|
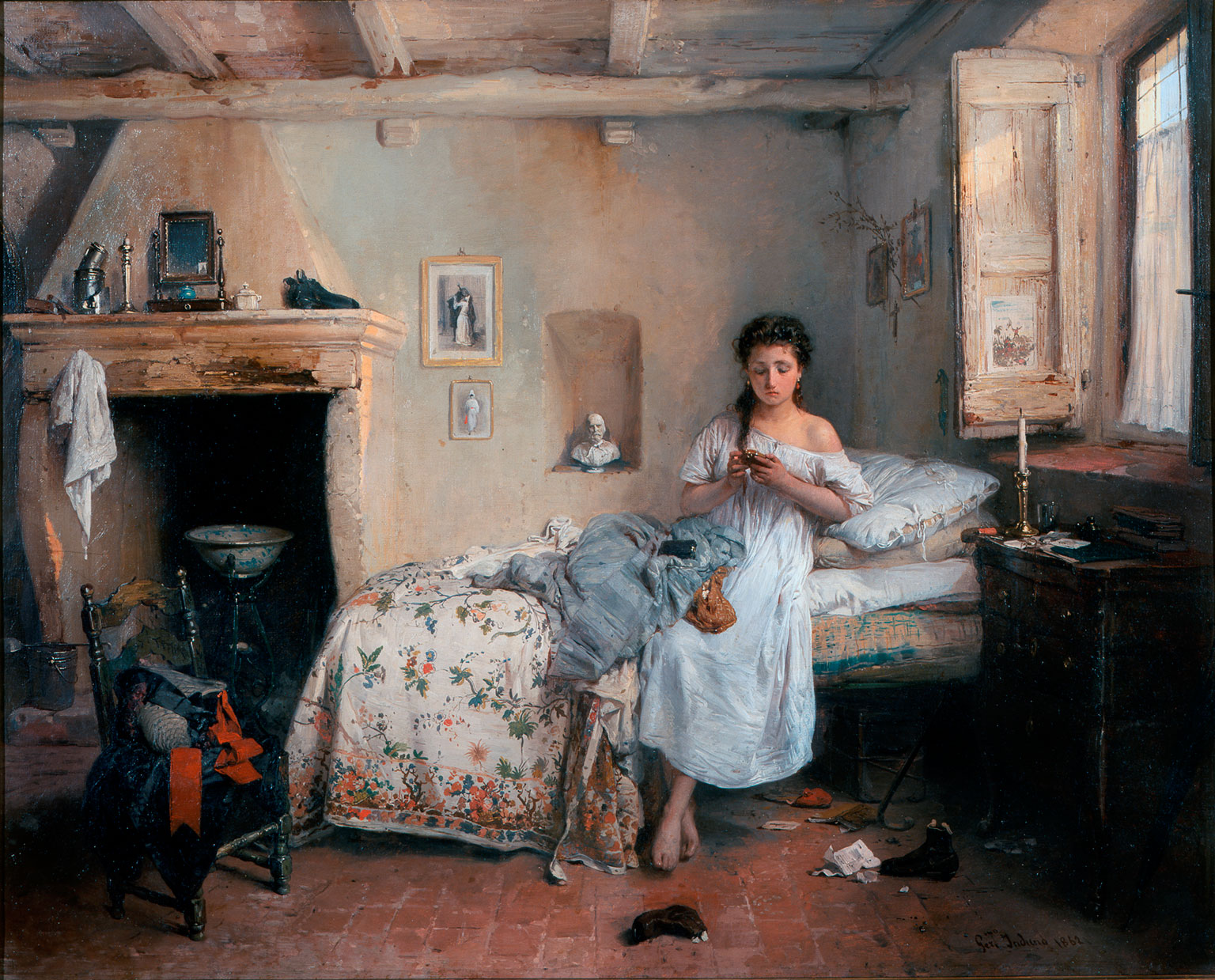
Il Bacio
''Il bacio'' (; ''The Kiss'') is an 1859 painting by the Italian artist Francesco Hayez. It is possibly his best known work. This painting conveys the main features of Italian Romanticism and has come to represent the spirit of the Risorgimento. It was commissioned by Alfonso Maria Visconti di Saliceto, who donated it to the Pinacoteca di Brera after his death. Historical context After the defeat of Napoleonic France in the 19th century, the Congress of Vienna was held in 1815 to redraw the map of Europe. Italy had a very marginal role compared to other European countries and was slated to be divided into several states. Every state was either ruled directly, or strongly influenced, by the Habsburgs of the Austrian Empire. That fragmentation went against the growing nationalist sentiment for Italy's unification, and caused the creation of secret societies with democratic-radical orientations, such as the Carboneria and Young Italy. Although those associations were unsuccessful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francesco Hayez
Francesco Hayez (; 10 February 1791 – 12 February 1882) was an Italian painter. He is considered one of the leading artists of Romanticism in mid-19th-century Milan, and is renowned for his grand historical paintings, political allegories, and portraits. Biography Francesco Hayez was from a relatively poor family from Venice. His father, Giovanni, was of French origin while his mother, Chiara Torcella, was from Murano. Francesco was the youngest of five sons. He was brought up by his mother's sister, who had married Giovanni Binasco, a well-off shipowner and art collector. Hayez displayed a predisposition for drawing since childhood. His uncle, having noticed his precocious talent, apprenticed him to an art restorer in Venice. Hayez would later become a pupil of the painter Francesco Maggiotto with whom he continued his studies for three years. He was admitted to the painting course of the New Academy of Fine Arts in Venice in 1806, where he studied under Teodoro Matteini. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to an 1946 Italian institutional referendum, institutional referendum to abandon the monarchy and form the modern Italy, Italian Republic. The state resulted from a decades-long process, the ''Italian unification, Risorgimento'', of consolidating the different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single state. That process was influenced by the House of Savoy, Savoy-led Kingdom of Sardinia, which can be considered Italy's legal Succession of states, predecessor state. Italy Third Italian War of Independence, declared war on Austrian Empire, Austria in alliance with Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia in 1866 and received the region of Veneto following their victory. Italian troops Capture of Rome, entered Rome in 1870, ending Papal States, more tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proclamation Of The Kingdom Of Italy
The proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy was the formal act that sanctioned the birth of the unified Kingdom of Italy. It happened with a normative act of the Savoyard Kingdom of Sardinia — the law 17 March 1861, n. 4761 — with which Victor Emmanuel II assumed for himself and for his successors the title of King of Italy. 17 March is commemorated annually by the anniversary of the unification of Italy, a national holiday established in 1911 on the occasion of the 50th anniversary, and also celebrated, in the Republican era, in 1961 and 2011. History Following the Second Italian War of Independence and the Expedition of the Thousand, led by Giuseppe Garibaldi, in the two-year period 1859-60, the goal of the unification of Italy had been largely achieved, with the sole exception of the Triveneto and Lazio. The annexation to the Kingdom of Sardinia of the various provinces had been sanctioned by a series of plebiscites. However, the new state still carried the name of Kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Unification
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single state in 1861, the Kingdom of Italy. Inspired by the rebellions in the 1820s and 1830s against the outcome of the Congress of Vienna, the unification process was precipitated by the Revolutions of 1848, and reached completion in 1871 after the Capture of Rome and its designation as the capital of the Kingdom of Italy. Some of the states that had been targeted for unification ('' terre irredente'') did not join the Kingdom of Italy until 1918 after Italy defeated Austria-Hungary in the First World War. For this reason, historians sometimes describe the unification period as continuing past 1871, including activities during the late 19th century and the First World War (1915–1918), and reaching completion only with the Armistice of Villa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas and achievements of classical antiquity. It occurred after the Crisis of the Late Middle Ages and was associated with great social change. In addition to the standard periodization, proponents of a "long Renaissance" may put its beginning in the 14th century and its end in the 17th century. The traditional view focuses more on the early modern aspects of the Renaissance and argues that it was a break from the past, but many historians today focus more on its medieval aspects and argue that it was an extension of the Middle Ages. However, the beginnings of the period – the early Renaissance of the 15th century and the Italian Proto-Renaissance from around 1250 or 1300 – overlap considerably with the Late Middle Ages, conventionally da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanishing Point
A vanishing point is a point on the image plane of a perspective drawing where the two-dimensional perspective projections of mutually parallel lines in three-dimensional space appear to converge. When the set of parallel lines is perpendicular to a picture plane, the construction is known as one-point perspective, and their vanishing point corresponds to the oculus, or "eye point", from which the image should be viewed for correct perspective geometry.Kirsti Andersen (2007) ''Geometry of an Art'', p. xxx, Springer, Traditional linear drawings use objects with one to three sets of parallels, defining one to three vanishing points. Italian humanist polymath and architect Leon Battista Alberti first introduced the concept in his treatise on perspective in art, '' De pictura'', written in 1435. Vector notation The vanishing point may also be referred to as the "direction point", as lines having the same directional vector, say ''D'', will have the same vanishing point. Mathem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Eastern Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biblioteca Ambrosiana
The Biblioteca Ambrosiana is a historic library in Milan, Italy, also housing the Pinacoteca Ambrosiana, the Ambrosian art gallery. Named after Ambrose, the patron saint of Milan, it was founded in 1609 by Cardinal Federico Borromeo, whose agents scoured Western Europe and even Greece and Syria for books and manuscripts. Some major acquisitions of complete libraries were the manuscripts of the Benedictine monastery of Bobbio (1606) and the library of the Paduan Vincenzo Pinelli, whose more than 800 manuscripts filled 70 cases when they were sent to Milan and included the famous ''Iliad'', the '' Ilias Picta''. History During Cardinal Borromeo's sojourns in Rome, 1585–95 and 1597–1601, he envisioned developing this library in Milan as one open to scholars and that would serve as a bulwark of Catholic scholarship in the service of the Counter-Reformation against the treatises issuing from Protestant presses. To house the cardinal's 15,000 manuscripts and twice that many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carolina Zucchi
Carolina may refer to: Geography * The Carolinas, the U.S. states of North and South Carolina ** North Carolina, a U.S. state ** South Carolina, a U.S. state * Province of Carolina, a British province until 1712 * Carolina, Alabama, a town in the United States * Carolina, North Carolina (other), multiple places * Carolina, Rhode Island, a village that straddles the border of two towns in the U.S. state of Rhode Island * Carolina, West Virginia * Carolina, Puerto Rico, a municipality in the United States * Carolina, U.S. Virgin Islands, a neighborhood * Carolina, Maranhão, a city in Brazil * Carolina, Mpumalanga, a town in South Africa * Carolina, Suriname, a city * The Carolina terrane, a geologic terrane in the southeastern United States * Carolina, San Luis, Argentina * Carolina, San Miguel, El Salvador * Carolina, Santa Maria, Brazil Music * "Carolina" (Taylor Swift song) (2022) * Carolina (Seu Jorge album) or ''Samba Esporte Fino'', also a track on the albu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sotheby's Auction House
Sotheby's () is a British-founded American multinational corporation with headquarters in New York City. It is one of the world's largest brokers of fine and decorative art, jewellery, and collectibles. It has 80 locations in 40 countries, and maintains a significant presence in the UK. Sotheby's was established on 11 March 1744 in London by Samuel Baker, a bookseller. In 1767 the firm became Baker & Leigh, after George Leigh became a partner, and was renamed to Leigh and Sotheby in 1778 after Baker's death when Leigh's nephew, John Sotheby, inherited Leigh's share. Other former names include: Leigh, Sotheby and Wilkinson; Sotheby, Wilkinson and Hodge (1864–1924); Sotheby and Company (1924–83); Mssrs Sotheby; Sotheby & Wilkinson; Sotheby Mak van Waay; and Sotheby's & Co. The American holding company was initially incorporated in August 1983 in Michigan as Sotheby's Holdings, Inc. In June 2006, it was reincorporated in the State of Delaware and was renamed Sotheby's. In Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exposition Universelle (1867)
The International Exposition of 1867 (french: Exposition universelle 'art et d'industriede 1867), was the second world's fair to be held in Paris, from 1 April to 3 November 1867. A number of nations were represented at the fair. Following a decree of Emperor Napoleon III, the exposition was prepared as early as 1864, in the midst of the renovation of Paris, marking the culmination of the Second French Empire. Visitors included Tsar Alexander II of Russia, a brother of the King William and Otto von Bismarck of Prussia, Prince Metternich and Franz Josef of Austria, Ottoman Sultan Abdülaziz, and the Khedive of Egypt Isma'il. Conception In 1864, Napoleon III issued a decree stating that an international exposition should be held in Paris in 1867. A commission was appointed with Prince Jerome Napoleon as president, under whose direction the preliminary work began. The site chosen for the Exposition Universelle of 1867 was the Champ de Mars, the great military parade ground ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia,The name of the state was originally Latin: , or when the kingdom was still considered to include Corsica. In Italian it is , in French , in Sardinian , and in Piedmontese . also referred to as the Kingdom of Savoy-Sardinia, Piedmont-Sardinia, or Savoy-Piedmont-Sardinia during the Savoyard period, was a state in Southern Europe from the early 14th until the mid-19th century. The Kingdom was a member of the Council of Aragon and initially consisted of the islands of Corsica and Sardinia, sovereignty over both of which was claimed by the Papacy, which granted them as a fief, the ("kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica"), to King James II of Aragon in 1297. Beginning in 1324, James and his successors conquered the island of Sardinia and established ''de facto'' their ''de jure'' authority. In 1420, after the Sardinian–Aragonese war, the last competing claim to the island was bought out. After the union of the crowns of Aragon and Castile, Sardinia becam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |