|
Iceland Plateau
The Iceland Plateau or Icelandic Plateau is an oceanic plateau in the North Atlantic Ocean consisting of Iceland and its contiguous shelf and marginal slopes. The landscape is constantly experiencing deformation due to the continual addition of magma to the surface and the shifting of the ocean ridge. Location and Characteristics The Iceland Plateau is bounded on the south by the Reykjanes Ridge, on the west by the Greenland-Iceland Ridge, on the north by the Kolbeinsey Ridge, and on the east by the Iceland-Faeroe Ridge. It consists of a large igneous province that has been volcanically active since at least the Miocene epoch. The plateau has an average elevation of 1,700 meters above sea level. The geology of the Icelandic Plateau consists of three layers, closely mimicking the structure of oceanic crust but with one key difference, the second layer of the oceanic crust does not contain piles of lava flow like the Icelandic Plateau does. The first layer is composed of mainly se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icelandic Ocean
Icelandic refers to anything of, from, or related to Iceland and may refer to: *Icelandic people *Icelandic language *Icelandic alphabet *Icelandic cuisine See also * Icelander (other) * Icelandic Airlines, a predecessor of Icelandair * Icelandic horse, a breed of domestic horse * Icelandic sheep, a breed of domestic sheep * Icelandic Sheepdog, a breed of domestic dog * Icelandic cattle Icelandic cattle ( is, íslenskur nautgripur ) are a breed of cattle native to Iceland. Cattle were first brought to the island during the Settlement of Iceland a thousand years ago. Icelandic cows are an especially colorful breed with a wide v ..., a breed of cattle * Icelandic chicken, a breed of chicken {{disambig Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
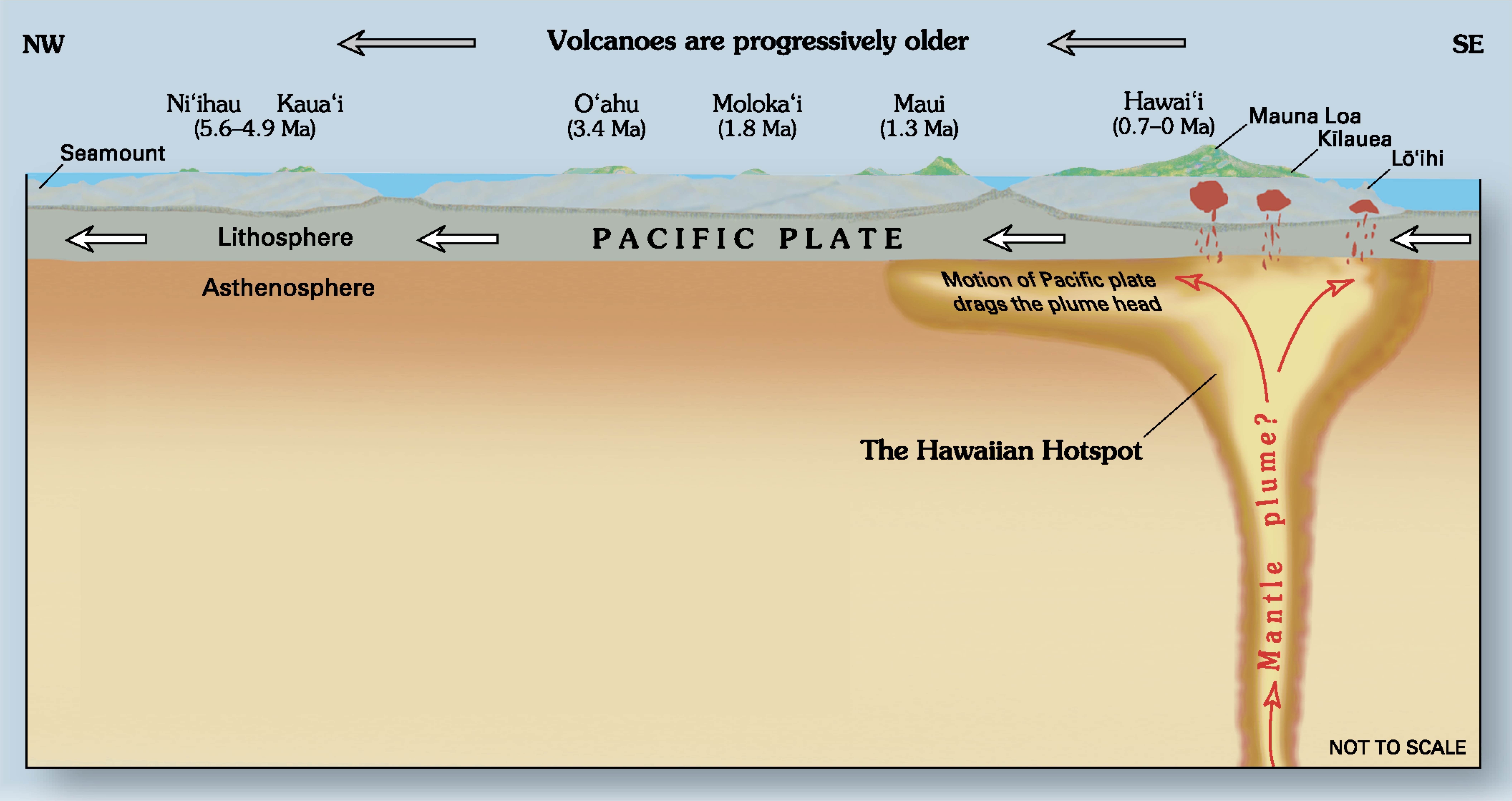
Hotspot (geology)
In geology, hotspots (or hot spots) are volcanic locales thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. Examples include the Hawaii, Iceland, and Yellowstone hotspots. A hotspot's position on the Earth's surface is independent of tectonic plate boundaries, and so hotspots may create a chain of volcanoes as the plates move above them. There are two hypotheses that attempt to explain their origins. One suggests that hotspots are due to mantle plumes that rise as thermal diapirs from the core–mantle boundary. The alternative plate theory is that the mantle source beneath a hotspot is not anomalously hot, rather the crust above is unusually weak or thin, so that lithospheric extension permits the passive rising of melt from shallow depths. Origin The origins of the concept of hotspots lie in the work of J. Tuzo Wilson, who postulated in 1963 that the formation of the Hawaiian Islands resulted from the slow movement of a tecton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene Volcanism
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago. It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the . The Pliocene follows the Epoch and is followed by the Epoch. Prior to the 2009 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene Volcanism
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
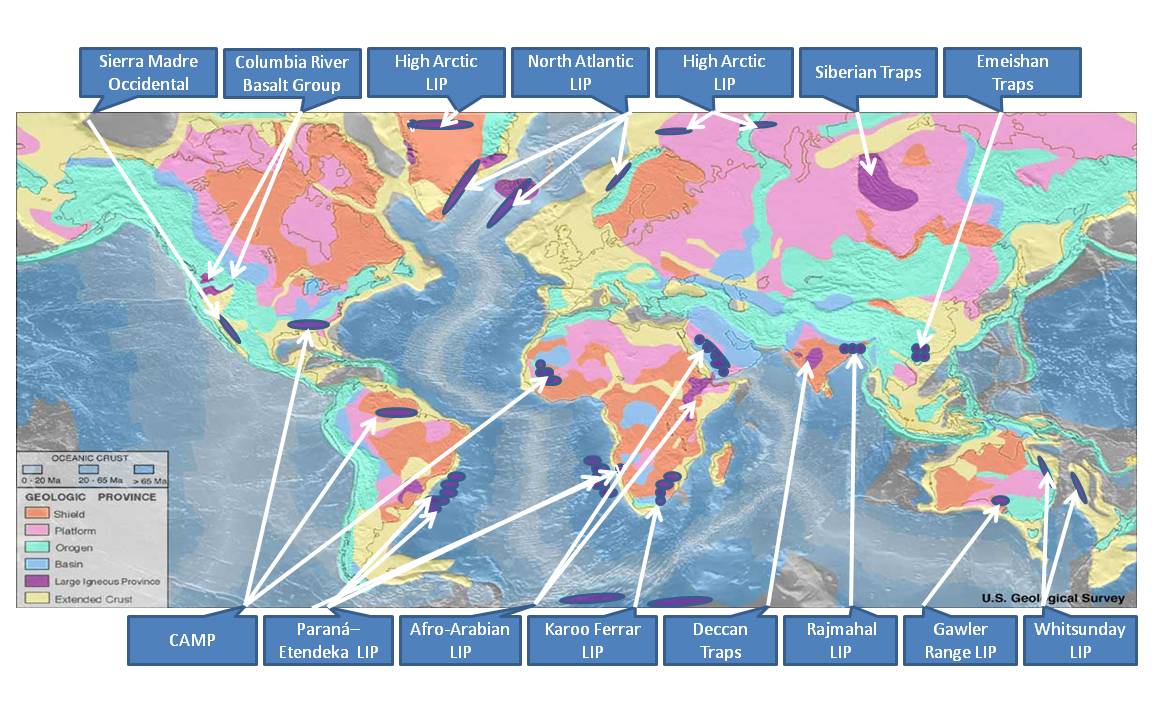
Large Igneous Provinces
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive (sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation of LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with divergent plate tectonics. The formation of some of the LIPs in the past 500 million years coincide in time with mass extinctions and rapid climatic changes, which has led to numerous hypotheses about causal relationships. LIPs are fundamentally different from any other currently active volcanoes or volcanic systems. Definition In 1992 researchers first used the term ''large igneous province'' to describe very large accumulations—areas greater than 100,000 square kilometers (approximately the area of Iceland)—of mafic igneous rocks that were erupted or emplaced at depth within an extremely short geological time interval: a few million years or less. Maf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hotspot Volcanism
Hotspot, Hot Spot or Hot spot may refer to: Places * Hot Spot, Kentucky, a community in the United States Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Hot Spot (comics), a name for the DC Comics character Isaiah Crockett * Hot Spot (Transformers), any of several characters Films * ''Hot Spot'' (1941 film), later retitled ''I Wake Up Screaming'' * ''Hot Spot'' (1945 film), a Private Snafu film * ''The Hot Spot'', a 1990 neo-noir film Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * ''Hot Spot'' (board game), a 1979 board game published by Metagaming Concepts * "Hot Spot" (''Burn Notice''), a television episode * ''Hot Spot'' (musical), 1963 * "Hot Spot" (song), by Foxy Brown * ''Hotspot'' (album), a 2020 album by Pet Shop Boys * ''The Hot Spot'' (Podcast), a GameSpot podcast Computing * Hot spot (computer programming), a compute-intensive region of a program * Hot spot, an area which is customizable by users in software frameworks * Hotspot (Wi-Fi), a wireless n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanism Of Iceland
:''The volcano system in Iceland that started activity on August 17, 2014, and ended on February 27, 2015, is Bárðarbunga.'' :''The volcano in Iceland that erupted in May 2011 is Grímsvötn.'' Iceland experiences frequent volcanic activity, due to its location both on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a divergent tectonic plate boundary, and over a hot spot. Nearly thirty volcanoes are known to have erupted in the Holocene epoch; these include Eldgjá, source of the largest lava eruption in human history. Volcanic systems and volcanic zones of Iceland Holocene volcanism in Iceland is mostly to be found in the ''Neovolcanic Zone'', comprising the Reykjanes Volcanic Belt (RVB), the West Volcanic Zone (WVZ), the Mid-Iceland Belt (MIB), the East Volcanic Zone (EVZ) and the North Volcanic Zone (NVZ). Two lateral volcanic zones play a minor role: Öræfi Volcanic Belt (ÖVB) and Snæfellsnes Volcanic Belt (SVB). Outside of the main island are the Reykjanes Ridge (RR), as part of the Mid-At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plateaus Of Iceland
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides have deep hills or escarpments. Plateaus can be formed by a number of processes, including upwelling of volcanic magma, extrusion of lava, and erosion by water and glaciers. Plateaus are classified according to their surrounding environment as intermontane, piedmont, or continental. A few plateaus may have a small flat top while others have wide ones. Formation Plateaus can be formed by a number of processes, including upwelling of volcanic magma, extrusion of lava, Plate tectonics movements and erosion by water and glaciers. Volcanic Volcanic plateaus are produced by volcanic activity. The Columbia Plateau in the north-western United States is an example. They may be formed by upwelling of volcanic magma or extrusion of lava. The un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lava Dome
In volcanology, a lava dome is a circular mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano. Dome-building eruptions are common, particularly in convergent plate boundary settings. Around 6% of eruptions on Earth are lava dome forming. The geochemistry of lava domes can vary from basalt (e.g. Semeru, 1946) to rhyolite (e.g. Chaiten, 2010) although the majority are of intermediate composition (such as Santiaguito, dacite-andesite, present day) The characteristic dome shape is attributed to high viscosity that prevents the lava from flowing very far. This high viscosity can be obtained in two ways: by high levels of silica in the magma, or by degassing of fluid magma. Since viscous basaltic and andesitic domes weather fast and easily break apart by further input of fluid lava, most of the preserved domes have high silica content and consist of rhyolite or dacite. Existence of lava domes has been suggested for some domed structures on the Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhyolitic
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The mineral assemblage is predominantly quartz, sanidine, and plagioclase. It is the extrusive equivalent to granite. Rhyolitic magma is extremely viscous, due to its high silica content. This favors explosive eruptions over effusive eruptions, so this type of magma is more often erupted as pyroclastic rock than as lava flows. Rhyolitic ash-flow tuffs are among the most voluminous of continental igneous rock formations. Rhyolitic tuff has been extensively used for construction. Obsidian, which is rhyolitic volcanic glass, has been used for tools from prehistoric times to the present day because it can be shaped to an extremely sharp edge. Rhyolitic pumice finds use as an abrasive, in concrete, and as a soil amendment. Description Rhyolite is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial planet, rocky planet or natural satellite, moon. More than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt is chemically equivalent to slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro. The eruption of basalt lava is observed by geologists at about 20 volcanoes per year. Basalt is also an important rock type on other planetary bodies in the Solar System. For example, the bulk of the plains of volcanism on Venus, Venus, which cover ~80% of the surface, are basaltic; the lunar mare, lunar maria are plains of flood-basaltic lava flows; and basalt is a common rock on the surface of Mars. Molten basalt lava has a low viscosity due to its relatively low silica content (between 45% and 52%), resulting in rapidly moving lava flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tholeiitic
The tholeiitic magma series is one of two main magma series in subalkaline igneous rocks, the other being the calc-alkaline series. A magma series is a chemically distinct range of magma compositions that describes the evolution of a mafic magma into a more evolved, silica rich end member. Rock types of the tholeiitic magma series include tholeiitic basalt, ferro-basalt, tholeiitic basaltic andesite, tholeiitic andesite, dacite and rhyolite. The variety of basalt in the series was originally called ''tholeiite'' but the International Union of Geological Sciences recommends that ''tholeiitic basalt'' be used in preference to that term.Le Maitre ''et al.'' 2002 Tholeiitic rock types tend to be more enriched in iron and less enriched in aluminium than calc-alkaline rock types. They are thought to form in a less oxidized environment than calc-alkaline rocks. Tholeiitic basalt is formed at mid-ocean ridges and makes up much of the oceanic crust. Almost all the basalt found on the Moon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |