|
ISAAC (cipher)
ISAAC (indirection, shift, accumulate, add, and count) is a cryptographically secure pseudorandom number generator and a stream cipher designed by Robert J. Jenkins Jr. in 1993. The reference implementation source code was dedicated to the public domain. "I developed (...) tests to break a generator, and I developed the generator to pass the tests. The generator is ISAAC." Operation The ISAAC algorithm has similarities with RC4. It uses an array of 256 four-octet integers as the internal state, writing the results to another 256 four-octet integer array, from which they are read one at a time until empty, at which point they are recomputed. The computation consists of altering ''i''-element with (''i''⊕128)-element, two elements of the state array found by indirection, an accumulator, and a counter, for all values of ''i'' from 0 to 255. Since it only takes about 19 32-bit operations for each 32-bit output word, it is very fast on 32-bit computers. Cryptanalysis Cryptanal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cryptographically Secure Pseudorandom Number Generator
A cryptographically secure pseudorandom number generator (CSPRNG) or cryptographic pseudorandom number generator (CPRNG) is a pseudorandom number generator (PRNG) with properties that make it suitable for use in cryptography. It is also referred to as a cryptographic random number generator (CRNG). Background Most cryptographic applications require random numbers, for example: * key generation * initialization vectors * nonces * salts in certain signature schemes, including ECDSA and RSASSA-PSS * token generation The "quality" of the randomness required for these applications varies. For example, creating a nonce in some protocols needs only uniqueness. On the other hand, the generation of a master key requires a higher quality, such as more entropy. And in the case of one-time pads, the information-theoretic guarantee of perfect secrecy only holds if the key material comes from a true random source with high entropy, and thus just any kind of pseudorandom number gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cryptanalysis
Cryptanalysis (from the Greek ''kryptós'', "hidden", and ''analýein'', "to analyze") refers to the process of analyzing information systems in order to understand hidden aspects of the systems. Cryptanalysis is used to breach cryptographic security systems and gain access to the contents of encrypted messages, even if the cryptographic key is unknown. In addition to mathematical analysis of cryptographic algorithms, cryptanalysis includes the study of side-channel attacks that do not target weaknesses in the cryptographic algorithms themselves, but instead exploit weaknesses in their implementation. Even though the goal has been the same, the methods and techniques of cryptanalysis have changed drastically through the history of cryptography, adapting to increasing cryptographic complexity, ranging from the pen-and-paper methods of the past, through machines like the British Bombes and Colossus computers at Bletchley Park in World War II, to the mathematically advanced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cryptographically Secure Pseudorandom Number Generators
Cryptography, or cryptology (from "hidden, secret"; and ''graphein'', "to write", or ''-logia'', "study", respectively), is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of adversarial behavior. More generally, cryptography is about constructing and analyzing protocols that prevent third parties or the public from reading private messages. Modern cryptography exists at the intersection of the disciplines of mathematics, computer science, information security, electrical engineering, digital signal processing, physics, and others. Core concepts related to information security ( data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation) are also central to cryptography. Practical applications of cryptography include electronic commerce, chip-based payment cards, digital currencies, computer passwords, and military communications. Cryptography prior to the modern age was effectively synonymous with encryption, converting read ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
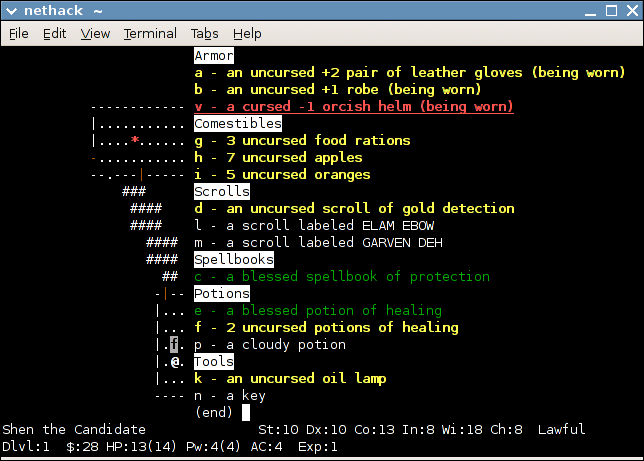
NetHack
''NetHack'' is an open source single-player roguelike video game, first released in 1987 and maintained by the NetHack DevTeam. The game is a fork of the 1984 game ''Hack'', itself inspired by the 1980 game '' Rogue''. The player takes the role of one of several pre-defined character classes to descend through multiple dungeon floors, fighting monsters and collecting treasure, to recover the "Amulet of Yendor" at the lowest floor and then escape. As an exemplar of the traditional "roguelike" game, ''NetHack'' features turn-based, grid-based hack and slash and dungeon crawling gameplay, procedurally generated dungeons and treasure, and permadeath, requiring the player to restart the game anew should the player character die. The game uses simple ASCII graphics by default so as to display readily on a wide variety of computer displays, but can use curses with box-drawing characters, as well as substitute graphical tilesets on machines with graphics. While ''Rogue'', ''Hack'' an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Shred (Unix)
is a command on Unix-like operating systems that can be used to securely delete files and devices so that it is extremely difficult to recover them, even with specialized hardware and technology; assuming recovery is possible at all, which is not always the case. It is a part of GNU Core Utilities. Being based on the Gutmann method paper, it suffers from the same criticisms and possible shortcomings. Background For efficiency, the process of erasing a file from storage using the command usually only erases the file's file-system entry while keeping the content of the file intact. This frequently allows commonly available software to recover the "erased" file's data. If the file data is stored on magnetic media such as a HDD, even if the file is overwritten, residual magnetic fields may allow data recovery using specialist hardware equipment (this claim is disputed; see ). To prevent this, overwrites the contents of a file multiple times, using patterns chosen to maximiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bart Preneel
Bart Preneel (born 15 October 1963 in Leuven, Belgium) is a Belgium, Belgian cryptographer and cryptanalyst. He is a professor at Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, in the COSIC group. He was the president of the International Association for Cryptologic Research in 2008–2013 and project manager of ECRYPT. Education In 1987, Preneel received a degree in Electrical Engineering from the Katholieke Universiteit, Leuven. In 1993, Preneel received a PhD in Applied Sciences from the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven. His dissertation in computer science, entitled ''Analysis and Design of Cryptographic Hash Functions'', was advised by Joos Vandewalle, Joos (Joseph) P. L. Vandewalle and René Govaerts, René J. M. Govaerts. Career Along with Shoji Miyaguchi, he independently invented the One-way compression function#Miyaguchi–Preneel, Miyaguchi–Preneel scheme, a structure that converts a block cipher into a hash function, used eg. in the hash function Whirlpool (algorithm), Whirlpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Souradyuti Paul
Souradyuti Paul (born 1976) is an Indian cryptologist. Formerly a member of COSIC, he is currently working as an associate professor at Indian Institute of Technology Bhilai and a Guest Researcher for the National Institute of Standards and Technology in the United States. He participated in cryptanalysis of RC4, Helix A helix (; ) is a shape like a cylindrical coil spring or the thread of a machine screw. It is a type of smooth space curve with tangent lines at a constant angle to a fixed axis. Helices are important in biology, as the DNA molecule is for ... and Py family of ciphers among others. He has co-designed the following ciphers * RC4A * RCR-32, RCR-64. He also contributed to the design of a hash function iteration mode of operation Fast-widepipe.Mridul Nandi and Souradyuti Paul. Speeding Up the Widepipe: Secure and Fast Hashing. In Guang Gong and Kishan Gupta, editor, Indocrypt 2010, Springer, 2010. While working at NIST Dr. Paul has worked towards the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fluhrer, Mantin And Shamir Attack
In cryptography, the Fluhrer, Mantin and Shamir attack is a stream cipher attack on the widely used RC4 stream cipher. The attack allows an attacker to recover the key in an RC4 encrypted stream from a large number of messages in that stream. The Fluhrer, Mantin and Shamir attack applies to specific key derivation methods, but does not apply in general to RC4-based SSL (TLS), since SSL generates the encryption keys it uses for RC4 by hashing, meaning that different SSL sessions have unrelated keys. However, the closely related bar mitzvah attack, based on the same research and revealed in 2015, does exploit those cases where weak keys are generated by the SSL keying process. Background The Fluhrer, Mantin and Shamir (FMS) attack, published in their 2001 paper "Weaknesses in the Key Scheduling Algorithm of RC4",Fluhrer, S., Mantin, I., and A. Shamir,Weaknesses in the Key Scheduling Algorithm of RC4, Selected Areas of Cryptography: SAC 2001, Lecture Notes in Computer Science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Integer (computer Science)
In computer science, an integer is a datum of integral data type, a data type that represents some interval (mathematics), range of mathematical integers. Integral data types may be of different sizes and may or may not be allowed to contain negative values. Integers are commonly represented in a computer as a group of binary digits (bits). The size of the grouping varies so the set of integer sizes available varies between different types of computers. Computer hardware nearly always provides a way to represent a processor word size, register or memory address as an integer. Value and representation The ''value'' of an item with an integral type is the mathematical integer that it corresponds to. Integral types may be ''unsigned'' (capable of representing only non-negative integers) or ''signed'' (capable of representing negative integers as well). An integer value is typically specified in the source code of a program as a sequence of digits optionally prefixed with + or −. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stream Cipher
stream cipher is a symmetric key cipher where plaintext digits are combined with a pseudorandom cipher digit stream ( keystream). In a stream cipher, each plaintext digit is encrypted one at a time with the corresponding digit of the keystream, to give a digit of the ciphertext stream. Since encryption of each digit is dependent on the current state of the cipher, it is also known as ''state cipher''. In practice, a digit is typically a bit and the combining operation is an exclusive-or (XOR). The pseudorandom keystream is typically generated serially from a random seed value using digital shift registers. The seed value serves as the cryptographic key for decrypting the ciphertext stream. Stream ciphers represent a different approach to symmetric encryption from block ciphers. Block ciphers operate on large blocks of digits with a fixed, unvarying transformation. This distinction is not always clear-cut: in some modes of operation, a block cipher primitive is used in such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Array Data Structure
In computer science, an array is a data structure consisting of a collection of ''elements'' (value (computer science), values or variable (programming), variables), of same memory size, each identified by at least one ''array index'' or ''key'', a collection of which may be a tuple, known as an index tuple. An array is stored such that the position (memory address) of each element can be computed from its index tuple by a mathematical formula. The simplest type of data structure is a linear array, also called a one-dimensional array. For example, an array of ten 32-bit (4-byte) integer variables, with indices 0 through 9, may be stored as ten Word (data type), words at memory addresses 2000, 2004, 2008, ..., 2036, (in hexadecimal: 0x7D0, 0x7D4, 0x7D8, ..., 0x7F4) so that the element with index ''i'' has the address 2000 + (''i'' × 4). The memory address of the first element of an array is called first address, foundation address, or base address. Because the mathematical conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can use Conditional (computer programming), conditionals to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making) and deduce valid inferences (referred to as automated reasoning). In contrast, a Heuristic (computer science), heuristic is an approach to solving problems without well-defined correct or optimal results.David A. Grossman, Ophir Frieder, ''Information Retrieval: Algorithms and Heuristics'', 2nd edition, 2004, For example, although social media recommender systems are commonly called "algorithms", they actually rely on heuristics as there is no truly "correct" recommendation. As an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |