|
ITPKB
Inositol-trisphosphate 3-kinase B is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ITPKB'' gene. Function The protein encoded by the ITPKB gene is one of 3 isoforms of Inositol-trisphosphate 3-kinase expressed in humans. ITPKB protein regulates inositol phosphate metabolism by phosphorylation of second messenger inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, which releases calcium from intracellular store in the endoplasmic reticulum by gating the inositol trisphosphate receptor. ITPKB produces Ins(1,3,4,5)P4, which does ''not'' gate the inositol trisphosphate receptor Inositol trisphosphate receptor (InsP3R) is a membrane glycoprotein complex acting as a Ca2+ channel activated by inositol trisphosphate (InsP3). InsP3R is very diverse among organisms, and is necessary for the control of cellular and physiol .... The enzyme specifically phosphorylates the 1,4,5 isomer of IP3. The activity of this encoded protein is responsible for regulating the levels of a large number of inositol polypho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inositol-trisphosphate 3-kinase
Inositol (1,4,5) trisphosphate 3-kinase (), abbreviated here as ITP3K, is an enzyme that facilitates a phospho-group transfer from adenosine triphosphate to 1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically those transferring phosphorus-containing groups (phosphotransferases) with an alcohol group as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is ATP:1D-myo-inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphotransferase. ITP3K catalyzes the transfer of the gamma-phosphate from ATP to the 3-position of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate to form inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate. ITP3K is highly specific for the 1,4,5-isomer of IP3, and it exclusively phosphorylates the 3-OH position, producing Ins(1,3,4,5)P4, also known as inositol tetrakisphosphate or IP4. In biology, the enzyme ITP3K is abbreviated a number of different ways, including 1D-myo-inositol-trisphosphate 3-kinase, ITP3K, ITPK, IP3-kinase, IP3-3-kinase, Ins(1,4,5)P3 3-kinase. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inositol Phosphate
Inositol phosphates are a group of mono- to hexaphosphorylated inositols. They play crucial roles in diverse cellular functions, such as cell growth, apoptosis, cell migration, endocytosis, and cell differentiation. The group comprises: * inositol monophosphate (IP) * inositol bisphosphate (IP2) * inositol trisphosphate (IP3) * inositol pentakisphosphate (IP5) * inositol hexaphosphate (IP6) also known as phytic acid, or phytate (as a salt). Functions Inositol triphosphate Inositol trisphosphates act on the inositol triphosphate receptor to release calcium into the cytoplasm. ''Further reading: Function of calcium in humans'' Other Inositol tetra-, penta-, and hexa-phosphates have been implicated in gene expression Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. The .... Inositol hexa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes. Glucose Phosphorylation of sugars is often the first stage in their catabolism. Phosphorylation allows cells to accumulate sugars because the phosphate group prevents the molecules from diffusing back across their transporter. Phosphorylation of glucose is a key reaction in sugar metabolism. The chemical equation for the conversion of D-glucose to D-glucose-6-phosphate in the first step of glycolysis is given by :D-glucose + ATP → D-glucose-6-phosphate + ADP : ΔG° = −16.7 kJ/mol (° indicates measurement at standard condition) Hepatic cells are freely permeable to glucose, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate
Inositol trisphosphate or inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate abbreviated InsP3 or Ins3P or IP3 is an inositol phosphate signaling molecule. It is made by hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2), a phospholipid that is located in the plasma membrane, by phospholipase C (PLC). Together with diacylglycerol (DAG), IP3 is a second messenger molecule used in signal transduction in biological cells. While DAG stays inside the membrane, IP3 is soluble and diffuses through the cell, where it binds to its receptor, which is a calcium channel located in the endoplasmic reticulum. When IP3 binds its receptor, calcium is released into the cytosol, thereby activating various calcium regulated intracellular signals. Properties Chemical formula and molecular weight IP3 is an organic molecule with a molecular mass of 420.10 g/mol. Its empirical formula is C6H15O15P3. It is composed of an inositol ring with three phosphate groups bound at the 1, 4, and 5 carbon positions, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
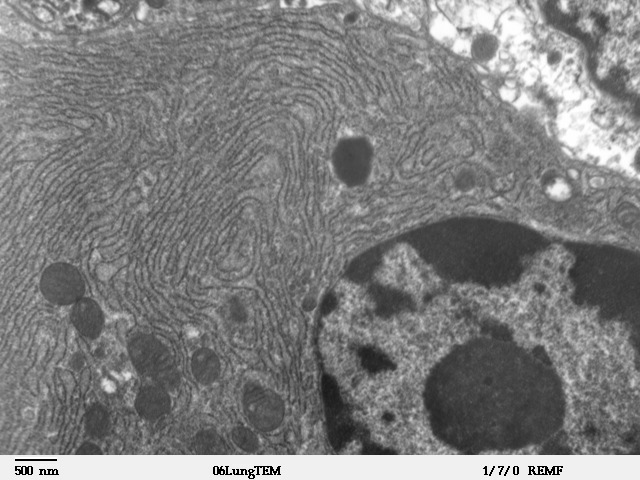
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The endoplasmic reticulum is found in most eukaryotic cells and forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs known as cisternae (in the RER), and tubular structures in the SER. The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum is not found in red blood cells, or spermatozoa. The two types of ER share many of the same proteins and engage in certain common activities such as the synthesis of certain lipids and cholesterol. Different types of cells contain different ratios of the two types of ER depending on the activities of the cell. RER is found mainly toward the nucleus of cell and SER towards the cell membrane or plasma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inositol Trisphosphate Receptor
Inositol trisphosphate receptor (InsP3R) is a membrane glycoprotein complex acting as a Ca2+ channel activated by inositol trisphosphate (InsP3). InsP3R is very diverse among organisms, and is necessary for the control of cellular and physiological processes including cell division, cell proliferation, apoptosis, fertilization, development, behavior, learning and memory. Inositol triphosphate receptor represents a dominant second messenger leading to the release of Ca2+ from intracellular store sites. There is strong evidence suggesting that the InsP3R plays an important role in the conversion of external stimuli to intracellular Ca2+ signals characterized by complex patterns relative to both space and time, such as Ca2+ waves and oscillations. Discovery The InsP3 receptor was first purified from rat cerebellum by neuroscientists Surachai Supattapone and Solomon Snyder at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. The cDNA of the InsP3 receptor was first cloned in the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |