|
IV Brigade, Royal Horse Artillery
IV Brigade, Royal Horse Artillery was a brigade of the Royal Horse Artillery which existed in the early part of the 20th century. It served with 3rd Cavalry Division throughout World War I but was dissolved shortly thereafter. The successor unit, 4th Regiment, RHA, was formed in 1939 and still exists as 4th Regiment Royal Artillery. The brigade had an earlier incarnation as D Brigade, Royal Horse Artillery, formed from the Horse Artillery Brigade of the Honourable East India Company's Madras Army in 1862 before being broken up in 1877. History D Brigade, RHA The Madras Army of the Honourable East India Company formed its first battery of Horse Artillery ''The Troop of Madras Horse Artillery'' on 4 April 1805 (still in existence as J Battery, RHA). By 5 August 1825, the Madras Horse Artillery had grown to a peak strength of eight batteries and was organized as two brigades; on 4 January 1831 the brigade system was discontinued and the Madras Horse Artillery shrank to six b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and led to heavy, fairly immobile siege engines. As technology improved, lighter, more mobile field artillery cannons developed for battlefield use. This development continues today; modern self-propelled artillery vehicles are highly mobile weapons of great versatility generally providing the largest share of an army's total firepower. Originally, the word "artillery" referred to any group of soldiers primarily armed with some form of manufactured weapon or armor. Since the introduction of gunpowder and cannon, "artillery" has largely meant cannons, and in contemporary usage, usually refers to shell-firing guns, howitzers, and mortars (collectively called ''barrel artillery'', ''cannon artillery'', ''gun artillery'', or - a layman t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J Battery, Royal Horse Artillery
J, or j, is the tenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its usual name in English is ''jay'' (pronounced ), with a now-uncommon variant ''jy'' ."J", ''Oxford English Dictionary,'' 2nd edition (1989) When used in the International Phonetic Alphabet for the ''y'' sound, it may be called ''yod'' or ''jod'' (pronounced or ). History The letter ''J'' used to be used as the swash letter ''I'', used for the letter I at the end of Roman numerals when following another I, as in XXIIJ or xxiij instead of XXIII or xxiii for the Roman numeral twenty-three. A distinctive usage emerged in Middle High German. Gian Giorgio Trissino (1478–1550) was the first to explicitly distinguish I and J as representing separate sounds, in his ''Ɛpistola del Trissino de le lettere nuωvamente aggiunte ne la lingua italiana'' ("Trissino's epistle about the letters recently added in the It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
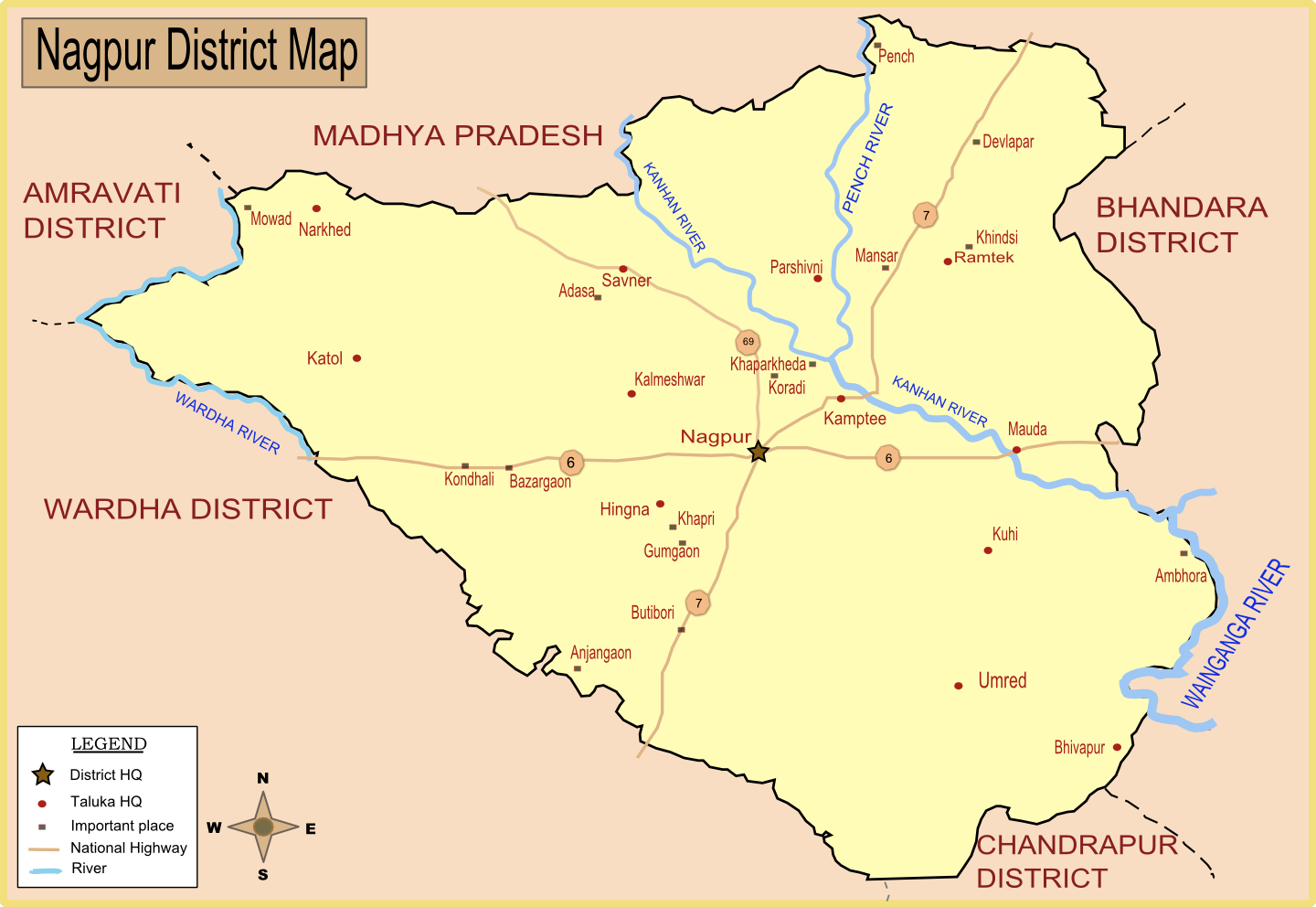
Kamptee
Kamptee is a suburb of Nagpur city and a municipal council in Nagpur district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is part of the Nagpur metropolitan region development authority. It is the administrative center for Kamptee taluka. It is below the confluence of the Kanhan River with the rivers Pench and Kolar. History Kamptee was founded in 1821 when the British established a military cantonment on the banks of the Kanhan. Kamptee was previously named Camp-T for its shape. The town quickly became a center for trade, but trade dwindled with the arrival of the railway in the late 19th century. An Iron Age hoard of weapons was excavated by Major George Pearse of the Royal Artillery from the Wurreegaon barrow near Kamptee in the mid-nineteenth century. Dating to between the 7th and 1st centuries BCE, it was one of the first hoards from this period discovered in the Indian Sub-Continent and is now kept in the British Museum, London. Geography National Highway No.7 passes thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F Brigade, Royal Horse Artillery
6th Regiment, Royal Horse Artillery was a Regiment of the Royal Horse Artillery that acted as a training formation during World War II. It was the last RHA unit to serve in India between December 1945 and April 1947, before being redesignated as 6th Field Regiment, Royal Artillery in Palestine in 1948. The regiment had an earlier incarnation as F Brigade, RHA, formed from the 2nd Brigade of the Bengal Horse Artillery in 1862 before being broken up in 1877. It was reestablished in 1901 as VI Brigade, RHA but was broken up at the outbreak of World War I as its constituent batteries were posted to other formations. History F Brigade, RHA The Bengal Army of the Honourable East India Company formed its first battery of Horse Artillery, the ''Experimental Brigade, Bengal Horse Artillery'' on 4 December 1800 (still in existence as F Battery, RHA). By the time the Indian Rebellion of 1857 broke out, the Bengal Horse Artillery had grown to 13 batteries, organized as three brigades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E Brigade, Royal Horse Artillery
V Brigade, Royal Horse Artillery was a brigade of the Royal Horse Artillery which existed in the early part of the 20th century. It served with 8th Division on the Western Front in World War I before becoming V Army Brigade, RHA in January 1917. It was reformed after the war but was disbanded in October 1928. The successor unit, 5th Regiment, RHA, was formed in 1939 and still exists as 5th Regiment Royal Artillery. The brigade had an earlier incarnation as E Brigade, RHA, formed from the Horse Artillery Brigade of the Honourable East India Company's Bombay Army in 1862 before being broken up in 1877. History E Brigade, RHA The Bombay Army of the Honourable East India Company was the last of the Presidency armies to form Horse Artillery, only forming the ''1st Troop, Bombay Horse Artillery'' on 11 November 1811 (still in existence as N Battery, RHA). By the time the Indian Rebellion of 1857 broke out, the Bombay Horse Artillery had grown to four batteries, organized a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C Brigade, Royal Horse Artillery
III Brigade, Royal Horse Artillery was a brigade of the Royal Horse Artillery which existed in the early part of the 20th century. It served with the 1st and 2nd Cavalry Divisions on the Western Front throughout World War I. Post-war, the brigade served in the UK and India before being redesignated as 3rd Regiment, RHA in August 1938 in Egypt. The regiment had an earlier incarnation as C Brigade, RHA, formed from the 1st Brigade of the Honourable East India Company's Bengal Horse Artillery in 1862 before being broken up in 1882. History C Brigade, RHA The Bengal Army of the Honourable East India Company formed its first battery of Horse Artillery, the ''Experimental Brigade, Bengal Horse Artillery'' on 4 December 1800 (still in existence as F Battery, RHA). By the time the Indian Rebellion of 1857 broke out, the Bengal Horse Artillery had grown to 13 batteries, organised as three brigades. four of these batteries were manned by sepoys (native Indian soldiers) and two mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B Brigade, Royal Horse Artillery
2nd Regiment Royal Horse Artillery was a regiment of the Royal Horse Artillery that served in the Second World War. It saw action in France, Greece, North Africa and Italy. It was redesignated as 2nd Field Regiment, Royal Artillery in 1958. The regiment had an earlier incarnation as B Brigade, RHA, formed from the Horse Brigade, Royal Artillery in 1864 before being broken up in 1889. It was reestablished in 1901 as II Brigade, RHA but was broken up at the outbreak of the First World War as its constituent battery was posted away. History B Brigade, RHA Royal Horse Artillery brigades did not exist as an organizational or operational grouping of batteries until 1 July 1859 when the Horse Brigade, Royal Artillery was formed. As a result of the Indian Rebellion of 1857, the British Crown took direct control of India from the East India Company on 1 November 1858 under the provisions of the Government of India Act 1858. The Presidency armies transferred to the direct authority o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Brigade, Royal Horse Artillery
I Brigade, Royal Horse Artillery was a brigade of the Royal Horse Artillery which existed in the early part of the 20th century. It was dissolved at the outbreak of World War I as its constituent batteries were posted to other formations. Post-war, the brigade was reformed, serving in the UK, Egypt and India before being redesignated as 1st Regiment, RHA in May 1938 at Aldershot. The brigade had an earlier incarnation as A Brigade, RHA, formed from the Horse Brigade, Royal Artillery in 1864 before being broken up in 1889. History A Brigade, RHA Royal Horse Artillery brigades did not exist as an organizational or operational grouping of batteries until 1 July 1859 when the Horse Brigade, Royal Artillery was formed. It commanded all the existing horse artillery batteries of the Royal Artillery: *A Battery, Horse Brigade, Royal Artillery at Aldershot *B Battery, Horse Brigade, Royal Artillery at Woolwich *C Battery, Horse Brigade, Royal Artillery at Cahir *D Battery, Horse Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R Battery, Royal Horse Artillery
R, or r, is the eighteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ar'' (pronounced ), plural ''ars'', or in Ireland ''or'' . The letter is the eighth most common letter in English and the fourth-most common consonant (after , , and ). The letter is used to form the ending "-re", which is used in certain words such as ''centre'' in some varieties of English spelling, such as British English. Canadian English also uses the "-re" ending, unlike American English, where the ending is usually replaced by "-er" (''center''). This does not affect pronunciation. Name The name of the letter in Latin was (), following the pattern of other letters representing continuants, such as F, L, M, N and S. This name is preserved in French and many other languages. In Middle English, the name of the letter changed from to , following a pattern exhibited in many o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P Battery, Royal Horse Artillery
P, or p, is the sixteenth letter (alphabet), letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is English alphabet#Letter names, ''pee'' (pronounced ), plural ''pees''. History The Semitic languages, Semitic Pê (mouth), as well as the Greek language, Greek Π or π (Pi (letter), Pi), and the Etruscan language, Etruscan and Latin letters that developed from the former alphabet, all symbolized , a voiceless bilabial plosive. Use in writing systems In English orthography and most other European languages, represents the sound . A common Digraph (orthography), digraph in English is , which represents the sound , and can be used to transliterate ''phi'' in loanwords from Greek language, Greek. In German, the digraph is common, representing a labial affricate . Most English words beginning with are of foreign origin, primarily French, Latin and Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M Battery Royal Horse Artillery
M (Headquarters) Battery Royal Horse Artillery is the Headquarters Battery of 3rd Regiment Royal Horse Artillery, part of the Royal Horse Artillery of the British Army. As of 2015, it is based at Albemarle Barracks, Northumberland, England. The Battery Commander is Maj B Johnston RHA. History Madras Horse Artillery M Battery, Royal Horse Artillery was formed on 23 January 1809 as 2nd Troop, Madras Horse Artillery, a horse artillery battery of the Honourable East India Company's Madras Army. On 5 August 1825, it was redesignated as B Troop, 1st Brigade, Madras Horse Artillery as the Madras Horse Artillery expanded to 8 troops and was organized as two brigades. A reduction to 6 troops on 4 January 1831 resulted in the brigades being discontinued and the remaining troops lettered in a single sequence, hence becoming B Troop, Madras Horse Artillery. As a result of the Indian Rebellion of 1857, the British Crown took direct control of India from the East India Company on 1 Novembe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkhas, and 28,330 volunteer reserve personnel. The modern British Army traces back to 1707, with antecedents in the English Army and Scots Army that were created during the Restoration in 1660. The term ''British Army'' was adopted in 1707 after the Acts of Union between England and Scotland. Members of the British Army swear allegiance to the monarch as their commander-in-chief, but the Bill of Rights of 1689 and Claim of Right Act 1689 require parliamentary consent for the Crown to maintain a peacetime standing army. Therefore, Parliament approves the army by passing an Armed Forces Act at least once every five years. The army is administered by the Ministry of Defence and commanded by the Chief of the General Staff. The Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |