|
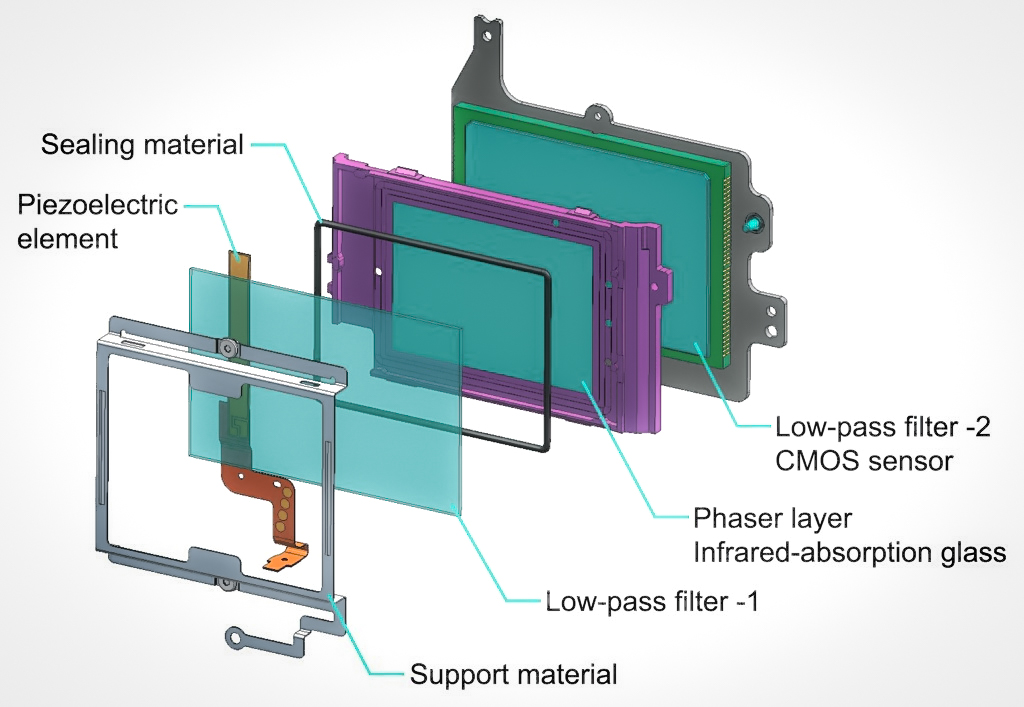
IR Filter
Infrared cut-off filters, sometimes called IR filters or heat-absorbing filters, are designed to reflect or block near-infrared wavelengths while passing visible light. They are often used in devices with bright incandescent light bulbs (such as slide and overhead projectors) to prevent unwanted heating. There are also filters which are used in solid state ( CCD or CMOS) video cameras to block IR due to the high sensitivity of many camera sensors to near-infrared light. These filters typically have a blue hue to them as they also sometimes block some of the light from the longer red wavelengths. IR transmitting/passing filters in photography In contrast to the naming convention of optical filters where the name of the filter denotes the wavelengths that are blocked, and in line with the convention for air filters and oil filters, photographic filters are named for the color of light they ''pass''. Thus a blue filter makes the picture look blue. A ''blue filter'' marginally a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gandhi Commons
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (; ; 2 October 1869 – 30 January 1948), popularly known as Mahatma Gandhi, was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist Quote: "... marks Gandhi as a hybrid cosmopolitan figure who transformed ... anti-colonial nationalist politics in the twentieth-century in ways that neither indigenous nor westernized Indian nationalists could." and political ethicist Quote: "Gandhi staked his reputation as an original political thinker on this specific issue. Hitherto, violence had been used in the name of political rights, such as in street riots, regicide, or armed revolutions. Gandhi believes there is a better way of securing political rights, that of nonviolence, and that this new way marks an advance in political ethics." who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from British rule, and to later inspire movements for civil rights and freedom across the world. The honorific ''Mahātmā'' (Sanskrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Temperature
Color temperature is the color of light emitted by an idealized opaque, non-reflective body at a particular temperature measured in kelvins. The color temperature scale is used to categorize the color of light emitted by other light sources regardless of their temperature. Color temperature is a characteristic of visible light that has important applications in lighting, photography, videography, publishing, manufacturing, astrophysics, horticulture, and other fields. In practice, color temperature is meaningful only for light sources that do in fact correspond somewhat closely to the color of some black body, i.e., light in a range going from red to orange to yellow to white to bluish white; it does not make sense to speak of the color temperature of, e.g., a green or a purple light. Color temperature is conventionally expressed in kelvins, using the symbol K, a unit of measure for absolute temperature. Color temperatures over 5000 K are called "cool colors" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
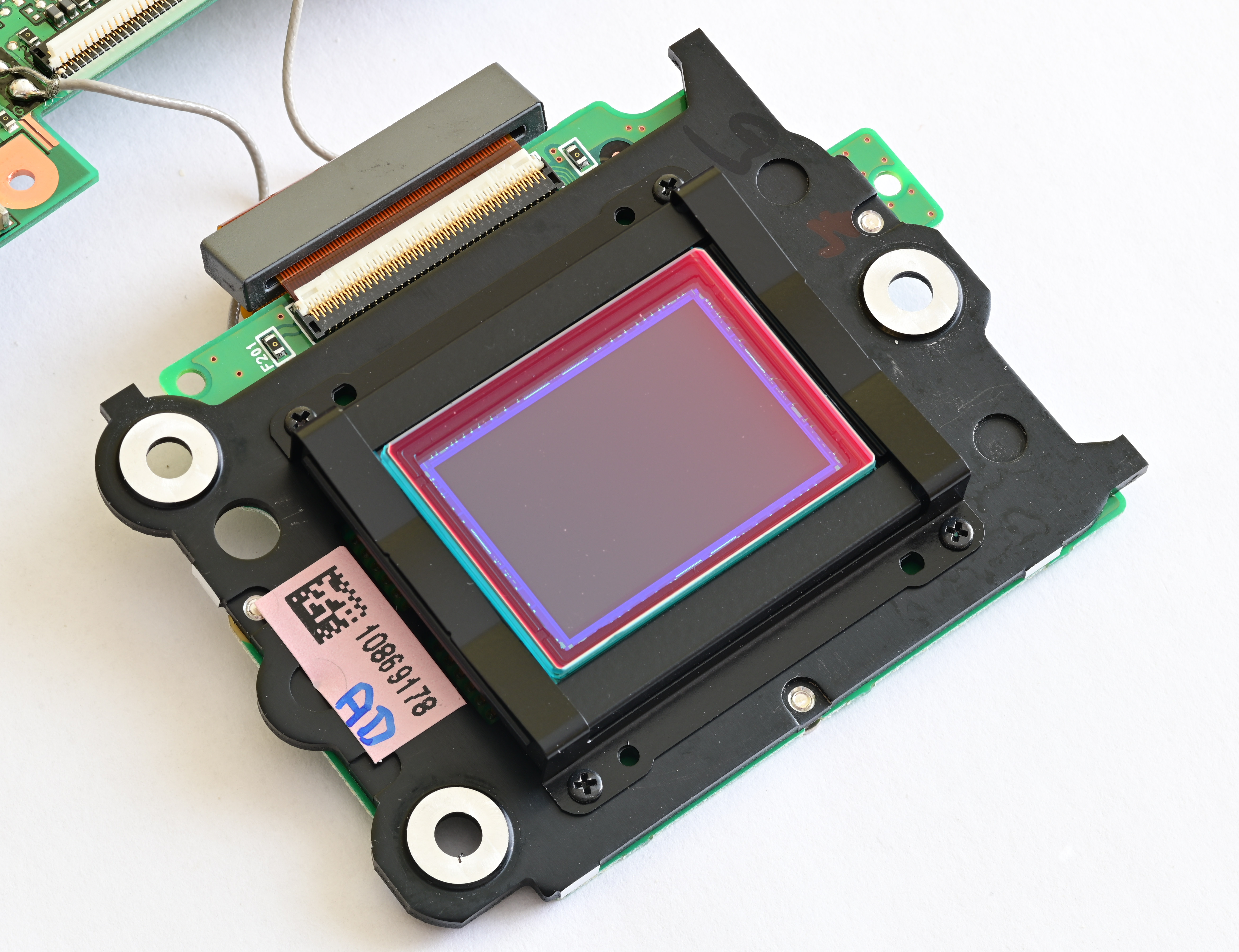
Hot Mirror
A hot mirror is a specialized dielectric mirror, a dichroic filter, often employed to protect optical systems by reflecting infrared light back into a light source, while allowing visible light to pass. Hot mirrors can be designed to be inserted into the optical system at an Angle of incidence (optics), incidence angle varying between zero and 45 degrees, and are useful in a variety of applications where the buildup of waste heat can damage components or adversely affect spectral characteristics of the illumination source. Wavelengths reflected by an infrared hot mirror range from about 750 to 1250 nanometers. By transmitting visible light wavelengths while reflecting infrared, hot mirrors can also serve as dichromatic beam splitters for specialized applications in Microscopy#Fluorescence Microscopy, fluorescence microscopy or optical eye tracking. Some early digital cameras designed for visible light capture, such as the Kodak DCS 400 series, Associated Press NC2000 and Nikon Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Mirror
A cold mirror is a specialized dielectric mirror, a dichroic filter, that reflects the entire visible light spectrum while very efficiently transmitting infrared wavelengths. Similar to hot mirrors, cold mirrors can be designed for an incidence angle ranging between zero and 45 degrees, and are constructed with multi-layer dielectric coatings, in a manner similar to interference filters. Cold mirrors can be employed as dichroic beamsplitters with laser systems to reflect visible light wavelengths while transmitting infrared. See also *Mirror A mirror or looking glass is an object that Reflection (physics), reflects an image. Light that bounces off a mirror will show an image of whatever is in front of it, when focused through the lens of the eye or a camera. Mirrors reverse the ... Mirrors {{optics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UV Filter
UV filters are compounds, mixtures, or materials that block or absorb ultraviolet (UV) light. One of the major applications of UV filters is their use as sunscreens to protect skin from sunburn and other sun/UV related damage. After the invention of digital cameras changed the field of photography, UV filters have been used to coat glass discs fitted to camera lenses to protect hardware that is sensitive to UV light. Background Earlier types of photographic film were quite sensitive to UV light, which used to cause haziness or fogginess, and a bluish hue in color film. UV filters were used to filter out shorter ultraviolet wavelengths while remaining transparent to visible light. However, the modern-day photographic film and digital cameras are less sensitive to UV wavelengths. UV filters are sometimes referred to as L37 or L39 filters, depending on the wavelengths of light they filter out. For example, an L37 filter removes ultraviolet light with wavelengths shorter than 37 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-aliasing Filter
An anti-aliasing filter (AAF) is a filter used before a signal sampler to restrict the bandwidth of a signal to satisfy the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem over the band of interest. Since the theorem states that unambiguous reconstruction of the signal from its samples is possible when the power of frequencies above the Nyquist frequency is zero, a brick wall filter is an idealized but impractical AAF. A practical AAF makes a trade off between reduced bandwidth and increased aliasing. A practical anti-aliasing filter will typically permit some aliasing to occur or attenuate or otherwise distort some in-band frequencies close to the Nyquist limit. For this reason, many practical systems sample higher than would be theoretically required by a perfect AAF in order to ensure that all frequencies of interest can be reconstructed, a practice called oversampling. Optical applications The Pentax K-3 from Ricoh introduced a unique sensor-based anti-aliasing filter. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emission Nebula
An emission nebula is a nebula formed of ionized gases that emit light of various wavelengths. The most common source of ionization is high-energy ultraviolet photons emitted from a nearby hot star. Among the several different types of emission nebulae are H II regions, in which star formation is taking place and young, massive stars are the source of the ionizing photons; and planetary nebulae, in which a dying star has thrown off its outer layers, with the exposed hot core then ionizing them. General information Usually, a young star will ionize part of the same cloud from which it was born, although only massive, hot stars can release sufficient energy to ionize a significant part of a cloud. In many emission nebulae, an entire cluster of young stars is contributing energy. Stars that are cooler than around 25,000K don't give off enough ultraviolet radiation with wavelengths shorter than 91.2nm (the wavelength needed in order to ionize Hydrogen atoms). This results in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrophotography
Astrophotography, also known as astronomical imaging, is the photography or imaging of astronomical objects, celestial events, or areas of the night sky. The first photograph of an astronomical object (the Moon) was taken in 1840, but it was not until the late 19th century that advances in technology allowed for detailed stellar photography. Besides being able to record the details of extended objects such as the Moon, Sun, and planets, modern astrophotography has the ability to image objects invisible to the human eye such as dim stars, nebulae, and galaxies. This is done by long time exposure since both film and digital cameras can accumulate and sum photons over these long periods of time. Photography using extended exposure-times revolutionized the field of professional astronomical research, recording hundreds of thousands of new stars, and nebulae invisible to the human eye. Specialized and ever-larger optical telescopes were constructed as essentially big cameras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. Short-wave ultraviolet light damages DNA and sterilizes surfaces with which it comes into contac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visible Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 terahertz, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). In physics, the term "light" may refer more broadly to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. The primary properties of light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum and polarization. Its speed in a vacuum, 299 792 458 metres a second (m/s), is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Like all types of electromagnetic radiation, visible light propagates by massless elementary particles called photons that represents the quanta of electromagnetic field, and can be analyzed as both waves and particl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared Photography
''Top:'' tree photographed in the near infrared range. ''Bottom:'' same tree in the visible part of the spectrum. In infrared photography, the film or image sensor used is sensitive to infrared light. The part of the spectrum used is referred to as near-infrared to distinguish it from far-infrared, which is the domain of thermal imaging. Wavelengths used for photography range from about 700 nm to about 900 nm. Film is usually sensitive to visible light too, so an infrared-passing filter is used; this lets infrared (IR) light pass through to the camera, but blocks all or most of the visible light spectrum (the filter thus looks black or deep red). ("Infrared filter" may refer either to this type of filter or to one that blocks infrared but passes other wavelengths.) When these filters are used together with infrared-sensitive film or sensors, "in-camera effects" can be obtained; false-color or black-and-white images with a dreamlike or sometimes lurid appearance kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
