|
Inaros II
Inaros (II), also known as Inarus, (fl. ca. 460 BC) was an Egyptian rebel ruler who was the son of an Egyptian prince named Psamtik, presumably of the old Saite line, and grandson of Psamtik III. In 460 BC, he revolted against the Persians with the help of his Athenian allies under Admiral Charitimides, and defeated the Persian army commanded by satrap Achaemenes. The Persians retreated to Memphis, but the Athenians were finally defeated in 454 BC by the Persian army led by Megabyzus, satrap of Syria, and Artabazus, satrap of Phrygia, after a two-year siege. Inaros was captured and carried away to Susa where he was reportedly crucified in 454 BC. Revolt and aftermath He held a kingship over the Libyans from Mareia (above Pharos) and the part of the Nile Delta around Sais. With help from Amyrtaeus, also from Sais, who took the northern marshes, Inarus drove out the tax-collectors while collecting mercenaries. These actions started a revolt in Egypt at the beginning of the rei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artaxerxes I
Artaxerxes I (, peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης) was the fifth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, from 465 to December 424 BC. He was the third son of Xerxes I. He may have been the " Artasyrus" mentioned by Herodotus as being a satrap of the royal satrapy of Bactria. In Greek sources he is also surnamed "long-handed" ( grc, μακρόχειρ ''Makrókheir''; la, Longimanus), allegedly because his right hand was longer than his left. Succession to the throne Artaxerxes was probably born in the reign of his grandfather Darius I, to the emperor's son and heir, Xerxes I. In 465 BC, Xerxes I was murdered by ''Hazarapat'' ("commander of thousand") Artabanus, the commander of the royal bodyguard and the most powerful official in the Persian court, with the help of a eunuch, Aspamitres. Greek historians give contradicting accounts of events. According to Ctesias (in ''Persica'' 20), Artabanus then accused Crown Prince Darius, X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It is a unitary republic that consists of 14 governorates (subdivisions), and is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east and southeast, Jordan to the south, and Israel and Lebanon to the southwest. Cyprus lies to the west across the Mediterranean Sea. A country of fertile plains, high mountains, and deserts, Syria is home to diverse ethnic and religious groups, including the majority Syrian Arabs, Kurds, Turkmens, Assyrians, Armenians, Circassians, Albanians, and Greeks. Religious groups include Muslims, Christians, Alawites, Druze, and Yazidis. The capital and largest city of Syria is Damascus. Arabs are the largest ethnic group, and Mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athenian
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates and is the capital of the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, with its recorded history spanning over 3,400 years and its earliest human presence beginning somewhere between the 11th and 7th millennia BC. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state. It was a centre for the arts, learning and philosophy, and the home of Plato's Academy and Aristotle's Lyceum. It is widely referred to as the cradle of Western civilization and the birthplace of democracy, largely because of its cultural and political influence on the European continent—particularly Ancient Rome. In modern times, Athens is a large cosmopolitan metropolis and central to economic, financial, industrial, maritime, political and cultural life in Greec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xerxes I Tomb Libyan Soldier Circa 480 BCE
Xerxes ( ) may refer to: People * Xerxes I of Persia, "Xerxes the Great", reigned 486–465 BC * Xerxes II of Persia, briefly reigned 424 BC * Xerxes of Sophene, ruler of Sophene and Commagene, 228–201 BC * Xerxes (Sasanian prince), 6th-century prince and general * Xerxes (name), a list of people with the name Fiction, stage and video *'' Il Xerse'', (in its 1660 French version, ''Xerxès''), Francesco Cavalli's opera of 1654 *''Xerse'', Giovanni Bononcini's opera of 1694 *''Serse'' (''Xerxes''), George Frideric Handel's opera of 1738 *''Xerxes'', novel by Louis Couperus * ''Xerxes'' (TV series), a Swedish TV series for children * ''Xerxes'' (graphic novel), a 2018 graphic novel by Frank Miller Other *''Xerxes The God-King'', a 2010 album by American rapper King Gordy *Xerxes Peak, a mountain in the Canadian Rockies *XerxesDZB, a Dutch professional football team based in Rotterdam *Roksan Xerxes, a series of record turntables from Roksan Audio (UK) *XerXeS, a denial-of-service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Crawley
Richard Crawley (26 December 1840 – 30 March 1893) was a Welsh writer and academic, best known for his translation of Thucydides's ''History of the Peloponnesian War''. Life Crawley was born at a Bryngwyn rectory on 26 December 1840, the eldest son of William Crawley, Archdeacon of Monmouth, by his wife, Mary Gertrude, third daughter of Sir Love Jones Parry of Madryn, Carnarvonshire. From 1851 to 1861 he was at Marlborough College. He matriculated at University College, Oxford, as an exhibitioner on 22 May 1861, and graduated with a B.A. in 1866, having taken a first class both in moderations and in the school of Literae Humaniores. In 1866, he was elected to a fellowship at Worcester College, Oxford, which he held till 1880. Called to the bar at Lincoln's Inn on 7 June 1869, Crawley never practised; in poor health, he lived abroad for many years. In April 1875, he became director of a life assurance company, and that business largely occupied him until his death on 30 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trie
In computer science, a trie, also called digital tree or prefix tree, is a type of ''k''-ary search tree, a tree data structure used for locating specific keys from within a set. These keys are most often strings, with links between nodes defined not by the entire key, but by individual characters. In order to access a key (to recover its value, change it, or remove it), the trie is traversed depth-first, following the links between nodes, which represent each character in the key. Unlike a binary search tree, nodes in the trie do not store their associated key. Instead, a node's position in the trie defines the key with which it is associated. This distributes the value of each key across the data structure, and means that not every node necessarily has an associated value. All the children of a node have a common prefix of the string associated with that parent node, and the root is associated with the empty string. This task of storing data accessible by its prefix can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Athens
Athens is one of the oldest named cities in the world, having been continuously inhabited for perhaps 5,000 years. Situated in southern Europe, Athens became the leading city of Ancient Greece in the first millennium BC, and its cultural achievements during the 5th century BC laid the foundations of Western civilization. During the early Middle Ages, the city experienced a decline, then recovered under the later Byzantine Empire and was relatively prosperous during the period of the Crusades (12th and 13th centuries), benefiting from Italian trade. Following a period of sharp decline under the rule of the Ottoman Empire, Athens in the 19th century as the capital of the independent and self-governing Greek state. Name The name of Athens, connected to the name of its patron goddess Athena, originates from an earlier Pre-Greek language. The origin myth explaining how Athens acquired this name through the legendary contest between Poseidon and Athena was described by Herodotus,Hero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xerxes I
Xerxes I ( peo, 𐎧𐏁𐎹𐎠𐎼𐏁𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ξέρξης ; – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, ruling from 486 to 465 BC. He was the son and successor of Darius the Great () and his mother was Atossa, a daughter of Cyrus the Great (), the founder of the Achaemenid empire. Like his father, he ruled the empire at its territorial peak. He ruled from 486 BC until his assassination in 465 BC at the hands of Artabanus, the commander of the royal bodyguard. Xerxes I is notable in Western history for his invasion of Greece in 480 BC. His forces temporarily overran mainland Greece north of the Isthmus of Corinth until losses at Salamis and Plataea a year later reversed these gains and ended the second invasion decisively. However, Xerxes successfully crushed revolts in Egypt and Babylon. Xerxes also oversaw the completion of various construction projects at Susa and Persepolis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest empire in history, spanning a total of from the Balkans and Egypt in the west to Central Asia and the Indus Valley in the east. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the formal establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognized for its imposition of a successful model of centralized, bureaucratic administration; its multicultural policy; building complex infrastructure, such as road systems and an organized postal system; the use of official languages across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sais
Sais ( grc, Σάϊς, cop, Ⲥⲁⲓ) was an ancient Egyptian city in the Western Nile Delta on the Canopic branch of the Nile,Mish, Frederick C., Editor in Chief. "Saïs." '' Webster's Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary''. 9th ed. Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster Inc., 1985. , (indexed), and (deluxe). known by the ancient Egyptians as Sꜣw. It was the provincial capital of Sap-Meh, the fifth nome of Lower Egypt and became the seat of power during the Twenty-fourth Dynasty of Egypt (c. 732–720 BC) and the Saite Twenty-sixth Dynasty of Egypt (664–525 BC) during the Late Period.Ian Shaw & Paul Nicholson, The Dictionary of Ancient Egypt, British Museum Press, 1995. p.250 On its ruins today stands the town of Sa el-Hagar ( ar, صا الحجر) or Sa El Hajar. Neolithic period A Neolithic settlement has been identified at Sais recently (1999), dating to 5000 BC. Agriculture appears here during this period, as well as at another similar site, Merimde Beni Salama, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
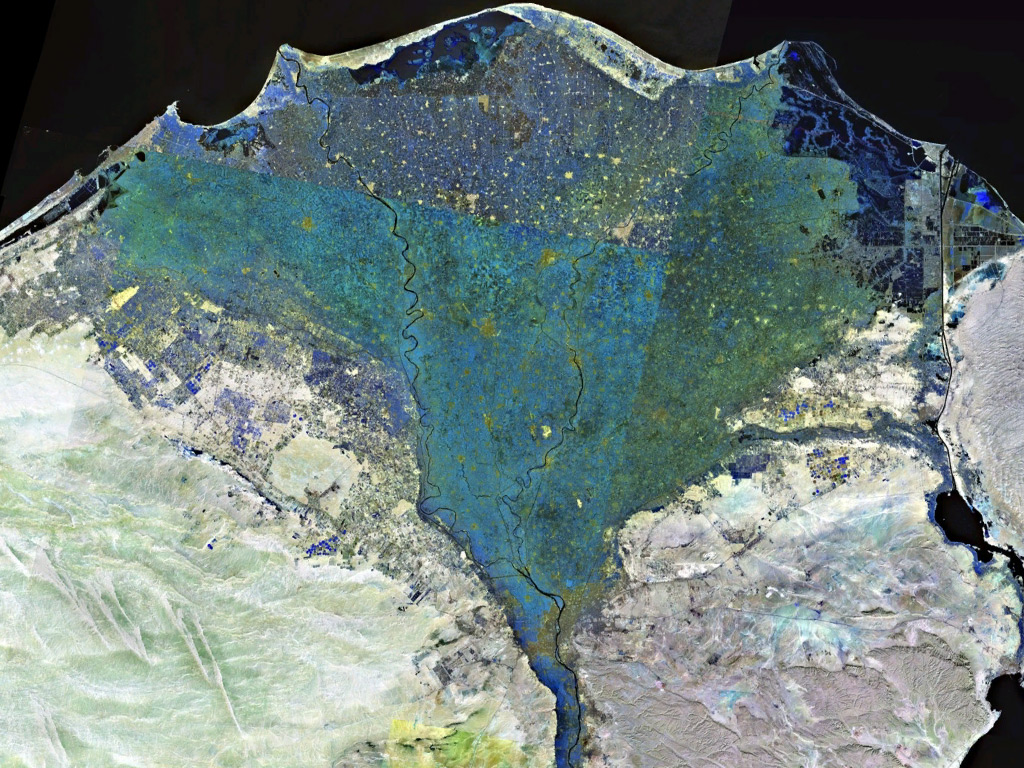
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east, it covers of Mediterranean coastline and is a rich agricultural region. From north to south the delta is approximately in length. The Delta begins slightly down-river from Cairo. Geography From north to south, the delta is approximately in length. From west to east, it covers some of coastline. The delta is sometimes divided into sections, with the Nile dividing into two main distributaries, the Damietta and the Rosetta, flowing into the Mediterranean at port cities with the same name. In the past, the delta had several distributaries, but these have been lost due to flood control, silting and changing relief. One such defunct distributary is Wadi Tumilat. The Suez Canal is east of the delta and enters the coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lighthouse Of Alexandria
The Lighthouse of Alexandria, sometimes called the Pharos of Alexandria (; Ancient Greek: ὁ Φάρος τῆς Ἀλεξανδρείας, contemporary Koine ), was a lighthouse built by the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Ancient Egypt, during the reign of Ptolemy II Philadelphus (280–247 BC). It has been estimated to have been at least in overall height. One of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, for many centuries it was one of the tallest man-made structures in the world. The lighthouse was severely damaged by three earthquakes between 956 and 1323 AD and became an abandoned ruin. It was the third-longest surviving ancient wonder (after the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus and the extant Great Pyramid of Giza), surviving in part until 1480, when the last of its remnant stones were used to build the Citadel of Qaitbay on the site. In 1994, a team of French archaeologists dove into the water of Alexandria's Eastern Harbour and discovered some remains of the lighthouse on the sea f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |