|
IEEE Honorary Membership
IEEE Honorary Membership is an honorary type of membership of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), that is given for life to an individual. It is awarded by the board of directors of IEEE to people 'who have rendered meritorious service to humanity in heIEEE's designated fields of interest' while not being members of IEEE. This membership provides all the rights and privileges of a normal IEEE membership, except the right to hold an IEEE office. The recipients of this grade will receive a certificate, an 'Honorary Member' pin and a crystal sculpture. In a given year, if the IEEE Medal of Honor recipient is not an IEEE member, he/she will be automatically recommended to the IEEE Board of Directors for IEEE Honorary Membership. Recipients The following people received the IEEE Honorary Membership: References Honorary Membership H {{sci-award-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Title Of Honor
A title of honor or honorary title is a title bestowed upon individuals or organizations as an award in recognition of their merits. Sometimes the title bears the same or nearly the same name as a title of authority, but the person bestowed does not have to carry out any duties, except for ceremonial ones. In some cases, these titles are bestowed posthumously. Some examples of honorary titles from various areas are: * Academician – Honorary title (academic) * Fellow of an academic, artistic, or professional society * Freeman of the City of London * Hero of the Russian Federation * Colonel (U.S. honorary title), Honorary Colonel * Honorary degree or position, such as honorary Professor * Knight, Dame (title), Dame, or Lady's companion, Companion of an honorific order * New Knowledge Worker of Korea * People's Artist * Honorary counselors (''neuvos'') in Finland, such as Counselor of State (Finland), valtioneuvos (Counselor of State) and vuorineuvos (Counselor of Mining) Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Dantzig
George Bernard Dantzig (; November 8, 1914 – May 13, 2005) was an American mathematical scientist who made contributions to industrial engineering, operations research, computer science, economics, and statistics. Dantzig is known for his development of the simplex algorithm, an algorithm for solving linear programming problems, and for his other work with linear programming. In statistics, Dantzig solved two open problems in statistical theory, which he had mistaken for homework after arriving late to a lecture by Jerzy Neyman.Joe Holley (2005)"Obituaries of George Dantzig" In: ''Washington Post'', May 19, 2005; B06 At his death, Dantzig was the Professor Emeritus of Transportation Sciences and Professor of Operations Research and of Computer Science at Stanford University. Early life Born in Portland, Oregon, George Bernard Dantzig was named after George Bernard Shaw, the Irish writer.Richard W. Cottle, B. Curtis Eaves and Michael A. Saunders (2006)"Memorial Resolution: Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Foster Ramsey, Jr
Norman Foster Ramsey Jr. (August 27, 1915 – November 4, 2011) was an American physicist who was awarded the 1989 Nobel Prize in Physics, for the invention of the separated oscillatory field method, which had important applications in the construction of atomic clocks. A physics professor at Harvard University for most of his career, Ramsey also held several posts with such government and international agencies as NATO and the United States Atomic Energy Commission. Among his other accomplishments are helping to found the United States Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory and Fermilab. Early life Norman Foster Ramsey Jr. was born in Washington, D.C., on August 27, 1915, to Minna Bauer Ramsey, an instructor at the University of Kansas, and Norman Foster Ramsey, a 1905 graduate of the United States Military Academy at West Point and an officer in the Ordnance Department who rose to the rank of brigadier general during World War II, commanding the Rock Island Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert A
Herbert may refer to: People Individuals * Herbert (musician), a pseudonym of Matthew Herbert Name * Herbert (given name) * Herbert (surname) Places Antarctica * Herbert Mountains, Coats Land * Herbert Sound, Graham Land Australia * Herbert, Northern Territory, a rural locality * Herbert, South Australia. former government town * Division of Herbert, an electoral district in Queensland * Herbert River, a river in Queensland * County of Herbert, a cadastral unit in South Australia Canada * Herbert, Saskatchewan, Canada, a town * Herbert Road, St. Albert, Canada New Zealand * Herbert, New Zealand, a town * Mount Herbert (New Zealand) United States * Herbert, Illinois, an unincorporated community * Herbert, Michigan, a former settlement * Herbert Creek, a stream in South Dakota * Herbert Island, Alaska Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Herbert (Disney character) This list of Donald Duck universe characters focuses on Disney cartoon and comics characte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mambillikalathil Govind Kumar Menon
Mambillikalathil Govind Kumar Menon (28 August 1928 – 22 November 2016) also known as M. G. K. Menon, was a physicist and policy maker from India. He had a prominent role in the development of science and technology in India over four decades. One of his most important contributions was nurturing the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai, which his mentor Homi J. Bhabha founded in 1945. Born in Mangalore, he attended the University of Bristol for his PhD in elementary particle physics under the guidance of Nobel Laureate Cecil F. Powell. He joined the TIFR in 1955. He undertook experiments with cosmic rays to explore the properties of fundamental particles. He was actively involved in setting up balloon flight experiments, as well as deep underground experiments with cosmic ray neutrinos in the mines at Kolar Gold Fields. He was the Director of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai (1966–1975), President of the Indian Statistical Institute, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur E
Arthur is a common male given name of Brythonic origin. Its popularity derives from it being the name of the legendary hero King Arthur. The etymology is disputed. It may derive from the Celtic ''Artos'' meaning “Bear”. Another theory, more widely believed, is that the name is derived from the Roman clan '' Artorius'' who lived in Roman Britain for centuries. A common spelling variant used in many Slavic, Romance, and Germanic languages is Artur. In Spanish and Italian it is Arturo. Etymology The earliest datable attestation of the name Arthur is in the early 9th century Welsh-Latin text ''Historia Brittonum'', where it refers to a circa 5th to 6th-century Briton general who fought against the invading Saxons, and who later gave rise to the famous King Arthur of medieval legend and literature. A possible earlier mention of the same man is to be found in the epic Welsh poem ''Y Gododdin'' by Aneirin, which some scholars assign to the late 6th century, though this is still a ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
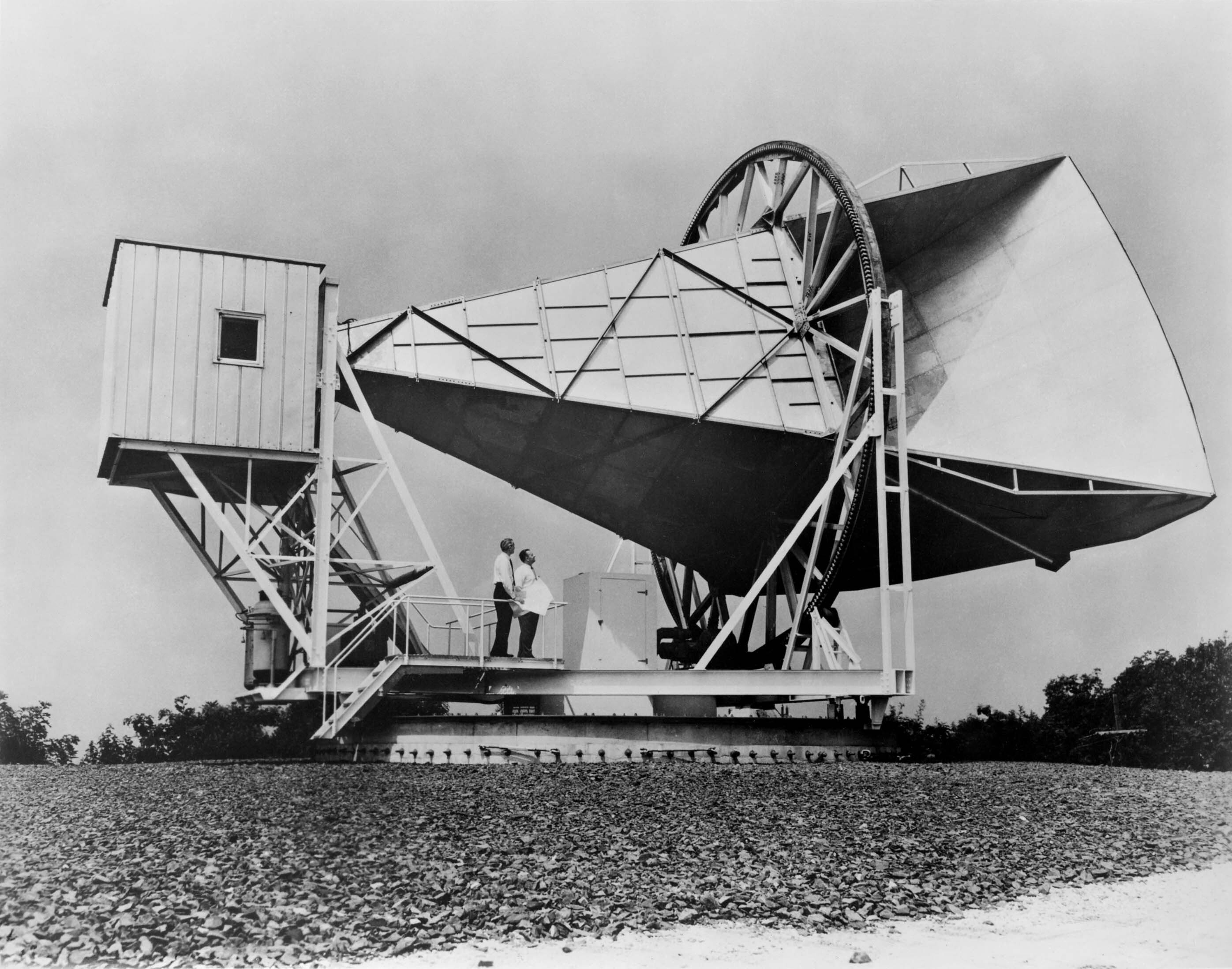
Arno Allan Penzias
Arno Allan Penzias (; born April 26, 1933) is an American physicist, radio astronomer and Nobel laureate in physics. Along with Robert Woodrow Wilson, he discovered the cosmic microwave background radiation, which helped establish the Big Bang theory of cosmology. Early life and education Penzias was born in Munich, Germany, the son of Justine (née Eisenreich) and Karl Penzias, who ran a leather business. His grandparents had come to Munich from Poland and were among the leaders of the Reichenbach Strasse Shul. At age six, he and his brother Gunther were among the Jewish children evacuated to Britain as part of the Kindertransport rescue operation. Some time later, including the Nobel Lecture, December 8, 1978 ''The Origin of Elements'' his parents also fled Nazi Germany for the U.S., and the family settled in the Garment District of New York City in 1940. In 1946, Penzias became a naturalized citizen of the United States. He graduated from Brooklyn Technical High School in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene H
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gene– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luis Walter Alvarez
Luis Walter Alvarez (June 13, 1911 – September 1, 1988) was an American experimental physicist, inventor, and professor who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1968 for his discovery of resonance states in particle physics using the hydrogen bubble chamber. In 2007 the ''American Journal of Physics'' commented, "Luis Alvarez was one of the most brilliant and productive experimental physicists of the twentieth century." After receiving his PhD from the University of Chicago in 1936, Alvarez went to work for Ernest Lawrence at the Radiation Laboratory at the University of California, Berkeley. Alvarez devised a set of experiments to observe K-electron capture in radioactive nuclei, predicted by the beta decay theory but never before observed. He produced tritium using the cyclotron and measured its lifetime. In collaboration with Felix Bloch, he measured the magnetic moment of the neutron. In 1940, Alvarez joined the MIT Radiation Laboratory, where he contributed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akio Morita
was a Japanese businessman and co-founder of Sony along with Masaru Ibuka. Early life Akio Morita was born in Nagoya. Morita's family was involved in sake, miso and soy sauce production in the village of Kosugaya (currently a part of Tokoname City) on the western coast of Chita Peninsula in Aichi Prefecture since 1665. He was the oldest of four siblings and his father Kyuzaemon trained him as a child to take over the family business. Akio, however, found his true calling in mathematics and physics, and in 1944 he graduated from Osaka Imperial University with a degree in physics. He was later commissioned as a sub-lieutenant in the Imperial Japanese Navy, and served in World War II. During his service, Morita met his future business partner Masaru Ibuka in the Navy's Wartime Research Committee. Sony In September 1945, Ibuka founded a radio repair shop in the bombed out Shirokiya Department Store in Nihonbashi, Tokyo. Morita saw a newspaper article about Ibuka's new venture and, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bob Galvin
Robert William "Bob" Galvin (October 9, 1922 – October 11, 2011) was an American executive. He was the son of the founder of Motorola, Paul Galvin, and served as the CEO of Motorola from 1959 to 1986. Motorola career Born in Marshfield, Wisconsin, Galvin went to work for Motorola in 1940. He graduated from the University of Notre Dame in 1944. In 1956 he was named the president of the company. Two years later he succeeded his father as a chief executive officer. In 1986, Bob Galvin gave up the title of CEO while remaining chairman of the board. Under his leadership, Motorola sales had grown from $216.6 million in 1958 to $6.7 billion in 1987 and cash flow per share had grown from 89 cents to $6.10. Bob Galvin also was instrumental, along with Dr. Mikel J Harry and Motorola engineer Bill Smith, in implementing the Six Sigma quality system at Motorola. As a result of the Six Sigma program, Motorola received the first Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award in 1988, which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |