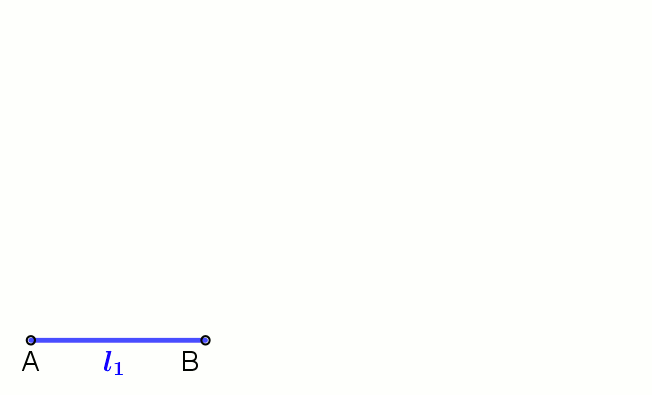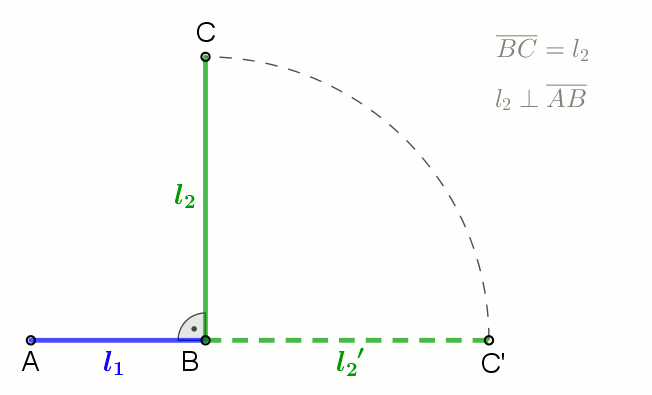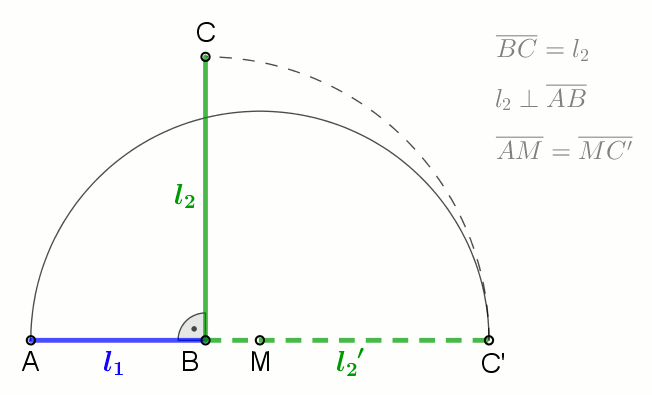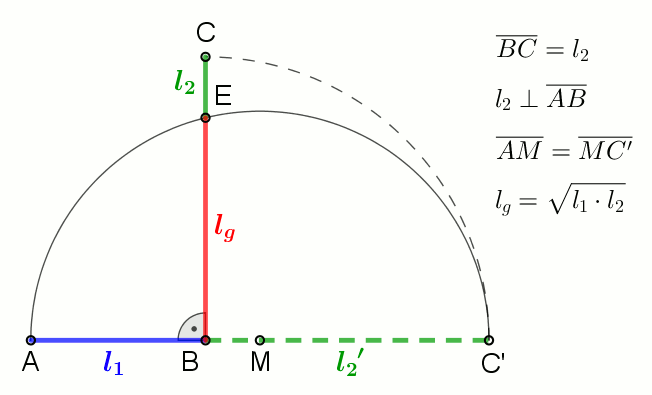|
Isotope Dilution
Isotope dilution analysis is a method of determining the quantity of chemical substances. In its most simple conception, the method of isotope dilution comprises the addition of known amounts of isotopically enriched substance to the analyzed sample. Mixing of the isotopic standard with the sample effectively "dilutes" the isotopic enrichment of the standard and this forms the basis for the isotope dilution method. Isotope dilution is classified as a method of internal standardisation, because the standard (isotopically enriched form of analyte) is added directly to the sample. In addition, unlike traditional analytical methods which rely on signal intensity, isotope dilution employs signal ratios. Owing to both of these advantages, the method of isotope dilution is regarded among chemistry measurement methods of the highest metrological standing. Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number. All isotopes of a given element have the same num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principle Of Isotope Dilution
A principle is a proposition or value that is a guide for behavior or evaluation. In law, it is a rule that has to be or usually is to be followed. It can be desirably followed, or it can be an inevitable consequence of something, such as the laws observed in nature or the way that a system is constructed. The principles of such a system are understood by its users as the essential characteristics of the system, or reflecting system's designed purpose, and the effective operation or use of which would be impossible if any one of the principles was to be ignored. A system may be explicitly based on and implemented from a document of principles as was done in IBM's 360/370 ''Principles of Operation''. Examples of principles are, entropy in a number of fields, least action in physics, those in descriptive comprehensive and fundamental law: doctrines or assumptions forming normative rules of conduct, separation of church and state in statecraft, the central dogma of molecular biology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Volume
Blood volume (volemia) is the volume of blood (blood cells and plasma) in the circulatory system of any individual. Humans A typical adult has a blood volume of approximately 5 liters, with females and males having approximately the same blood percentage by weight (approx 7 to 8%) Blood volume is regulated by the kidneys. Blood volume (BV) can be calculated given the hematocrit (HC; the fraction of blood that is red blood cells) and plasma volume (PV), with the hematocrit being regulated via the blood oxygen content regulator: :BV = \frac Blood volume measurement may be used in people with congestive heart failure, chronic hypertension, kidney failure and critical care. The use of relative blood volume changes during dialysis is of questionable utility. Total Blood Volume can be measured manually via the Dual Isotope or Dual Tracer Technique, a classic technique, available since the 1950s. This technique requires double labeling of the blood; that is 2 injections and 2 standar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Standard
An internal standard in analytical chemistry is a chemical substance that is added in a constant amount to samples, the blank and calibration standards in a chemical analysis. This substance can then be used for calibration by plotting the ratio of the analyte signal to the internal standard signal as a function of the analyte concentration of the standards. This is done to correct for the loss of analyte during sample preparation or sample inlet. The internal standard is a compound that is very similar, but not identical to the chemical species of interest in the samples, as the effects of sample preparation should, relative to the amount of each species, be the same for the signal from the internal standard as for the signal(s) from the species of interest in the ideal case. Adding known quantities of analyte(s) of interest is a distinct technique called standard addition, which is performed to correct for matrix effects. This ratio for the samples is then used to obtain their anal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Addition
The method of standard addition is a type of quantitative analysis approach often used in analytical chemistry whereby the standard is added directly to the aliquots of analyzed sample. This method is used in situations where sample matrix also contributes to the analytical signal, a situation known as the matrix effect, thus making it impossible to compare the analytical signal between sample and standard using the traditional calibration curve approach. Applications Standard addition is frequently used in chemical instrumental analysis such as atomic absorption spectroscopy and gas chromatography. Suppose that the concentration of silver in samples of photographic waste is to be determined by atomic-absorption spectrometry. Using the calibration curve method, an analyst could calibrate the spectrometer with some aqueous solutions of a pure silver salt and use the resulting calibration graph in the determination of the silver in the test samples. This method is only valid, howe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytica Chimica Acta
''Analytica Chimica Acta'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published since 1947 that covers original research and reviews of fundamental and applied aspects of analytical chemistry. See also * List of scientific journals in chemistry * Analytical chemistry * Chemistry Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions ... References Elsevier academic journals Chemistry journals Publications established in 1947 Weekly journals English-language journals 1947 establishments in the Netherlands {{chem-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Padé Approximant
In mathematics, a Padé approximant is the "best" approximation of a function near a specific point by a rational function of given order. Under this technique, the approximant's power series agrees with the power series of the function it is approximating. The technique was developed around 1890 by Henri Padé, but goes back to Georg Frobenius, who introduced the idea and investigated the features of rational approximations of power series. The Padé approximant often gives better approximation of the function than truncating its Taylor series, and it may still work where the Taylor series does not converge. For these reasons Padé approximants are used extensively in computer calculations. They have also been used as auxiliary functions in Diophantine approximation and transcendental number theory, though for sharp results ad hoc methods— in some sense inspired by the Padé theory— typically replace them. Since Padé approximant is a rational function, an artificial singul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Journal Of Mass Spectrometry
The ''International Journal of Mass Spectrometry'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of mass spectrometry, including instrumentation and applications in biology, chemistry, geology, and physics. It was established in 1968 as the ''International Journal of Mass Spectrometry and Ion Physics'' and was renamed ''International Journal of Mass Spectrometry and Ion Processes'' in 1983, before obtaining its current title in 1998. It is published by Elsevier and the editors-in-chief are Julia Laskin (Purdue University) and Zheng Ouyang (Tsinghua University). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: *Chemical Abstracts Service *Current Contents/Physical, Chemical & Earth Sciences * EBSCO databases * Embase *Food Science and Technology Abstracts *FRANCIS * Inspec *PASCAL *Science Citation Index Expanded *Scopus According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fresenius' Journal Of Analytical Chemistry
''Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing research articles in the broad field of analytical and bioanalytical chemistry. Some of the subjects covered are the development of instruments for mass spectrometry, metallomics, ionics, and the analytical characterization of nano- and biomaterials. The journal was first published in 1862 under the name ''Fresenius’ Journal of Analytical Chemistry''. In 2002 the journal was renamed to ''Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry''. Impact factor ''Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry'' had a 2018 impact factor of 3.286, ranking it 18th out of 84 in the subject category " Chemistry, Analytical" and 21st out of 79 in "Biochemical Research Methods". Editors The editors of the journal are A.J Baeumner H. Cui, G. Gauglitz, G. Hopfgartner, L. Mondello, M.C. Moreno-Bondi, D.C. Muddiman, S. Szunerits, Q. Qang and S.A. Wise. Literature * Wilhelm Fresenius Wilhelm may refer to: People and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrochimica Acta B
''Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering spectroscopy. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2019 impact factor of 3.086. Currently, the editors-in-chief are M. T. C. de Loos-Vollebregt (Delft University of Technology) and A. De Giacomo (University of Bari The University of Bari Aldo Moro ( it, Università degli Studi di Bari Aldo Moro) is a state-supported higher education institution founded in 1925 in Bari, Apulia, in Southern Italy. The university is one of the most prestigious universities in ...). The journal was established in 1939 as ''Spectrochimica Acta''. In 1967, ''Spectrochimica Acta'' was split into two journals, '' Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy'' and ''Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy''. Part B obtained its current title around the time of the split. References External links * Spectroch. Acta B at CAS Source Inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accreditation And Quality Assurance
Accreditation is the independent, third-party evaluation of a conformity assessment body (such as certification body, inspection body or laboratory) against recognised standards, conveying formal demonstration of its impartiality and competence to carry out specific conformity assessment tasks (such as certification, inspection and testing). Accreditation bodies are established in many economies with the primary purpose of ensuring that conformity assessment bodies are subject to oversight by an authoritative body. Accreditation bodies, that have been peer evaluated as competent, sign regional and international arrangements to demonstrate their competence. These accreditation bodies then assess and accredit conformity assessment bodies to the relevant standards. An authoritative body that performs accreditation is called an 'accreditation body'. The International Accreditation Forum (IAF) and International Laboratory Accreditation Cooperation (ILAC) provide international recognitio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytical And Bioanalytical Chemistry
''Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing research articles in the broad field of analytical and bioanalytical chemistry. Some of the subjects covered are the development of instruments for mass spectrometry, metallomics, ionics, and the analytical characterization of nano- and biomaterials. The journal was first published in 1862 under the name ''Fresenius’ Journal of Analytical Chemistry''. In 2002 the journal was renamed to ''Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry''. Impact factor ''Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry'' had a 2018 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 3.286, ranking it 18th out of 84 in the subject category " Chemistry, Analytical" and 21st out of 79 in "Biochemical Research Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Mean
In mathematics, the geometric mean is a mean or average which indicates a central tendency of a set of numbers by using the product of their values (as opposed to the arithmetic mean which uses their sum). The geometric mean is defined as the th root of the product of numbers, i.e., for a set of numbers , the geometric mean is defined as :\left(\prod_^n a_i\right)^\frac = \sqrt /math> or, equivalently, as the arithmetic mean in logscale: :\exp For instance, the geometric mean of two numbers, say 2 and 8, is just the square root of their product, that is, \sqrt = 4. As another example, the geometric mean of the three numbers 4, 1, and 1/32 is the cube root of their product (1/8), which is 1/2, that is, \sqrt = 1/2. The geometric mean applies only to positive numbers. The geometric mean is often used for a set of numbers whose values are meant to be multiplied together or are exponential in nature, such as a set of growth figures: values of the human population or inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |