|
IRIG Timecode
Inter-range instrumentation group timecodes, commonly known as IRIG timecode, are standard formats for transferring timing information. Atomic frequency standards and GPS receivers designed for precision timing are often equipped with an IRIG output. The standards were created by the Tele Communications Working Group of the U.S. military's Inter-Range Instrumentation Group (IRIG), the standards body of the Range Commanders Council. Work on these standards started in October 1956, and the original standards were accepted in 1960. The original formats were described in IRIG Document 104-60, later revised and reissued in August 1970 as IRIG Document 104-70, upgraded later that year as the IRIG Document to the status of a Standard, IRIG Standard 200-70. The latest version of the Standard is IRIG Standard 200-16 from August 2016. Timecodes The different timecodes defined in the Standard have alphabetic designations. A, B, D, E, G, and H are the standards currently defined by IRIG S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inter-Range Instrumentation Group
The Inter-Range Instrumentation Group (IRIG) is the standards body of the Range Commanders Council (RCC). The group publishes standards through the RCC Secretariat at White Sands Missile Range. The best known IRIG standard is the IRIG timecode used to timestamp video, film, telemetry, radar, and other data collected at test ranges. The following radio time sources broadcast IRIG timecodes: * BPM (China) * CHU (Canada) * WWV and WWVH (United States) The RCC's IRIG Standard 106 is a comprehensive telemetry standard for aeronautical applications at RCC member ranges. Chapter 10 of Standard 106 governs digital flight data recorders. IRIG Standard 313-01 prescribes test standards for flight termination receivers. See also Related topics * Rocket range A spaceport or cosmodrome is a site for launching or receiving spacecraft, by analogy to a seaport for ships or an airport for aircraft. The word ''spaceport'', and even more so ''cosmodrome'', has traditionally been use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase-locked Loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input signal. There are several different types; the simplest is an electronic circuit consisting of a variable frequency oscillator and a phase detector in a feedback loop. The oscillator's frequency and phase are controlled proportionally by an applied voltage, hence the term voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). The oscillator generates a periodic signal of a specific frequency, and the phase detector compares the phase of that signal with the phase of the input periodic signal, to adjust the oscillator to keep the phases matched. Keeping the input and output phase in lockstep also implies keeping the input and output frequencies the same. Consequently, in addition to synchronizing signals, a phase-locked loop can track an input frequency, or it can generate a frequency that is a multiple of the input frequency. These properties are use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
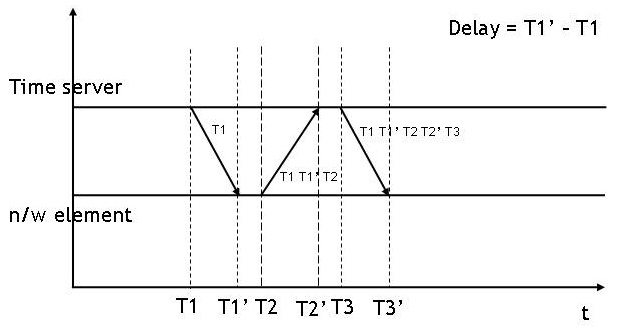
Network Time Protocol
The Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a networking protocol for clock synchronization between computer systems over packet-switched, variable- latency data networks. In operation since before 1985, NTP is one of the oldest Internet protocols in current use. NTP was designed by David L. Mills of the University of Delaware. NTP is intended to synchronize all participating computers to within a few milliseconds of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). It uses the intersection algorithm, a modified version of Marzullo's algorithm, to select accurate time servers and is designed to mitigate the effects of variable network latency. NTP can usually maintain time to within tens of milliseconds over the public Internet, and can achieve better than one millisecond accuracy in local area networks under ideal conditions. Asymmetric routes and network congestion can cause errors of 100 ms or more. The protocol is usually described in terms of a client–server model, but can as easily be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precision Time Protocol
The Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is a protocol used to synchronize clocks throughout a computer network. On a local area network, it achieves clock accuracy in the sub-microsecond range, making it suitable for measurement and control systems. PTP is employed to synchronize financial transactions, mobile phone tower transmissions, sub-sea acoustic arrays, and networks that require precise timing but lack access to satellite navigation signals. The first version of PTP, IEEE 1588-2002, was published in 2002. IEEE 1588-2008, also known as PTP Version 2 is not backward compatible with the 2002 version. IEEE 1588-2019 was published in November 2019 and includes backward-compatible improvements to the 2008 publication. IEEE 1588-2008 includes a ''profile'' concept defining PTP operating parameters and options. Several profiles have been defined for applications including telecommunications, electric power distribution and audiovisual. is an adaptation of PTP for use with Audio Vid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newline
Newline (frequently called line ending, end of line (EOL), next line (NEL) or line break) is a control character or sequence of control characters in character encoding specifications such as ASCII, EBCDIC, Unicode, etc. This character, or a sequence of characters, is used to signify the end of a line of text and the start of a new one. History In the mid-1800s, long before the advent of teleprinters and teletype machines, Morse code operators or telegraphists invented and used Morse code prosigns to encode white space text formatting in formal written text messages. In particular the Morse prosign (mnemonic reak ext) represented by the concatenation of literal textual Morse codes "B" and "T" characters sent without the normal inter-character spacing is used in Morse code to encode and indicate a ''new line'' or ''new section'' in a formal text message. Later, in the age of modern teleprinters, standardized character set control codes were developed to aid in white space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordinal Date
An ordinal date is a calendar date typically consisting of a ''year'' and a day of the year or ordinal day number (or simply ordinal day or day number), an ordinal number ranging between 1 and 366 (starting on January 1), though year may sometimes be omitted. The two numbers can be formatted as YYYY-DDD to comply with the ISO 8601 ordinal date format. Nomenclature ''Ordinal date'' is the preferred name for what was formerly called the ''"Julian date"'' or , or , which still seen in old programming languages and spreadsheet software. The older names are deprecated because they are easily confused with the earlier dating system called ''Julian day number'' or , which was in prior use and which remains ubiquitous in astronomical and some historical calculations. Calculation Computation of the ordinal day within a year is part of calculating the ordinal day throughout the years from a reference date, such as the Julian date. It is also part of calculating the day of the week, thou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odd Parity
A parity bit, or check bit, is a bit added to a string of binary code. Parity bits are a simple form of error detecting code. Parity bits are generally applied to the smallest units of a communication protocol, typically 8-bit octets (bytes), although they can also be applied separately to an entire message string of bits. The parity bit ensures that the total number of 1-bits in the string is even or odd. Accordingly, there are two variants of parity bits: even parity bit and odd parity bit. In the case of even parity, for a given set of bits, the bits whose value is 1 are counted. If that count is odd, the parity bit value is set to 1, making the total count of occurrences of 1s in the whole set (including the parity bit) an even number. If the count of 1s in a given set of bits is already even, the parity bit's value is 0. In the case of odd parity, the coding is reversed. For a given set of bits, if the count of bits with a value of 1 is even, the parity bit value is set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASCII
ASCII ( ), abbreviated from American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Because of technical limitations of computer systems at the time it was invented, ASCII has just 128 code points, of which only 95 are , which severely limited its scope. All modern computer systems instead use Unicode, which has millions of code points, but the first 128 of these are the same as the ASCII set. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) prefers the name US-ASCII for this character encoding. ASCII is one of the List of IEEE milestones, IEEE milestones. Overview ASCII was developed from telegraph code. Its first commercial use was as a seven-bit teleprinter code promoted by Bell data services. Work on the ASCII standard began in May 1961, with the first meeting of the American Standards Association's (ASA) (now the American Nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asynchronous Serial Communication
Asynchronous serial communication is a form of serial communication in which the communicating endpoints' interfaces are not continuously synchronized by a common clock signal. Instead of a common synchronization signal, the data stream contains synchronization information in form of start and stop signals, before and after each unit of transmission, respectively. The start signal prepares the receiver for arrival of data and the stop signal resets its state to enable triggering of a new sequence. A common kind of start-stop transmission is ASCII over RS-232, for example for use in teletypewriter operation. Origin Mechanical teleprinters using 5-bit codes (see Baudot code) typically used a stop period of 1.5 bit times.Dead link: 2015-Oct-03 Very early electromechanical teletypewriters (pre-1930) could require 2 stop bits to allow mechanical impression without buffering. Hardware which does not support fractional stop bits can communicate with a device that uses 1.5 bit time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RS-232
In telecommunications, RS-232 or Recommended Standard 232 is a standard originally introduced in 1960 for serial communication transmission of data. It formally defines signals connecting between a ''DTE'' (''data terminal equipment'') such as a computer terminal, and a ''DCE'' (''data circuit-terminating equipment'' or ''data communication equipment''), such as a modem. The standard defines the electrical characteristics and timing of signals, the meaning of signals, and the physical size and pinout of connectors. The current version of the standard is ''TIA-232-F Interface Between Data Terminal Equipment and Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment Employing Serial Binary Data Interchange'', issued in 1997. The RS-232 standard had been commonly used in computer serial ports and is still widely used in industrial communication devices. A serial port complying with the RS-232 standard was once a standard feature of many types of computers. Personal computers used them for connection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE 1344
IEEE 1344 is a standard that defines parameters for synchrophasors for power systems. The standard added extension to the IRIG-B time code to cover year, time quality, daylight saving time, local time offset and leap second information. IEEE 1344 was superseded by IEEE C37.118 in 2005 and the time extensions were adopted as part of the IRIG timing standard in the 2004 edition. IRIG-B timecode consists of 100 bits, repeated each second. Every tenth bit is a "position identifier", and most of the remainder encode the current time (date, hour, minute and second). Bits 60–68 and 70–78 are reserved for other uses; IEEE 1344 is such a use. It defines the bits as follows: The DST and leap warning bits are set no more than 59 seconds before the indicated change, and indicate the change at the end of the minute. During a leap second, the warning bit should be set, the seconds field should show "60", and the Straight Binary Seconds field should equal 60 + 60 × minutes + 3600 × ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordinal Date
An ordinal date is a calendar date typically consisting of a ''year'' and a day of the year or ordinal day number (or simply ordinal day or day number), an ordinal number ranging between 1 and 366 (starting on January 1), though year may sometimes be omitted. The two numbers can be formatted as YYYY-DDD to comply with the ISO 8601 ordinal date format. Nomenclature ''Ordinal date'' is the preferred name for what was formerly called the ''"Julian date"'' or , or , which still seen in old programming languages and spreadsheet software. The older names are deprecated because they are easily confused with the earlier dating system called ''Julian day number'' or , which was in prior use and which remains ubiquitous in astronomical and some historical calculations. Calculation Computation of the ordinal day within a year is part of calculating the ordinal day throughout the years from a reference date, such as the Julian date. It is also part of calculating the day of the week, thou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |