|
Immunocompetence
In immunology, immunocompetence is the ability of the body to produce a normal immune response following exposure to an antigen. Immunocompetence is the opposite of immunodeficiency (also known as ''immuno-incompetence'' or being ''immuno-compromised''). Examples include: * a newborn who does not yet have a fully functioning immune system but may have maternally transmitted antibodies – immunodeficient; * a late stage AIDS patient with a failed or failing immune system – immuno-incompetent; or * a transplant recipient taking medication so their body will not reject the donated organ – immunocompromised. There may be cases of overlap but these terms all describe immune system not fully functioning. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that household and other close contacts of persons with altered immunocompetence receive the MMR, varicella, and rotavirus vaccines according to the standard schedule of vaccines, as well as receiving an annual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasite-stress Theory
Parasite-stress theory, illustrated by researchers Corey Fincher and Randy Thornhill, is a theory of human evolution proposing that parasites and diseases encountered by a species shape the development of species' values and qualities. The differences in how parasites and diseases stress people's development is what leads to differences in their biological mate value and mate preferences, as well as differences across culture. Parasites causing diseases pose potential ecological hazards and, subsequently, selection pressures can alter psychological and social behaviours of humans, as well as have an influence on their immune systems. Theories of parasite-mediated mate choice Several hypotheses have attempted to explain how parasite load influences female mate choice, as certain traits are thought to be costly and the expression of such traits may be indicative of genetic quality. Hamilton–Zuk hypothesis According to the Hamilton–Zuk hypothesis, female mate choice is bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunology
Immunology is a branch of medicineImmunology for Medical Students, Roderick Nairn, Matthew Helbert, Mosby, 2007 and biology that covers the medical study of immune systems in humans, animals, plants and sapient species. In such we can see there is a difference of human immunology and comparative immunology in veterinary medicine and animal biosciences. Immunology measures, uses charts and differentiate in context in medicine the studies of immunity on cell and molecular level, and the immune system as part of the physiological level as its functioning is of major importance. In the different states of both health, occurring symptoms and diseases; the functioning of the immune system and immunological responses such as autoimmune diseases, allergic hypersensitivities, or in some cases malfunctioning of immune system as for example in immunological disorders or in immune deficiency, and the specific transplant rejection) Immunology has applications in numerous disciplines of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attenuated Vaccine
An attenuated vaccine (or a live attenuated vaccine, LAV) is a vaccine created by reducing the virulence of a pathogen, but still keeping it viable (or "live"). Attenuation takes an infectious agent and alters it so that it becomes harmless or less virulent. These vaccines contrast to those produced by "killing" the virus (inactivated vaccine). Attenuated vaccines stimulate a strong and effective immune response that is long-lasting. In comparison to inactivated vaccines, attenuated vaccines produce a stronger and more durable immune response with a quick immunity onset. Attenuated vaccines function by encouraging the body to create antibodies and memory immune cells in response to the specific pathogen which the vaccine protects against. Common examples of live attenuated vaccines are measles, mumps, rubella, yellow fever, and some influenza vaccines. Development Attenuated viruses Viruses may be attenuated using the principles of evolution via serial passage of the virus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunopharmacology And Immunotoxicology
''Immunopharmacology and Immunotoxicology'' is a bimonthly Peer review, peer-reviewed medical journal that covers preclinical and clinical studies on the regulatory effects of various agents on Immunocompetence, immunocompetent cells, as well as the immunotoxin, immunotoxicity exerted by xenobiotics and drugs. Hence, the journal encompasses a broad range of pathology, pathologies (e.g. acute and chronic infections, allergy, autoimmunity, cancer, degenerative disease, degenerative disorders, inflammation, and primary and secondary Immunodeficiency, immunodeficiencies). It is published by Informa. Editor-in-chief The editor-in-chief of ''Immunopharmacology and Immunotoxicology'' is Anders Elm Pedersen, University of Copenhagen, Danmark. accessed at Apri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
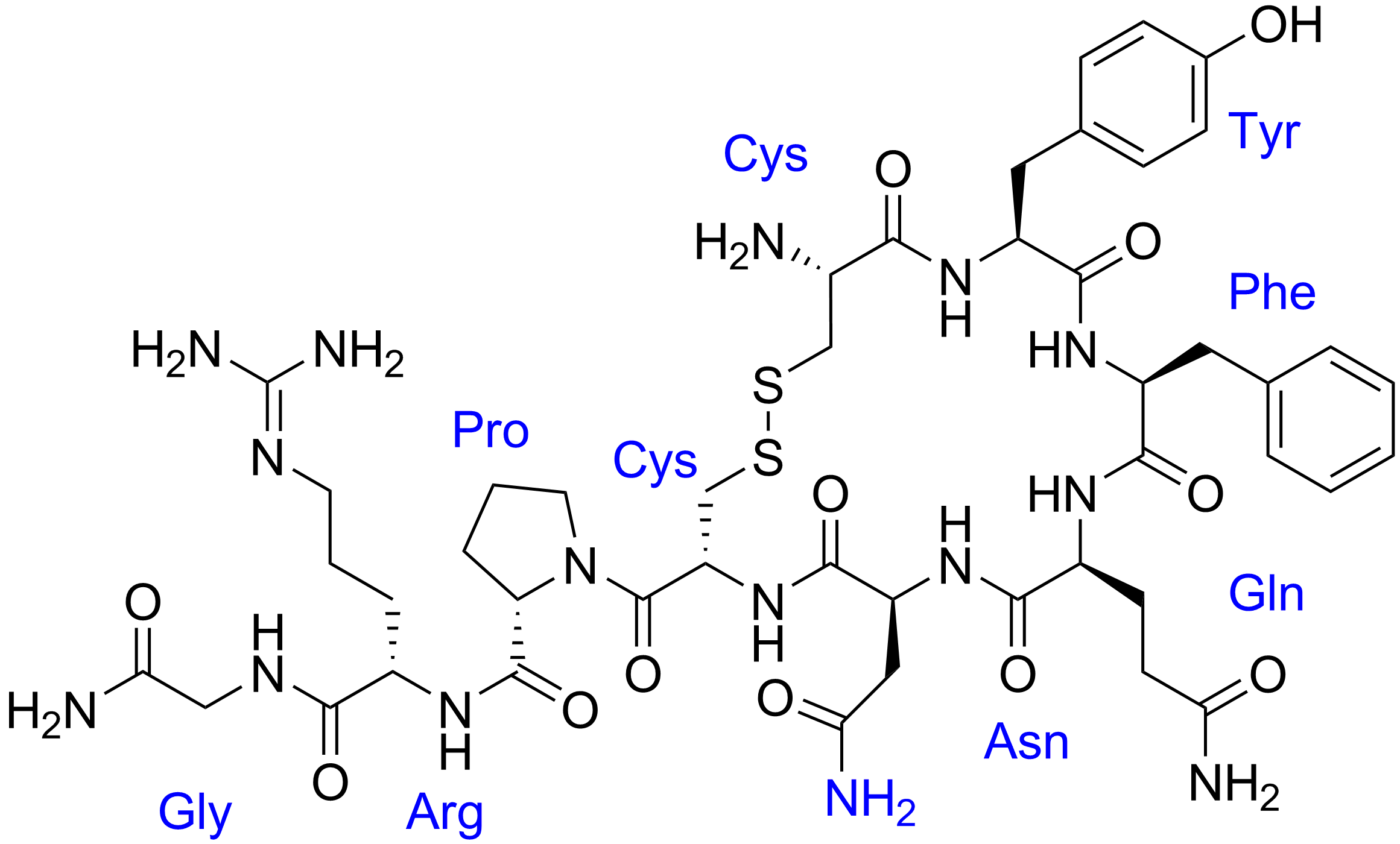
Vasopressin
Human vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the AVP gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travels down the axon terminating in the posterior pituitary, and is released from vesicles into the circulation in response to extracellular fluid hypertonicity (hyperosmolality). AVP has two primary functions. First, it increases the amount of solute-free water reabsorbed back into the circulation from the filtrate in the kidney tubules of the nephrons. Second, AVP constricts arterioles, which increases peripheral vascular resistance and raises arterial blood pressure. A third function is possible. Some AVP may be released directly into the brain from the hypothalamus, and may play an important role in social behavior, sexual motivation and pair bonding, and maternal responses to stress. Vasopressin induces differentiation of stem cells in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prolactin
Prolactin (PRL), also known as lactotropin, is a protein best known for its role in enabling mammals to produce milk. It is influential in over 300 separate processes in various vertebrates, including humans. Prolactin is secreted from the pituitary gland in response to eating, mating, estrogen treatment, ovulation and nursing. It is secreted heavily in pulses in between these events. Prolactin plays an essential role in metabolism, regulation of the immune system and pancreatic development. Discovered in non-human animals around 1930 by Oscar Riddle and confirmed in humans in 1970 by Henry Friesen, prolactin is a peptide hormone, encoded by the ''PRL'' gene. In mammals, prolactin is associated with milk production; in fish it is thought to be related to the control of water and salt balance. Prolactin also acts in a cytokine-like manner and as an important regulator of the immune system. It has important cell cycle-related functions as a growth-, differentiating- and anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in human development. GH also stimulates production of IGF-1 and increases the concentration of glucose and free fatty acids. It is a type of mitogen which is specific only to the receptors on certain types of cells. GH is a 191-amino acid, single-chain polypeptide that is synthesized, stored and secreted by somatotropic cells within the lateral wings of the anterior pituitary gland. A recombinant form of hGH called somatropin (INN) is used as a prescription drug to treat children's growth disorders and adult growth hormone deficiency. In the United States, it is only available legally from pharmacies by prescription from a licensed health care provider. In recent years in the United States, some health care providers are prescribing growth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigens
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. The term ''antigen'' originally referred to a substance that is an antibody generator. Antigens can be proteins, peptides (amino acid chains), polysaccharides (chains of monosaccharides/simple sugars), lipids, or nucleic acids. Antigens are recognized by antigen receptors, including antibodies and T-cell receptors. Diverse antigen receptors are made by cells of the immune system so that each cell has a specificity for a single antigen. Upon exposure to an antigen, only the lymphocytes that recognize that antigen are activated and expanded, a process known as clonal selection. In most cases, an antibody can only react to and bind one specific antigen; in some instances, however, antibodies may cross-react and bind more than one antigen. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins CD8 or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
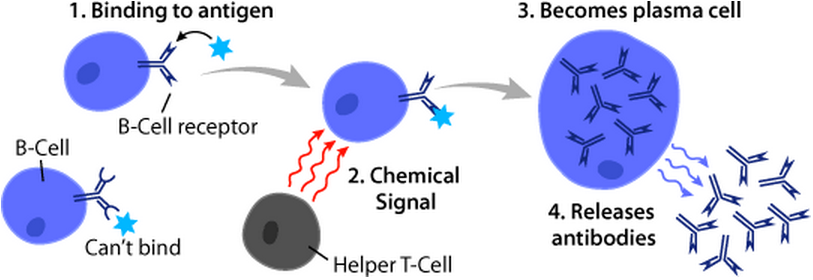
B Cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed. B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cells and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphocytes
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic adaptive immunity), and B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity). They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which prompted the name "lymphocyte". Lymphocytes make up between 18% and 42% of circulating white blood cells. Types The three major types of lymphocyte are T cells, B cells and natural killer (NK) cells. Lymphocytes can be identified by their large nucleus. T cells and B cells T cells (thymus cells) and B cells ( bone marrow- or bursa-derived cells) are the major cellular components of the adaptive immune response. T cells are involved in cell-mediated immunity, whereas B cells are primarily responsible for humoral immunity (relating to antibodies). The function of T cells and B cells is to recognize specif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inactivated Vaccine
An inactivated vaccine (or killed vaccine) is a vaccine consisting of virus particles, bacteria, or other pathogens that have been grown in culture and then killed to destroy disease-producing capacity. In contrast, live vaccines use pathogens that are still alive (but are almost always attenuated, that is, weakened). Pathogens for inactivated vaccines are grown under controlled conditions and are killed as a means to reduce infectivity and thus prevent infection from the vaccine. Inactivated vaccines were first developed in the late 1800s and early 1900s for cholera, plague, and typhoid. Today, inactivated vaccines exist for many pathogens, including influenza, polio (IPV), rabies, hepatitis A and pertussis. Because inactivated pathogens tend to produce a weaker response by the immune system than live pathogens, immunologic adjuvants and multiple "booster" injections may be required in some vaccines to provide an effective immune response against the pathogen. Attenuated vacci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |