and classify objects on Earth. It includes the surface and the atmosphere and oceans, based on propagated signals (e.g. electromagnetic radiation). It may be split into "active" remote sensing (when a signal is emitted by a satellite or aircraft to the object and its reflection detected by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drought In India
Drought in India has resulted in tens of millions of deaths over the 18th, 19th, and 20th centuries. Indian agriculture is heavily dependent on the country's climate: a favorable monsoon is critical to securing water for irrigating India's crops. In parts of India, failure of the monsoons causes water shortages, resulting in poor yields. This is particularly true of major drought-prone regions southeastern Maharashtra, northern Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Gujarat, Telangana, and Rajasthan. History Only about 35% of total agricultural land in India is irrigated and two-thirds of cultivated land is entirely dependent on rainfall. As such, the agricultural production system in the country is more vulnerable to damage from extreme climatic events, which causes increased water stress leading to inadequate water supplies for irrigation. Already, rises in average temperatures, changes in rainfall patterns, increasing frequency of extreme weather events, such as severe droughts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSLV-D2
PSLV-D2 was the second mission of the PSLV program by Indian Space Research Organisation. The vehicle carried IRS-P2 satellite which was deployed in the Sun-synchronous Low Earth orbit. Launch PSLV-D2 was launched at 5:05 a.m. IST on 15 October 1994 from Satish Dhawan Space Centre (then called "Sriharikota Launching Range"). The vehicle successfully achieved orbit, placing the IRS-P2 satellite in an 820 km sun-synchronous orbit. See also * Indian Space Research Organisation * Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle The Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) is an expendable medium-lift launch vehicle designed and operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). It was developed to allow India to launch its Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) satellites ... References {{PSLV Spacecraft launched in 1994 Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IRS-P2
IRS-P2 was an Earth observation satellite launched under the National Natural Resources Management System (NNRMS) programme undertaken by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). The objectives of the mission were to provide spaceborne capability to India in observing and managing natural resources and utilizing them in a productive manner. The satellite carried imaging multi-spectral radiometers on board for radio sensing of the resources. History The satellite was designed, developed and tested in just one and a half years. IRS-P2 is one of the satellites in the Indian Remote Sensing Programme of Earth Observation satellites, assembled, launched and maintained by the Indian Space Research Organisation. The satellite was controlled by ISRO Telemetry Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC) in Bangalore, Lucknow and Mauritius. The National Remote Sensing Agency (NRSC), Hyderabad received the first signal from IRS-P2, 98 minutes after the launch. The IRS-P2 was declared operat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSLV
The Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) is an expendable medium-lift launch vehicle designed and operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). It was developed to allow India to launch its Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) satellites into sun-synchronous orbits, a service that was, until the advent of the PSLV in 1993, only commercially available from Russia. PSLV can also launch small size satellites into Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO). Some notable payloads launched by PSLV include India's first lunar probe Chandrayaan-1, India's first interplanetary mission, Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan) and India's first space observatory, Astrosat. PSLV has gained credibility as a leading provider of rideshare services for small satellites, owing to its numerous multi-satellite deployment campaigns with auxiliary payloads, usually ride-sharing along with an Indian primary payload. As of June 2022, PSLV has launched 345 foreign satellites from 36 countries. Most notab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSLV-D1
PSLV-D1 was the first mission of the PSLV program. The rocket carried IRS-1E satellite but could not deploy it as the mission failed due to a software error in on board guidance and control processor. PSLV-D1 was launched at 5:12 a.m. IST on 20 September 1993. This mission was the only full failed mission under the PSLV program until the launch of PSLV-C39. Launch & failure PSLV-D1 was launched at 5:12 a.m. IST on 20 September 1993 from Satish Dhawan Space Centre (then called "Sriharikota Launching Range"). A large disturbance occurred at the point of second stage separation and one of the retro rockets of the second stage failed due to software error in on board guidance and control processor. About 12 minutes after launch, the vehicle fell back to earth and crashed in the Bay of Bengal. The satellite IRS-1E could not be placed in orbit and the mission was a total failure. See also * Indian Space Research Organisation * Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle The Polar Sat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IRS-P1
IRS-1E was an Earth observation mission launched under the National Natural Resources Management System (NNRMS) programme by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). Sometimes written IRS-P1. The objective of the mission was to develop Earth imagery using instruments carried on board. Due to a malfunction of the launch vehicle, the satellite deviated from its path and plunged into the Indian Ocean. History IRS-1E was a follow-up mission to the satellite IRS-1A, to develop India's capability in the field of remote sensing. The satellite was to take up missions in the area of ground-water exploration, land use, forest and flood mapping. The letter "E" indicates that the satellite was an engineering model. The letter "P" (IRS-P1) in the Indian Remote Sensing Programme of Earth observation satellite indicates that the satellite was to be launched aboard a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV). It was launched on 20 September 1993. Instruments IRS-1E carried two instruments: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IRS-1B
IRS-1B, Indian Remote Sensing satellite-1B, the second of the series of indigenous state-of-art remote sensing satellites, was successfully launched into a polar Sun-synchronous orbit on 29 August 1991 from the Soviet Cosmodrome at Baikonur. IRS-1B carries two sensors, LISS-1 and LISS-2, with resolutions of and respectively with a swath width of about during each pass over the country. It was a part-operational, part-experimental mission to develop Indian expertise in satellite imagery. It was a successor to the remote sensing mission IRS-1A, both undertaken by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). History IRS-1B was the second remote sensing mission to provide imagery for various land-based applications, such as agriculture, forestry, geology, and hydrology. Satellite description Improved features compared to its predecessor (IRS-1A): gyroscope referencing for better orientation sensing, time tagged commanding facility for more flexibility in camera operation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev ( Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vostok (rocket Family)
Vostok (Russian: Восток, translated as "East") was a family of rockets derived from the Soviet R-7 Semyorka ICBM and was designed for the human spaceflight programme. This family of rockets launched the first artificial satellite (Sputnik 1) and the first crewed spacecraft (Vostok) in human history. It was a subset of the R-7 family of rockets. On March 18, 1980, a Vostok-2M rocket exploded on its launch pad at Plesetsk during a fueling operation, killing 48 people. An investigation into a similarbut avoidedaccident revealed that the substitution of lead-based for tin-based solder in hydrogen peroxide filters allowed the breakdown of the H2O2, thus causing the resultant explosion. Variants The major versions of the rocket were: * Luna 8K72 – used to launch the early Luna spacecraft * Vostok-L 8K72 – Variant of the Luna, used to launch prototype Vostok spacecraft * Vostok-K 8K72K – a refined version of the above. This was the version actually used for human spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
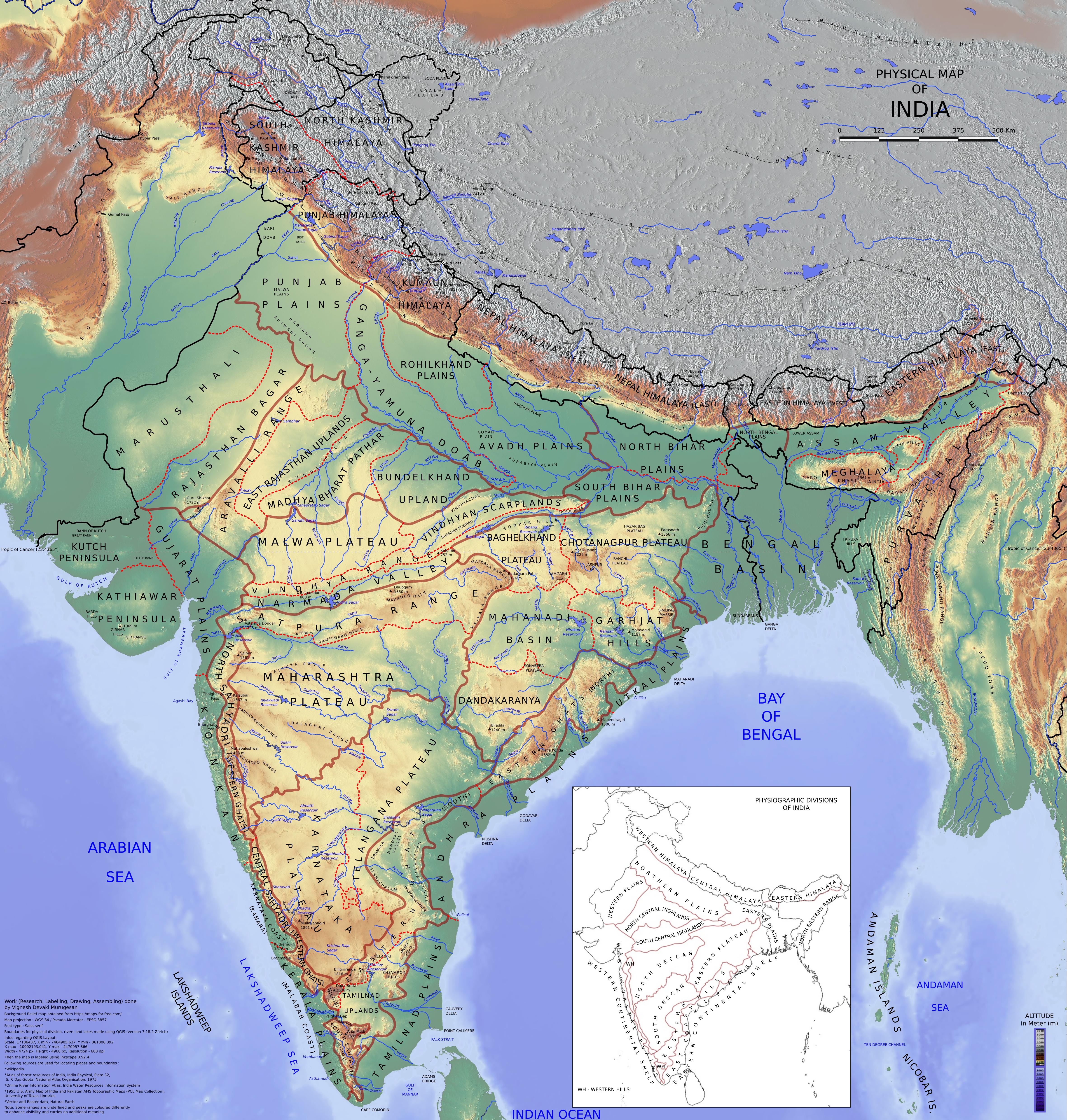
Natural Resources Of India
Resources are classified as either biotic or abiotic on the basis of their origin. The Indian landmass contains a multitude of both types of resource and its economy, especially in rural areas, is heavily dependent on their consumption or export. Due to overconsumption, they are rapidly being depleted. General The total cultivable area in India is 1,945,355 km2 (56.78% of it total land area), which is shrinking due to population pressures, desertification and rapid urbanisation. India has a total water surface area of 360,400 km2. India's major mineral resources include coal (4th largest reserves in the world), iron ore, manganese ore (7th largest reserve in the world as in 2013), mica, bauxite (5th largest reserve in the world as in 2013), chromite, natural gas, diamonds, limestone and thorium. India's oil reserves, found in Bombay High off the coast of Maharashtra, Gujarat, Rajasthan and in eastern Assam meet 25% of the country's demand. A national level agency Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetlands Of India
India is situated north of the equator between 8°4' north (the mainland) to 37°6' north latitude and 68°7' east to 97°25' east longitude. India Yearbook, p. 1 It is the seventh-largest country in the world, with a total area of . Total area excludes disputed territories not under Indian control. India measures from north to south and from east to west. It has a land frontier of and a coastline of . On the south, India projects into and is bounded by the Indian Ocean—in particular, by the Arabian Sea on the west, the Lakshadweep Sea to the southwest, the Bay of Bengal on the east, and the Indian Ocean proper to the south. The Palk Strait and Gulf of Mannar separate India from Sri Lanka to its immediate southeast, and the Maldives are some to the south of India's Lakshadweep Islands across the Eight Degree Channel. India's Andaman and Nicobar Islands, some southeast of the mainland, share maritime borders with Myanmar, Thailand and Indonesia. The southernmost tip o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |