|
INSNA
The International Network for Social Network Analysis (INSNA) is a professional academic association of researchers and practitioners of social network analysis. Members have interests in social networks as a new theoretical paradigm, in methodological developments, and in a variety of applications of different types of social networks approaches, social network software, and social networking. History INSNA was founded in 1977 by Barry Wellman, a sociologist. A key function of the organization was to provide a sense of identity for a set of researchers who were widely dispersed geographically and across scientific disciplines. Wellman served as "coordinator" of INSNA until 1988, when he passed the baton to Al Wolfe, an anthropologist at the University of South Florida. Wolfe in turn passed the leadership to Steve Borgatti, who served from 1993 to 1999. Borgatti incorporated INSNA as a legal entity, creating bylaws and establishing the positions of President, Vice-President and Tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
INSNA
The International Network for Social Network Analysis (INSNA) is a professional academic association of researchers and practitioners of social network analysis. Members have interests in social networks as a new theoretical paradigm, in methodological developments, and in a variety of applications of different types of social networks approaches, social network software, and social networking. History INSNA was founded in 1977 by Barry Wellman, a sociologist. A key function of the organization was to provide a sense of identity for a set of researchers who were widely dispersed geographically and across scientific disciplines. Wellman served as "coordinator" of INSNA until 1988, when he passed the baton to Al Wolfe, an anthropologist at the University of South Florida. Wolfe in turn passed the leadership to Steve Borgatti, who served from 1993 to 1999. Borgatti incorporated INSNA as a legal entity, creating bylaws and establishing the positions of President, Vice-President and Tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Networks
A social network is a social structure made up of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), sets of dyadic ties, and other social interactions between actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods for analyzing the structure of whole social entities as well as a variety of theories explaining the patterns observed in these structures. The study of these structures uses social network analysis to identify local and global patterns, locate influential entities, and examine network dynamics. Social networks and the analysis of them is an inherently interdisciplinary academic field which emerged from social psychology, sociology, statistics, and graph theory. Georg Simmel authored early structural theories in sociology emphasizing the dynamics of triads and "web of group affiliations". Jacob Moreno is credited with developing the first sociograms in the 1930s to study interpersonal relationships. These approaches were mathematically formalize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Networking
A social network is a social structure made up of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), sets of dyadic ties, and other social interactions between actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods for analyzing the structure of whole social entities as well as a variety of theories explaining the patterns observed in these structures. The study of these structures uses social network analysis to identify local and global patterns, locate influential entities, and examine network dynamics. Social networks and the analysis of them is an inherently interdisciplinary academic field which emerged from social psychology, sociology, statistics, and graph theory. Georg Simmel authored early structural theories in sociology emphasizing the dynamics of triads and "web of group affiliations". Jacob Moreno is credited with developing the first sociograms in the 1930s to study interpersonal relationships. These approaches were mathematically formalize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barry Wellman
Barry Wellman (born 1942) is a Canadian-American sociologist and is the co-director of the Toronto-based international NetLab Network. His areas of research are community sociology, the Internet, human-computer interaction and social structure, as manifested in social networks in communities and organizations. His overarching interest is in the paradigm shift from group-centered relations to ''networked individualism''. He has written or co-authored more than 300 articles, chapters, reports and books. Wellman was a professor at the Department of Sociology, University of Toronto for 46 years, from 1967 to 2013, including a five-year stint as S.D. Clark Professor. Among the concepts Wellman has published are: "network of networks" and "the network city" (both with Paul Craven), "the community question", "computer networks as social networks", "connected lives" and the "immanent Internet" (both with Bernie Hogan), "media-multiplexity" (with Caroline Haythornthwaite), "networked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Network Analysis Software
Social network analysis software (SNA software) is software which facilitates quantitative or qualitative analysis of social networks, by describing features of a network either through numerical or visual representation. Overview Networks can consist of anything from families, project teams, classrooms, sports teams, legislatures, nation-states, disease vectors, membership on networking websites like Twitter or Facebook, or even the Internet. Networks can consist of direct linkages between nodes or indirect linkages based upon shared attributes, shared attendance at events, or common affiliations. Network features can be at the level of individual nodes, dyads, triads, ties and/or edges, or the entire network. For example, node-level features can include network phenomena such as betweenness and centrality, or individual attributes such as age, sex, or income. SNA software generates these features from raw network data formatted in an edgelist, adjacency list, or adjacency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Network
A social network is a social structure made up of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), sets of dyadic ties, and other social interactions between actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods for analyzing the structure of whole social entities as well as a variety of theories explaining the patterns observed in these structures. The study of these structures uses social network analysis to identify local and global patterns, locate influential entities, and examine network dynamics. Social networks and the analysis of them is an inherently interdisciplinary academic field which emerged from social psychology, sociology, statistics, and graph theory. Georg Simmel authored early structural theories in sociology emphasizing the dynamics of triads and "web of group affiliations". Jacob Moreno is credited with developing the first sociograms in the 1930s to study interpersonal relationships. These approaches were mathematically formalize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Learned Society
A learned society (; also learned academy, scholarly society, or academic association) is an organization that exists to promote an discipline (academia), academic discipline, profession, or a group of related disciplines such as the arts and science. Membership may be open to all, may require possession of some qualification, or may be an honour conferred by election. Most learned societies are non-profit organizations, and many are professional associations. Their activities typically include holding regular academic conference, conferences for the presentation and discussion of new research results and publishing or sponsoring academic journals in their discipline. Some also act as Professional association, professional bodies, regulating the activities of their members in the public interest or the collective interest of the membership. History Some of the oldest learned societies are the Académie des Jeux floraux (founded 1323), the Sodalitas Litterarum Vistulana (founded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connections (journal)
The Partnership for Peace Consortium is a network of over 800 defense academies and security studies institutes across 60 countries. Founded in 1998 during the NATO Summit, the PfPC was chartered to promote defense institution building and foster regional stability through multinational education and research, which the PfPC accomplishes via a network of educators and researchers. It is based at the George C. Marshall European Center for Security Studies in Garmisch, Germany. According to the PfPC Annual Report of 2012, in 2012 eight hundred defense academies and security studies institutes in 59 countries worked with the PfPC in 69 defense education/defense institution building and policy-relevant events. The Consortium publishes an academic quarterly journal ''CONNECTIONS'' in English and Russian. The journal is run by an international Editorial Board of experts and is distributed to over 1,000 institutions in 54 countries. Background The PfPC was founded in 1998 in response to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
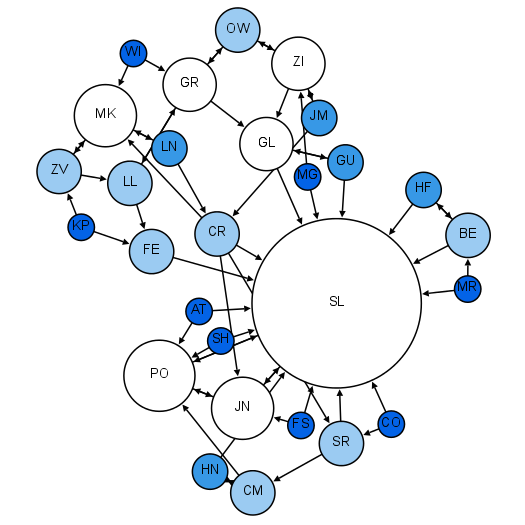
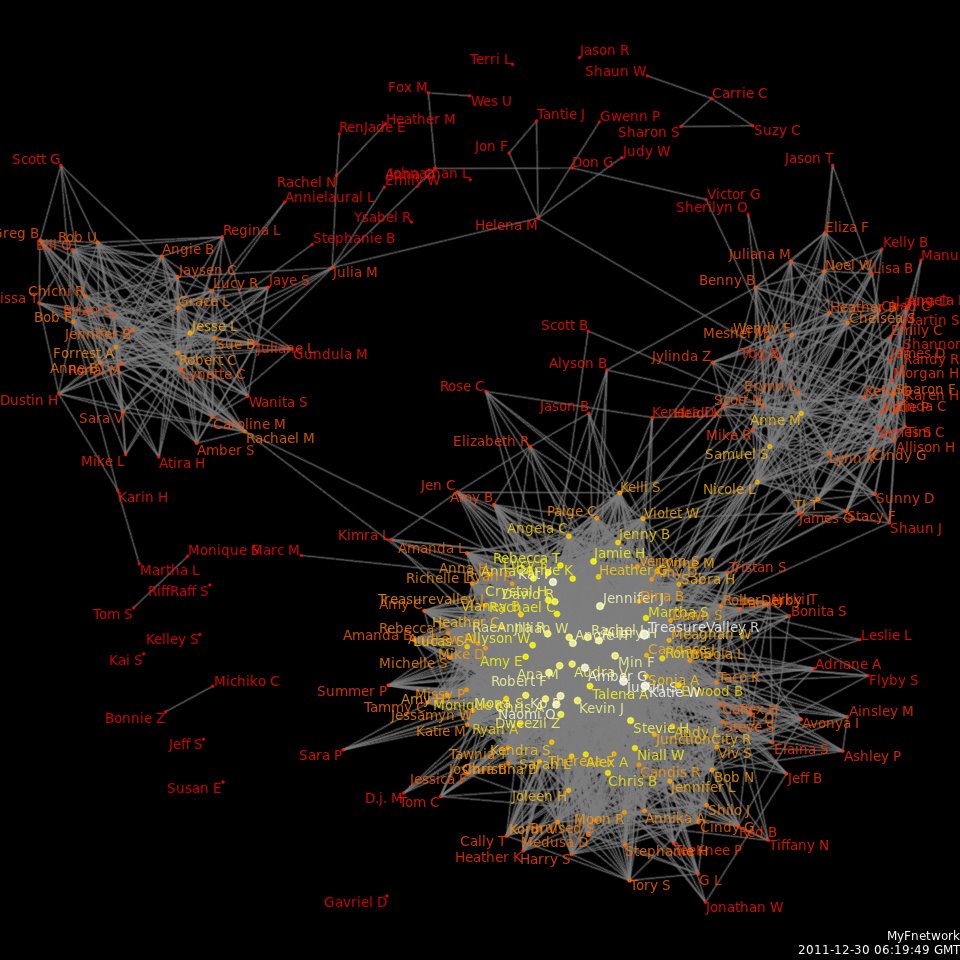
Social Network Analysis
Social network analysis (SNA) is the process of investigating social structures through the use of networks and graph theory. It characterizes networked structures in terms of ''nodes'' (individual actors, people, or things within the network) and the ''ties'', ''edges'', or ''links'' (relationships or interactions) that connect them. Examples of social structures commonly visualized through social network analysis include social media networks, memes spread, information circulation, friendship and acquaintance networks, business networks, knowledge networks, difficult working relationships, social networks, collaboration graphs, kinship, disease transmission, and sexual relationships. These networks are often visualized through ''sociograms'' in which nodes are represented as points and ties are represented as lines. These visualizations provide a means of qualitatively assessing networks by varying the visual representation of their nodes and edges to reflect attributes of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |