|
Italy‚ÄďJapan Relations
Italy‚ÄďJapan relations refers to the bilateral relations between the Italian Republic and Japan. Bilateral relations between Japan and Italy formally began on 25 August 1866, but the first contacts between the two countries date back at least to the 16th century, when the first Japanese mission to Europe arrived in Rome in 1585 led by ItŇć Mancio. In the 19th century Italy and Japan saw great changes in their political and social structure, with the former gaining national unity in 1861 and the latter entering, from 1868, into a process of profound modernization along Western lines that took the name of the Meiji Restoration. In this same period relations became increasingly close, culminating in the participation of the two countries as allies in both World Wars. After the Second World War, Italy and Japan both experienced a period of strong economic growth, which enabled them to recover from the disastrous situation in which they found themselves after the end of the conf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Embassy Of Italy In Tokyo Japan
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of pronoun ''thee'') when followed by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DaimyŇć
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji era, Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast, hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and nominally to the Emperor of Japan, emperor and the ''kuge''. In the term, means 'large', and stands for , meaning 'private land'. From the ''shugo'' of the Muromachi period through the Sengoku period, Sengoku to the ''daimyo'' of the Edo period, the rank had a long and varied history. The backgrounds of ''daimyo'' also varied considerably; while some ''daimyo'' clans, notably the MŇćri clan, MŇćri, Shimazu clan, Shimazu and Hosokawa clan, Hosokawa, were cadet branches of the Imperial family or were descended from the ''kuge'', other ''daimyo'' were promoted from the ranks of the samurai, notably during the Edo period. ''Daimyo'' often hired samurai to guard their land, and they paid the samurai in land or food as relatively few could aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogun
, officially , was the title of the military dictators of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, though during part of the Kamakura period, shoguns were themselves figureheads, with real power in hands of the Shikken of the HŇćjŇć clan. The office of shogun was in practice hereditary, though over the course of the history of Japan several different clans held the position. The title was originally held by military commanders during Heian period in the eighth and ninth centuries. When Minamoto no Yoritomo gained political ascendency over Japan in 1185, the title was revived to regularize his position, making him the first shogun in the usually understood sense. The shogun's officials were collectively referred to as the ; they were the ones who carried out the actual duties of administration, while the Imperial court retained only nominal authority.Beasley, William G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Unification
The unification of Italy ( it, Unit√† d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single state in 1861, the Kingdom of Italy. Inspired by the rebellions in the 1820s and 1830s against the outcome of the Congress of Vienna, the unification process was precipitated by the Revolutions of 1848, and reached completion in 1871 after the Capture of Rome and its designation as the capital of the Kingdom of Italy. Some of the states that had been targeted for unification ('' terre irredente'') did not join the Kingdom of Italy until 1918 after Italy defeated Austria-Hungary in the First World War. For this reason, historians sometimes describe the unification period as continuing past 1871, including activities during the late 19th century and the First World War (1915‚Äď1918), and reaching completion only with the Armistice of Villa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missionary
A missionary is a member of a Religious denomination, religious group which is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Thomas Hale 'On Being a Missionary' 2003, William Carey Library Pub, . In the Bible translations into Latin, Latin translation of the Bible, Jesus, Jesus Christ says the word when he sends the disciples into areas and commands them to preach the gospel in his name. The term is most commonly used in reference to Christian missions, but it can also be used in reference to any creed or ideology. The word ''mission'' originated in 1598 when Jesuits, the members of the Society of Jesus sent members abroad, derived from the Latin (nominative case, nom. ), meaning 'act of sending' or , meaning 'to send'. By religion Buddhist missions The first Buddhist missionaries were called "Dharma Bhanaks", and some see a missionary charge in the symbolis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and to the east by the Gulf of Mexico. Mexico covers ,Mexico ''''. . making it the world's 13th-largest country by are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Paul V
Pope Paul V ( la, Paulus V; it, Paolo V) (17 September 1550 ‚Äď 28 January 1621), born Camillo Borghese, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 16 May 1605 to his death in January 1621. In 1611, he honored Galileo Galilei as a member of the Papal Accademia dei Lincei and supported his discoveries. In 1616, Pope Paul V instructed Cardinal Bellarmine to inform Galileo that the Copernican theory could not be taught as fact, but Bellarmine's certificate allowed Galileo to continue his studies in search for evidence and use the geocentric model as a theoretical device. That same year Paul V assured Galileo that he was safe from persecution so long as he, the Pope, should live. Bellarmine's certificate was used by Galileo for his defense at the trial of 1633. Early life Camillo Borghese was born in Rome on 17 September 1550 into the Borghese family of Siena which had recently established itself in Rome. He was the eldest son of seven sons of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
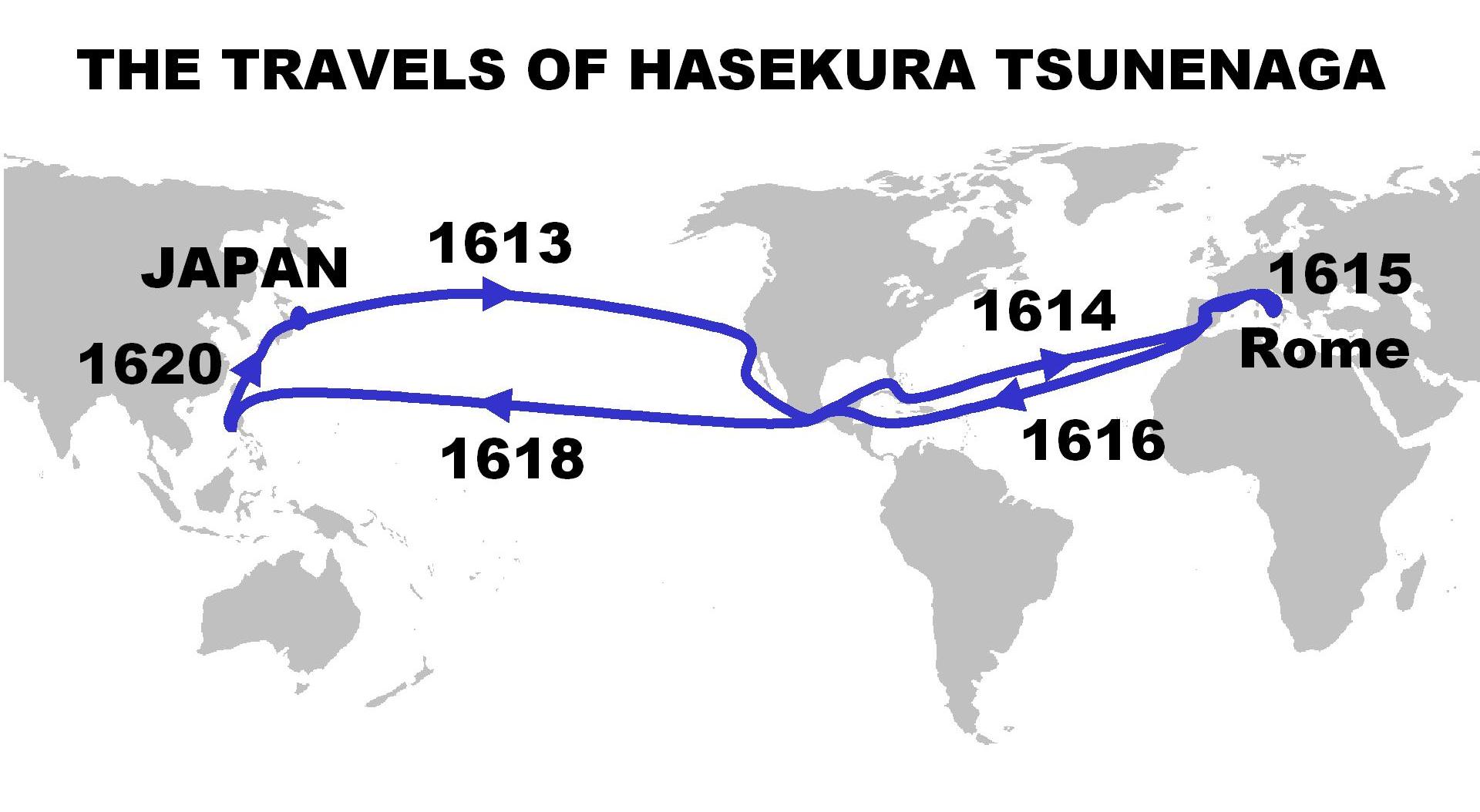
Hasekura Tsunenaga
was a kirishitan Japanese samurai and retainer of Date Masamune, the daimyŇć of Sendai. He was of Japanese imperial descent with ancestral ties to Emperor Kanmu. Other names include Philip Francis Faxicura, Felipe Francisco Faxicura, and Philippus Franciscus Faxecura Rocuyemon in period European sources. In the years 1613 through 1620, Hasekura headed the KeichŇć Embassy (), a diplomatic mission to Pope Paul V. He visited New Spain and various other ports-of-call in Europe on the way. On the return trip, Hasekura and his companions re-traced their route across New Spain in 1619, sailing from Acapulco for Manila, and then sailing north to Japan in 1620. He is considered the first Japanese ambassador in the Americas and in Spain, despite other less well-known and less well-documented missions preceding his mission. Although Hasekura's embassy was cordially received in Spain and Rome, it happened at a time when Japan was moving toward the suppression of Christianity. European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daimyo
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast, hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and nominally to the emperor and the '' kuge''. In the term, means 'large', and stands for , meaning 'private land'. From the ''shugo'' of the Muromachi period through the Sengoku to the ''daimyo'' of the Edo period, the rank had a long and varied history. The backgrounds of ''daimyo'' also varied considerably; while some ''daimyo'' clans, notably the MŇćri, Shimazu and Hosokawa, were cadet branches of the Imperial family or were descended from the ''kuge'', other ''daimyo'' were promoted from the ranks of the samurai, notably during the Edo period. ''Daimyo'' often hired samurai to guard their land, and they paid the samurai in land or food as relatively few could afford to pay samurai in money. The ''daimyo'' era ended soon after the Meiji Resto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arima Harunobu
was a Japanese samurai lord who was the daimyo of Shimabara Domain and the head of the Hizen-Arima clan''.''_In_his_early_years,_he_was_a_retainer_of_RyŇęzŇćji_clan.html" ;"title="DF 6-7 of 80/nowiki>">DF ...''.'' In his early years, he was a retainer of RyŇęzŇćji clan">DF 6-7 of 80/nowiki>">DF ...''.'' In his early years, he was a retainer of RyŇęzŇćji clan. Biography Harunobu was born in Hinoe Castle, the Hizen-Arima clan, Arima clan castle that controlled the Shimabara Peninsula, Shimabara area of Hizen Province. He was the second son and successor of Arima Yoshisada. After Yoshisada's death, he began the persecution of Kirishitan in his region. With RyŇęzŇćji Takanobu expanding into his domain, Harunobu turned to the help of the Jesuits. Harunobu was baptized by Alessandro Valignano in 1579. His conversion was spurred by the prospects of the goods and military assistance offered by the Portuguese. He took the baptismal name Protasius, and later took the name John when he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ŇĆmura Sumitada
ŇĆmura Sumitada (Ś§ßśĚĎ ÁīĒŚŅ†, 1533 ‚Äď June 23, 1587) was a Japanese ''daimyŇć'' lord of the Sengoku period. He achieved fame throughout the country for being the first of the daimyo to convert to Christianity following the arrival of the Jesuit missionaries in the mid-16th century. Following his baptism, he became known as "Dom Bartolomeu". Sumitada is also known as the lord who opened the port of Nagasaki to foreign trade. Early life ŇĆmura Sumitada was born in 1533, the son of Arima Haruzumi, lord of Shimabara, and his wife, who was a daughter of ŇĆmura Sumiyoshi. His childhood name was ShŇćdŇćmaru ŚčĚÁę•šłł. At age 5, he was adopted by his uncle ŇĆmura Sumisaki, and succeeded to the ŇĆmura family headship in 1550. As Sumisaki had no legitimate heirs, and the ŇĆmura clan had its origins in the family line of the Arima, Sumisaki readily adopted the young Shodomaru, who took the name Sumitada at the time of his succession. Career Following his succession, he was imm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ŇĆtomo SŇćrin
, also known as Fujiwara no Yoshishige (Ťó§Śéü Áĺ©ťéģ) and ŇĆtomo Yoshishige (Ś§ßŚŹč Áĺ©ťéģ), was a Japanese feudal lord (''daimyŇć'') of the ŇĆtomo clan, one of the few to have converted to Roman Catholicism (Christianity). The eldest son of , he inherited the Funai Domain, on KyŇęshŇę, Japan's southernmost main island, from his father. He is perhaps most significant for having appealed to Toyotomi Hideyoshi to intervene in KyŇęshŇę against the Shimazu clan, thus spurring Hideyoshi's KyŇęshŇę Campaign of 1587. Early life In 1545, SŇćrin married Lady Nata (Jezebel) who became one of the leading personalities against the spread of Christianity in western Japan. she was the daughter of Nata Akimoto, the head priest of the Nata Hachiman Shrine. SŇćrin's domain included the port of Funai, which was frequented by Jesuit priests, bandits, Chinese merchants, and Japanese sea lords. In addition to unifying much of KyŇęshŇę under his control, and securing a significant gain in his clan's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)