|
ISS Propulsion Module
The ISS Propulsion module, functions performed by the Zvezda (ISS module), Zvezda Service Module and Progress (spacecraft), Progress spacecraft. Critical ISS functionality such as guidance, navigation, control and propulsion are provided only by Russian (Zvezda and Progress) and the European (Automated Transfer Vehicle, ATV) spacecraft. A Propulsion Module would have been needed for ISS altitude maintenance and reboost, debris avoidance maneuvers, attitude control and propellant supply in the event the Zvezda Service Module was not available (launch failure, etc.) to the International Space Station. If the Zvezda had not been available, the Interim Control Module would have been used at first. It only had a lifetime of three years; then the Propulsion Module would have been necessary. History The ISS requires an average 7,000 kg of propellant each year for altitude maintenance, debris avoidance and attitude control. A Propulsion Module would have provided reserve propellant f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISS Propulsion Module
The ISS Propulsion module, functions performed by the Zvezda (ISS module), Zvezda Service Module and Progress (spacecraft), Progress spacecraft. Critical ISS functionality such as guidance, navigation, control and propulsion are provided only by Russian (Zvezda and Progress) and the European (Automated Transfer Vehicle, ATV) spacecraft. A Propulsion Module would have been needed for ISS altitude maintenance and reboost, debris avoidance maneuvers, attitude control and propellant supply in the event the Zvezda Service Module was not available (launch failure, etc.) to the International Space Station. If the Zvezda had not been available, the Interim Control Module would have been used at first. It only had a lifetime of three years; then the Propulsion Module would have been necessary. History The ISS requires an average 7,000 kg of propellant each year for altitude maintenance, debris avoidance and attitude control. A Propulsion Module would have provided reserve propellant f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zvezda (ISS Module)
''Zvezda'' (russian: Звезда, meaning "star"), ''Salyut'' DOS-8, also known as the ''Zvezda'' Service Module, is a module of the International Space Station (ISS). It was the third module launched to the station, and provided all of the station's life support systems, some of which are supplemented in the US Orbital Segment (USOS), as well as living quarters for two crew members. It is the structural and functional center of the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS), which is the Russian part of the ISS. Crew assemble here to deal with emergencies on the station. The module was manufactured in the USSR by RKK Energia, with major sub-contracting work by GKNPTs Khrunichev. ''Zvezda'' was launched on a Proton launch vehicle on 12 July 2000, and docked with the '' Zarya'' module on 26 July 2000. Origins The basic structural frame of ''Zvezda'', known as "DOS-8", was initially built in the mid-1980s to be the core of the ''Mir-2'' space station. This means that ''Zvezda'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress (spacecraft)
The Progress (russian: Прогресс) is a Russian expendable cargo spacecraft. Its purpose is to deliver the supplies needed to sustain a human presence in orbit. While it does not carry a crew, it can be boarded by astronauts when docked to a space station, hence it is classified as ''crewed'' by its manufacturer. Progress is derived from the crewed Soyuz spacecraft and launches on the same launch vehicle, a Soyuz rocket. Progress has supported space stations as early as Salyut 6 and as recently as the International Space Station (ISS). Each year there are between three and four Progress flights to the ISS. A Progress remains docked until shortly before being replaced with a new one or a Soyuz (which will use the same docking port). Then it is filled with waste, disconnected, and de-orbited, at which point it burns up in the atmosphere. Due to the variation in Progress vehicles flown to the ISS, NASA uses its own nomenclature where "ISS 1P" means the first Progress spacecra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, marine navigation, aeronautic navigation, and space navigation. It is also the term of art used for the specialized knowledge used by navigators to perform navigation tasks. All navigational techniques involve locating the navigator's position compared to known locations or patterns. Navigation, in a broader sense, can refer to any skill or study that involves the determination of position and direction. In this sense, navigation includes orienteering and pedestrian navigation. History In the European medieval period, navigation was considered part of the set of '' seven mechanical arts'', none of which were used for long voyages across open ocean. Polynesian navigation is probably the earliest form of open-ocean navigation; it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automated Transfer Vehicle
The Automated Transfer Vehicle, originally Ariane Transfer Vehicle or ATV, was an expendable cargo spacecraft developed by the European Space Agency (ESA), used for space cargo transport in 2008–2015. The ATV design was launched to orbit five times, exclusively by the Ariane 5 heavy-lift launch vehicle. It effectively was a larger European counterpart to the Russian Progress cargo spacecraft for carrying upmass to a single destination—the International Space Station (ISS)—but with three times the capacity. The five ATVs were named after important European figures in science and engineering: '' Jules Verne'', '' Johannes Kepler'', ''Edoardo Amaldi'', ''Albert Einstein'', and ''Georges Lemaître''. Following several delays to the program, the first of these was launched in March 2008. These ATVs performed supply missions to the ISS, transporting various payloads such as propellant, water, air, food, and scientific research equipment; ATVs also reboosted the station into a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada). The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements. The station serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields. The ISS is suited for testing the spacecraft systems and equipment required for possible future long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. The ISS programme evolved from the Space Station ''Freedom'', a 1984 American proposal to construct a permanently crewed Earth-orbiting station, and the contemporaneous Soviet/Russian '' Mir-2'' proposal from 1976 with similar aims. The ISS is the ninth space station to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interim Control Module
The Interim Control Module (ICM) is a NASA-constructed module designed to serve as a temporary "tug" for the International Space Station in case the Zvezda service module was destroyed or not launched for an extended period of time. It was derived from a formerly-classified Titan Launch Dispenser used to distribute reconnaissance satellites to different orbits. It would have been able to prolong the lifespan of the Zarya module by providing equivalent propulsion capabilities to the Service Module, although not any of the other life support capabilities. After the successful launch of Zvezda, ICM was placed in a caretaker status at NRL's Payload Processing Facility in Washington, D.C. Should it become necessary to complete and launch ICM, it was estimated that it would take between two and two-and-a-half years to do so. Since the ICM was mothballed, a variety of new uses for it have been proposed. Most seriously, it was proposed for use as part of a robotic servicing mission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unity (ISS Module)
upright=1.0, The ''Unity'' module as seen in May 2011 The ''Unity'' connecting module, also known as Node 1, is the first U.S.-built component of the International Space Station (ISS). It connects the Russian and United States segments of the station, and is where crew eat meals together. The module is cylindrical in shape, with six berthing locations (forward, aft, port, starboard, zenith, and nadir) facilitating connections to other modules. ''Unity'' measures in diameter, is long, made of steel, and was built for NASA by Boeing in a manufacturing facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. ''Unity'' is the first of the three connecting modules; the other two are '' Harmony'' and ''Tranquility''. Launch and initial berthing ''Unity'' (with its two attached PMAs) was carried into orbit as the primary cargo of the Space Shuttle ''Endeavour'' (OV 105) on STS-88, the first Space Shuttle mission dedicated to assembly of the station. On 6 Decemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Space Agency
, owners = , headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France , coordinates = , spaceport = Guiana Space Centre , seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png , seal_size = 130px , image = Views in the Main Control Room (12052189474).jpg , size = , caption = , acronym = , established = , employees = 2,200 , administrator = Director General Josef Aschbacher , budget = €7.2 billion (2022) , language = English and French (working languages) , website = , logo = European Space Agency logo.svg , logo_caption = Logo , image_caption = European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) Main Control Room The European Space Agency (ESA; french: Agence spatiale européenne , it, Agenzia Spaziale Europea, es, Agencia Espacial Europea ASE; german: Europäische Weltraumorganisation) is an intergovernmental organisation of 22 member states dedicated to the exploration of space. Established in 1975 and headquartered i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
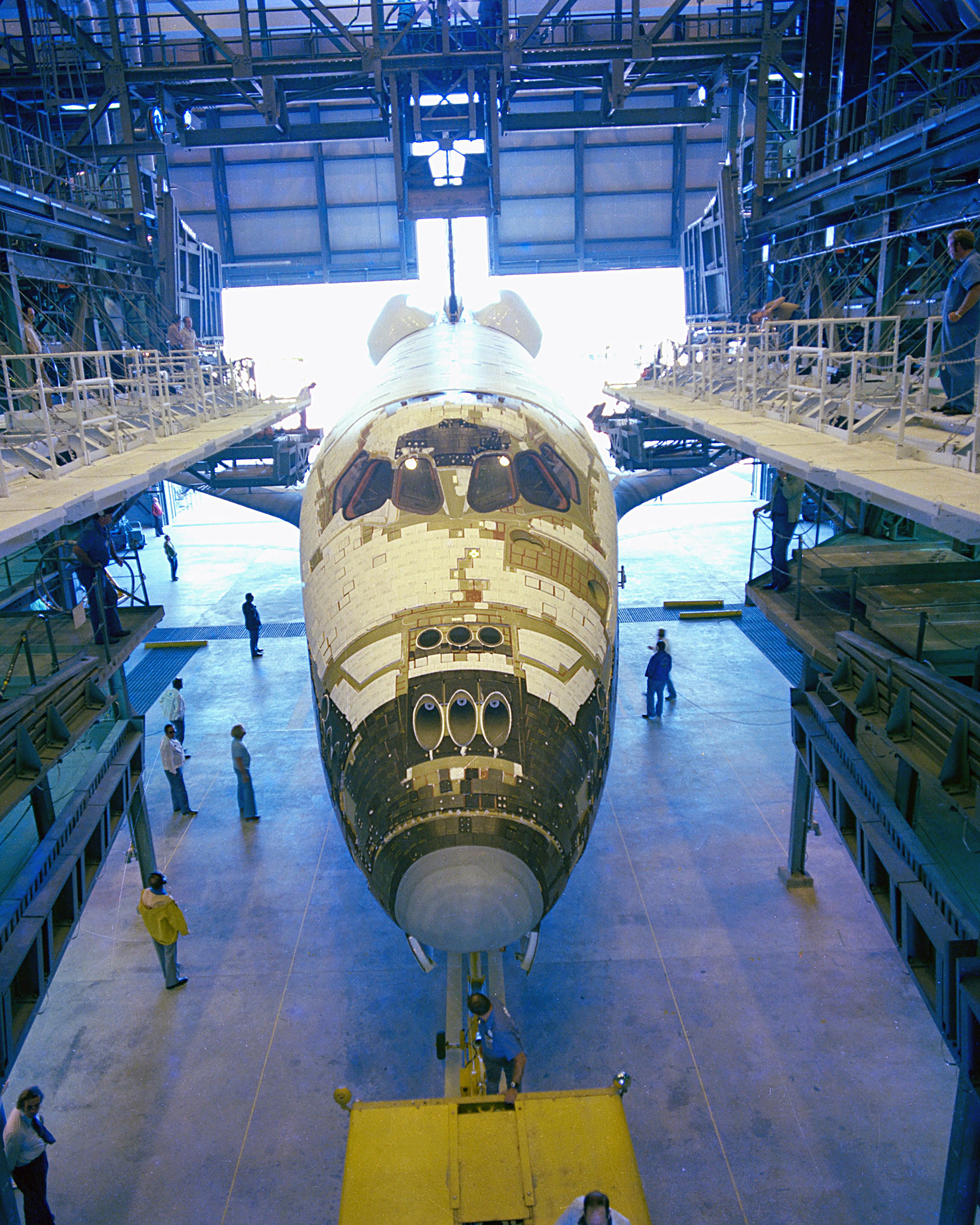
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program name was Space Transportation System (STS), taken from a 1969 plan for a system of reusable spacecraft where it was the only item funded for development. The first ( STS-1) of four orbital test flights occurred in 1981, leading to operational flights (STS-5) beginning in 1982. Five complete Space Shuttle orbiter vehicles were built and flown on a total of 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. They launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida. Operational missions launched numerous satellites, interplanetary probes, and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), conducted science experiments in orbit, participated in the Shuttle-''Mir'' program with Russia, and participated in construction and servicing of the International Space Station (ISS). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zarya (ISS Module)
''Zarya'' (russian: Заря, , Dawn), also known as the Functional Cargo Block or FGB (from the russian: "Функционально-грузовой блок", , ''Funktsionalno-gruzovoy blok'' or ''ФГБ''), is the first module of the International Space Station to have been launched.NASA, International Space StationZarya(accessed 19 Apr. 2014) The FGB provided electrical power, storage, propulsion, and guidance to the ISS during the initial stage of assembly. With the launch and assembly in orbit of other modules with more specialized functionality, it is primarily used for storage, both inside the pressurized section and in the externally mounted fuel tanks. The ''Zarya'' is a descendant of the TKS spacecraft designed for the Russian ''Salyut'' program. The name ''Zarya'' ("Dawn") was given to the FGB because it signified the dawn of a new era of international cooperation in space. Although it was built by a Russian company, it is owned by the United States. Construct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmony (ISS Module)
''Harmony'', also known as ''Node 2'', is the "utility hub" of the International Space Station. It connects the laboratory modules of the United States, Europe and Japan, as well as providing electrical power and electronic data. Sleeping cabins for four of the crew are housed here. ''Harmony'' was successfully launched into space aboard Space Shuttle The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program na ... flight STS-120 on 23 October 2007. After temporarily being attached to the port side of the Unity (ISS module), ''Unity'' module, it was moved to its permanent location on the forward end of the Destiny (ISS module), ''Destiny'' module on 14 November 2007. ''Harmony'' added to the station's living volume, an increase of almost 20%, from to . Its successful installation meant th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |