|
Impression Management
Impression management is a conscious or subconscious process in which people attempt to influence the perceptions of other people about a person, object or event by regulating and controlling information in social interaction.Sanaria, A. D. (2016). A conceptual framework for understanding the impression management strategies used by women in indian organizations. South Asian Journal of Human Resources Management, 3(1), 25-39. https://doi.org/10.1177/2322093716631118 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/299373178_A_Conceptual_Framework_for_Understanding_the_Impression_Management_Strategies_Used_by_Women_in_Indian_Organizations It was first conceptualized by Erving Goffman in 1959 in ''The Presentation of Self in Everyday Life,'' and then was expanded upon in 1967. Impression management behaviors include accounts (providing "explanations for a negative event to escape disapproval"), excuses (denying "responsibility for negative outcomes"), and opinion conformity ("speak(ing) or be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subconscious
In psychology, the subconscious is the part of the mind that is not currently of focal awareness. Scholarly use of the term The word ''subconscious'' represents an anglicized version of the French ''subconscient'' as coined in 1889 by the psychologist Pierre Janet (1859–1947), in his doctorate of letters thesis, ''De l'Automatisme Psychologique''. Janet argued that underneath the layers of critical-thought functions of the conscious mind lay a powerful awareness that he called the subconscious mind.Henri F. Ellenberger, ''The Discovery of the Unconscious'' (1970) In the strict psychological sense, the adjective is defined as "operating or existing outside of consciousness". Locke and Kristof write that there is a limit to what can be held in conscious focal awareness, an alternative storehouse of one's knowledge and prior experience is needed, which they label the subconscious. Psychoanalysis Sigmund Freud used the term "subconscious" in 1893 to describe associations and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Capital
Social capital is "the networks of relationships among people who live and work in a particular society, enabling that society to function effectively". It involves the effective functioning of social groups through interpersonal relationships, a shared sense of Identity (social science), identity, a shared understanding, shared Social norm, norms, shared Value (ethics), values, Trust (social sciences), trust, cooperation, and Reciprocity (social psychology), reciprocity. Social capital is a measure of the value of resources, both Tangibility, tangible (e.g., public spaces, private property) and intangible (e.g., Social actor, actors, human capital, people), and the impact that ideal creators have on the resources involved in each relationship, and on larger groups. Some have described it as a form of capital that produces Public good (economics), public goods for a common purpose, although this does not align with how it has been measured. Social capital has been used to expla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-monitoring Theory
Self-monitoring, a concept introduced in the 1970s by Mark Snyder, describes the extent to which people monitor their self-presentations, expressive behavior, and nonverbal affective displays. Snyder held that human beings generally differ in substantial ways in their abilities and desires to engage in expressive controls (see dramaturgy).Snyder, 1974 Self-monitoring is defined as a personality trait that refers to an ability to regulate behavior to accommodate social situations. People concerned with their expressive self-presentation (see impression management) tend to closely monitor their audience in order to ensure appropriate or desired public appearances. Self-monitors try to understand how individuals and groups will perceive their actions. Some personality types commonly act spontaneously (low self-monitors) and others are more apt to purposely control and consciously adjust their behavior (high self-monitors). Recent studies suggest that a distinction should be made betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interactionism
In micro-sociology, interactionism is a theoretical perspective that sees social behavior as an interactive product of the individual and the situation. In other words, it derives social processes (such as conflict, cooperation, identity formation) from social interaction, whereby subjectively held meanings are integral to explaining or understanding social behavior.Interactionism , Topics " ''ScienceDirect''. Retrieved 2021 March 12. This perspective studies the ways in which individuals shape, and are shaped by, society through their interactions. Interactionism thus argues that the individual is an active and piece of the social-context |
Dramaturgy (sociology)
Dramaturgy is a sociological perspective commonly used in micro-sociological accounts of social interaction in everyday life. The term was first adapted into sociology from the theatre by Erving Goffman, who developed most of the related terminology and ideas in his 1956 book, ''The Presentation of Self in Everyday Life''. Kenneth Burke, whom Goffman would later acknowledge as an influence, had earlier presented his notions of ''dramatism'' in 1945, which in turn derives from Shakespeare. The fundamental difference between Burke's and Goffman's view, however, is that Burke believed that life was in fact theatre, whereas Goffman viewed theatre as a metaphor. If we imagine ourselves as directors observing what goes on in the theatre of everyday life, we are doing what Goffman called dramaturgical analysis, the study of social interaction in terms of theatrical performance. In dramaturgical sociology, it is argued that the elements of human interactions are dependent upon time, pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-esteem
Self-esteem is confidence in one's own worth or abilities. Self-esteem encompasses beliefs about oneself (for example, "I am loved", "I am worthy") as well as emotional states, such as triumph, despair, pride, and shame. Smith and Mackie (2007) defined it by saying "The self-concept is what we think about the self; self-esteem, is the positive or negative evaluations of the self, as in how we feel about it." Self-esteem is an attractive psychological construct because it predicts certain outcomes, such as academic achievement, happiness, satisfaction in marriage and relationships, and criminal behavior. Self-esteem can apply to a specific attribute or globally. Psychologists usually regard self-esteem as an enduring personality characteristic (''trait self-esteem''), though normal, short-term variations (''state self-esteem'') also exist. Synonyms or near-synonyms of self-esteem include: self-worth, self-regard, self-respect, and self-integrity. History The concept of self-estee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assertive
Assertiveness is the quality of being self-assured and confident without being aggressive to defend a right point of view or a relevant statement. In the field of psychology and psychotherapy, it is a skill that can be learned and a mode of communication. ''Dorland's Medical Dictionary'' defines assertiveness as: :"a form of behavior characterized by a confident declaration or affirmation of a statement without need of proof; this affirms the person's rights or point of view without either aggressively threatening the rights of another (assuming a position of dominance) or submissively permitting another to ignore or deny one's rights or point of view." Assertiveness is a communication skill that can be taught and the skills of assertive communication effectively learned. Assertiveness is a method of critical thinking, where an individual speaks up in defense of their views or in light of erroneous information. Assertive people are able to be outspoken and analyze information and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
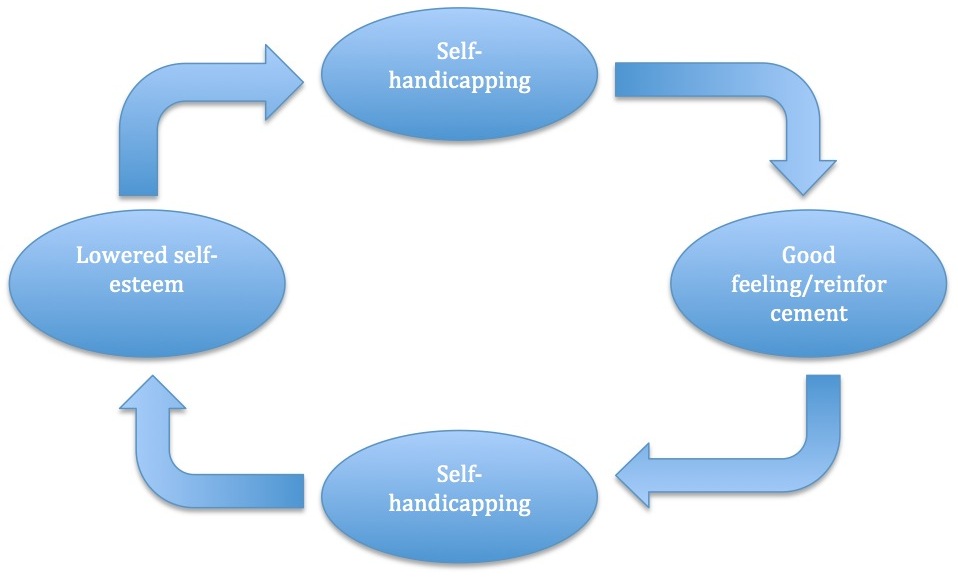
Self-handicapping
Self-handicapping is a cognitive strategy by which people avoid effort in the hopes of keeping potential failure from hurting self-esteem. It was first theorized by Edward E. Jones and Steven Berglas, according to whom self-handicaps are obstacles created, or claimed, by the individual in anticipation of failing performance.Feick, D.L., & Rhodewalt, F. (1997). The Double-Edged Sword of Self-Handicapping: Discounting, Augmentation, and the Protection and Enhancement of Self-Esteem. ''Motivation and Emotion, Vol. 21, No. 2. '' Self-handicapping can be seen as a method of preserving self-esteem but it can also be used for self-enhancement and to manage the impressions of others. Rhodewalt, F., & Vohs, K. D. (2005). Defensive strategies, motivation, and the self. In A. Elliot & C. Dweck (Eds.). ''Handbook of competence and motivation''(pp. 548-565). New York: Guilford Press. This conservation or augmentation of self-esteem is due to changes in causal attributions or the attributions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anger
Anger, also known as wrath or rage, is an intense emotional state involving a strong uncomfortable and non-cooperative response to a perceived provocation, hurt or threat. A person experiencing anger will often experience physical effects, such as increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and increased levels of adrenaline and noradrenaline. Some view anger as an emotion which triggers part of the fight or flight response. Anger becomes the predominant feeling behaviorally, cognitively, and physiologically when a person makes the conscious choice to take action to immediately stop the threatening behavior of another outside force. The English word originally comes from the term ''anger'' from the Old Norse language. Anger can have many physical and mental consequences. The external expression of anger can be found in facial expressions, body language, physiological responses, and at times public acts of aggression. Facial expressions can range from inward angling of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intimidation
Intimidation is to "make timid or make fearful"; or to induce fear. This includes intentional behaviors of forcing another person to experience general discomfort such as humiliation, embarrassment, inferiority, limited freedom, etc and the victim might be targeted based on multiple factors like gender, race, class, skin color, competency, knowledge, wealth, temperament, etc. Intimidation is done for making the other person submissive (also known as cowing), to destabilize/undermine the other, to force compliance, to hide one's insecurities, to socially valorize oneself, etc. There are active and passive coping mechanisms against intimidation that include, and not limited to not letting the intimidator cross your personal space, addressing their behavior directly, avoiding the person, being gingerly around them, honing breakaway skills, etc. Victims of intimidation would reasonably develop apprehension, experience fear of injury or harm, etc from the unwanted behaviors or tools of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praise
Praise as a form of social interaction expresses recognition, reassurance or admiration. Praise is expressed verbally as well as by body language (facial expression and gestures). Verbal praise consists of a positive evaluations of another's attributes or actions, where the evaluator presumes the validity of the standards on which the evaluation is based. As a form of social manipulation, praise becomes a form of reward and furthers behavioral reinforcement by conditioning. The influence of praise on an individual can depend on many factors, including the context, the meanings the praise may convey, and the characteristics and interpretations of the recipient. While praise may share some predictive relationships (both positive and negative) with tangible (material) rewards, praise tends to be less salient and expected, conveys more information about competence, and is typically given more immediately after the desired behavior. Praise is distinct from acknowledgement or fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flattery
Flattery (also called adulation or blandishment) is the act of giving excessive compliments, generally for the purpose of ingratiating oneself with the subject. It is also used in pick-up lines when attempting to initiate sexual or romantic courtship. Historically, flattery has been used as a standard form of discourse when addressing a king or queen. In the Renaissance, it was a common practice among writers to flatter the reigning monarch, as Edmund Spenser flattered Queen Elizabeth I in ''The Faerie Queene'', William Shakespeare flattered King James I in ''Macbeth'' and Niccolò Machiavelli flattered Lorenzo II de' Medici in ''The Prince''. Many associations with flattery, however, are negative. Negative descriptions of flattery range at least as far back in history as the Bible. In the ''Divine Comedy'', Dante depicts flatterers wading in human excrement, stating that their words were the equivalent of excrement, in the second bolgia of 8th Circle of Hell. An insincere fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |