|
Istanbul Greek Dialect
The Istanbul Greek dialect () is the endangered Greek dialect spoken by the millennia-old Greek community in Istanbul, which has now shrunk to a couple thousand individuals. It is differentiated from Standard Greek due to a number of internal divergent developments, preservation of characteristics of Ancient Greek that are absent from Standard Greek, and language contact, most notably with Turkish, French, Italian and Armenian. Various characteristics of Istanbul Greek are said to have parallels in Old Athenian Greek, as well as Tsakonian. The idiom is spoken mainly in Istanbul, and among the Istanbul Greek emigre community in Athens. History The Istanbul Greek idiom derives from the speech of Istanbul's indigenous Greek community, which, having comprised the majority population before 1453, and 35% of the city's population at the turn of the 20th century, has now shrunk to 0.01% of Istanbul's population, or 2000 individuals. One of the pivotal moments in the shrinkage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, cultural and historic hub. The city straddles the Bosporus strait, lying in both Europe and Asia, and has a population of over 15 million residents, comprising 19% of the population of Turkey. Istanbul is the list of European cities by population within city limits, most populous European city, and the world's List of largest cities, 15th-largest city. The city was founded as Byzantium ( grc-gre, Βυζάντιον, ) in the 7th century BCE by Ancient Greece, Greek settlers from Megara. In 330 CE, the Roman emperor Constantine the Great made it his imperial capital, renaming it first as New Rome ( grc-gre, Νέα Ῥώμη, ; la, Nova Roma) and then as Constantinople () after himself. The city grew in size and influence, eventually becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demotic Greek
Demotic Greek or Dimotiki ( el, Δημοτική Γλώσσα, , , ) is the standard spoken language of Greece in modern times and, since the resolution of the Greek language question in 1976, the official language of Greece. "Demotic Greek" (with a capital D) contrasts with Katharevousa, which was used in formal settings, during the same period. In that context, Demotic Greek describes the specific non-standardized vernacular forms of Greek used by the vast majority of Greeks during the 19th and 20th centuries. As is typical of diglossic situations, Katharevousa and Dimotiki complemented and influenced each other. Over time, Dimotiki became standardized. In 1976, it was made the official language of Greece. It continued to evolve and is now called Standard Modern Greek. The term "demotic Greek" (with a minuscule d) also refers to any variety of the Greek language which has evolved naturally from Ancient Greek and is popularly spoken. Basic features of Dimotiki Demotic Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Ideology
Language ideology (also known as linguistic ideology or language attitude) is, within anthropology (especially linguistic anthropology), sociolinguistics, and cross-cultural studies, any set of beliefs about languages as they are used in their social worlds. Language ideologies are conceptualizations about languages, speakers, and discursive practices. Like other kinds of ideologies, language ideologies are influenced by political and moral interests, and they are shaped in a cultural setting. When recognized and explored, language ideologies expose how the speakers' linguistic beliefs are linked to the broader social and cultural systems to which they belong, illustrating how the systems beget such beliefs. By doing so, language ideologies link implicit and explicit assumptions about a language or language in general to their social experience as well as their political and economic interests. Applications and approaches Definitions Scholars have noted difficulty in attempting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cypriot Greek
Cypriot Greek ( el, κυπριακή ελληνική or ) is the Varieties of Modern Greek, variety of Modern Greek that is spoken by the majority of the Cyprus, Cypriot populace and Greek Cypriot diaspora. It is considered a divergent dialect as it differs from Standard Modern Greek in various aspects of its lexicon, phonetics, phonology, Morphology (linguistics), morphology, syntax and even pragmatics, not only for historical reasons, but also because of geographical isolation, different settlement patterns, and extensive contact with Linguistic typology, typologically distinct languages. Classification Cypriot Greek is not an evolution of ancient Arcadocypriot Greek, but derives from Byzantine Medieval Greek. It has traditionally been placed in the Varieties of Modern Greek#Core dialects, southeastern group of Modern Greek varieties, along with the dialects of the Dodecanese and Chios (with which it shares several phonological phenomena). Though Cypriot Greek tends to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postalveolar Affricate
Postalveolar affricates are a type of consonant sound. The most common postalveolar affricates are: *Voiced postalveolar affricate () *Voiceless postalveolar affricate The voiceless palato-alveolar sibilant affricate or voiceless domed postalveolar sibilant affricate is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The sound is transcribed in the International Phonetic Alphabet with , (formerly ... () Affricates Postalveolar consonants Pulmonic consonants Central consonants {{set index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dark L
The voiced alveolar lateral approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar lateral approximants is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is . As a sonorant, lateral approximants are nearly always voiced. Voiceless lateral approximants, are common in Sino-Tibetan languages, but uncommon elsewhere. In such cases, voicing typically starts about halfway through the hold of the consonant. No language is known to contrast such a sound with a voiceless alveolar lateral fricative . In a number of languages, including most varieties of English, the phoneme becomes velarized (" dark ''l''") in certain contexts. By contrast, the non-velarized form is the "clear ''l''" (also known as: "light ''l''"), which occurs before and between vowels in certain English standards. Some languages have only clear ''l''. Others may not have a clear ''l'' at all, or have t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Back Vowel
A back vowel is any in a class of vowel sound used in spoken languages. The defining characteristic of a back vowel is that the highest point of the tongue is positioned relatively back in the mouth without creating a constriction that would be classified as a consonant. Back vowels are sometimes also called dark vowels because they are perceived as sounding darker than the front vowels. Near-back vowels are essentially a type of back vowels; no language is known to contrast back and near-back vowels based on backness alone. The category "back vowel" comprises both raised vowels and retracted vowels. Articulation In their articulation, back vowels do not form a single category, but may be either raised vowels such as or retracted vowels such as .Scott Moisik, Ewa Czaykowska-Higgins, & John H. Esling (2012"The Epilaryngeal Articulator: A New Conceptual Tool for Understanding Lingual-Laryngeal Contrasts"/ref> Partial list The back vowels that have dedicated symbols in the Intern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
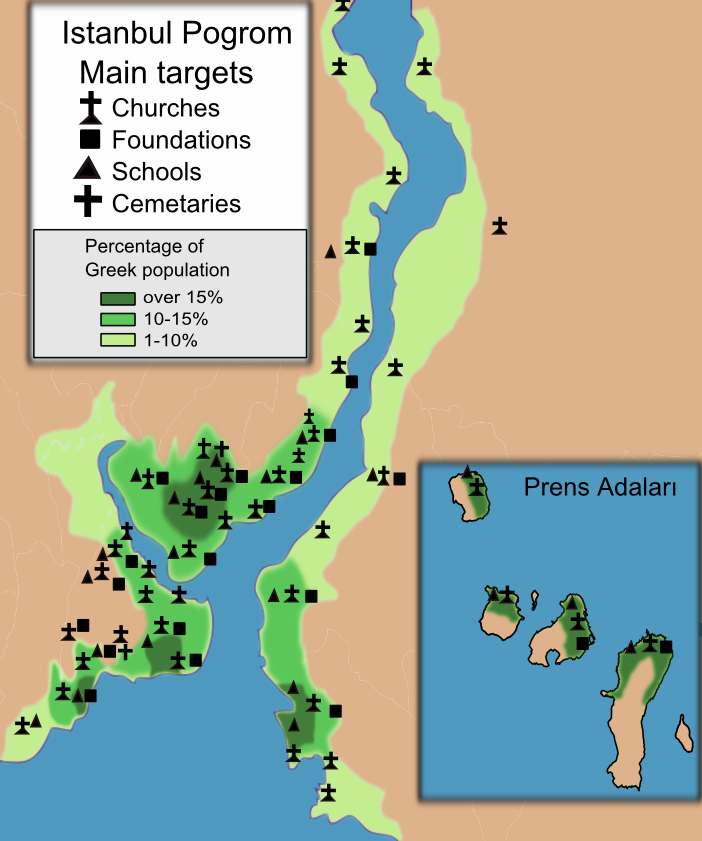
Expulsion Of Istanbul Greeks
The expulsion of Istanbul Greeks ( or ''1964 Rum Sürgünü'') in 1964–1965 was a series of discriminatory measures by the authorities of the Republic of Turkey aimed at the forced expulsion of the Greek population of Istanbul ( el, Κωνσταντινούπολις, translit=Kōnstantinoúpolis). Though the Greeks of Istanbul were initially excluded from the Greek-Turkish population exchange of 1923 and were allowed to remain in their native city, the Turkish government enacted a series of measures that resulted in a dramatic decrease in their numbers, such as the "wealth" tax of 1942 and later the anti-Greek pogrom of September 1955. Especially during the 1950s and 1960s, the Greek minority was used as an apparatus of pressure for the Cyprus issue as part of the Greek-Turkish relations. The anti-Greek measures of 1964–1965 resulted in a drastic reduction in the number of Greeks in Istanbul. As such, from a population of about 80,000 only about 30,000 remained in 1965.Kali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsakonian Language
Tsakonian or Tsaconian (also Tzakonian or Tsakonic, Greek and Tsakonian: , ) is a highly divergent modern variety of Greek, spoken in the Tsakonian region of the Peloponnese, Greece. Tsakonian derives from Doric Greek, being its only extant variant. Although it is conventionally treated as a dialect of Greek, some compendia treat it as a separate language. Tsakonian is critically endangered, with only a few hundred/thousand, mostly elderly, fluent speakers left. Although Tsakonian and standard Modern Greek are related, they are not mutually intelligible. Etymology The term Tsakonas or Tzakonas first emerges in the writings of Byzantine chroniclers who derive the ethnonym from a corruption of Lakonas, a Laconian/Lacedaemonian (Spartan)—a reference to the Doric roots of the Tsakonian language. Geographic distribution Tsakonian is found today in a group of mountain towns and villages slightly inland from the Argolic Gulf, although it was once spoken farther to the south and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Language
Armenian ( classical: , reformed: , , ) is an Indo-European language and an independent branch of that family of languages. It is the official language of Armenia. Historically spoken in the Armenian Highlands, today Armenian is widely spoken throughout the Armenian diaspora. Armenian is written in its own writing system, the Armenian alphabet, introduced in 405 AD by the priest Mesrop Mashtots. The total number of Armenian speakers worldwide is estimated between 5 and 7 million. History Classification and origins Armenian is an independent branch of the Indo-European languages. It is of interest to linguists for its distinctive phonological changes within that family. Armenian exhibits more satemization than centumization, although it is not classified as belonging to either of these subgroups. Some linguists tentatively conclude that Armenian, Greek (and Phrygian) and Indo-Iranian were dialectally close to each other;''Handbook of Formal Languages'' (1997p. 6 wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Language
Italian (''italiano'' or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. Together with Sardinian, Italian is the least divergent language from Latin. Spoken by about 85 million people (2022), Italian is an official language in Italy, Switzerland (Ticino and the Grisons), San Marino, and Vatican City. It has an official minority status in western Istria (Croatia and Slovenia). Italian is also spoken by large immigrant and expatriate communities in the Americas and Australia.Ethnologue report for language code:ita (Italy) – Gordon, Raymond G., Jr. (ed.), 2005. Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Fifteenth edition. Dallas, Tex.: SIL International. Online version Itali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |