|
Iskut Volcanic Field
The Iskut volcanic field is a group of volcanoes and lava flows on and adjacent to the Alaska–British Columbia border in the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains. All the volcanoes in this volcanic field are situated in British Columbia along the Iskut and Unuk rivers and their tributaries, with lava flows having reached Alaska. The oldest volcanoes in the Iskut volcanic field are Little Bear Mountain and Hoodoo Mountain, which are 146,000 and 85,000 years old, respectively. Younger volcanic centres include Second Canyon, King Creek, Tom MacKay Creek, Snippaker Creek, Iskut Canyon, Cone Glacier, Cinder Mountain and Lava Fork, all of which formed in the last 70,000 years. All of the volcanoes are mafic in composition except for Hoodoo Mountain which consists of peralkaline rocks. The latest volcanic eruption took place from the Lava Fork volcano in 1800, although an uncertain 1904 eruption is also attributed to this volcano. The name Iskut-Unuk River Cones is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinder Mountain
Cinder Mountain is a partly eroded cinder cone at the head of Snippaker Creek, British Columbia, Canada. It is one of the Iskut-Unuk River Cones and is the source of a basaltic lava flow that extends north into Copper King Creek. An isolated pile of subaerial basalt flows and associated pillow lava rest on varved clay and till in King Creek. Cinder Mountain last erupted during the Pleistocene. See also *List of volcanoes in Canada *List of Northern Cordilleran volcanoes *Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province * The Volcano *Volcanism of Canada *Volcanism of Western Canada Volcanism of Western Canada has produced lava flows, lava plateaus, lava domes, cinder cones, stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes, greenstone belts, submarine volcanoes, calderas, diatremes and maars, along with examples of more less common volcanic ... References Boundary Ranges Cinder cones of British Columbia Stikine Country Monogenetic volcanoes Pleistocene volcanoes {{BritishColumbiaIn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Bear Mountain
Little Bear Mountain is a basaltic Pleistocene age tuya in the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains that adjoins Hoodoo Mountain to the north. Little Bear Mountain is part of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province. See also * List of volcanoes in Canada * List of Northern Cordilleran volcanoes * Volcanism of Canada * Volcanism of Western Canada Volcanism of Western Canada has produced lava flows, lava plateaus, lava domes, cinder cones, stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes, greenstone belts, submarine volcanoes, calderas, diatremes and maars, along with examples of more less common volcanic ... References Catalogue of Canadian volcanoes: Little Bear Mountainh1> External links Global Volcanism Program: Hoodoo Mountain Volcanoes of British Columbia One-thousanders of British Columbia Boundary Ranges Tuyas of Canada Parasitic cones Stikine Country Pleistocene volcanoes {{BritishColumbiaInterior-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
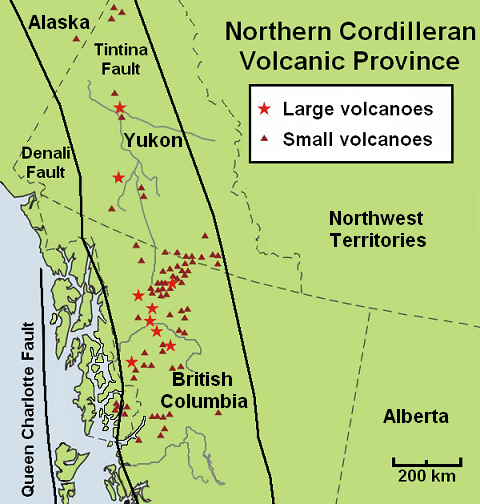
List Of Northern Cordilleran Volcanoes
The geography of northwestern British Columbia and Yukon, Canada is dominated by volcanoes of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province formed due to continental rifting of the North American Plate. It is the most active volcanic region in Canada. Some of the volcanoes are notable for their eruptions, for instance, Tseax Cone for its catastrophic eruption estimated to have occurred in the 18th century which was responsible for the death of at least 2,000 Nisga'a people from poisonous volcanic gases, the Mount Edziza volcanic complex for at least 20 eruptions throughout the past 10,000 years, and The Volcano (also known as Lava Fork volcano) for the most recent eruption in Canada during 1904. The majority of volcanoes in the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province lie in Canada while a very small portion of the volcanic province lies in the U.S. state of Alaska. Volcanoes of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province are a part of the Pacific Ring of Fire. The largest a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman and Viking ages, and there is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age. The first town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951. The city is most famous as the home of the University of Cambridge, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chapel, Cavendish Laboratory, and the Cambridge University Library, one of the largest legal deposit libraries in the world. The city's skyline is dominated by several college buildings, along with the spire of the Our Lady and the English Martyrs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press A university press is an academic publishing house specializing in monographs and scholarly journals. Most are nonprofit organizations and an integral component of a large research university. They publish work that has been reviewed by schola ... in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press is a department of the University of Cambridge and is both an academic and educational publisher. It became part of Cambridge University Press & Assessment, following a merger with Cambridge Assessment in 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 Country, countries, it publishes over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publishing includes more than 380 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peralkaline Rock
Peralkaline rocks include those igneous rocks which have a deficiency of aluminium such that sodium and potassium are in excess of that needed for feldspar. The presence of aegerine (sodium pyroxene) and riebeckite (sodium amphibole) are indicative of peralkaline conditions. Examples are the peralkaline rhyolites, comendite and pantellerite, with comendite being the more felsic (silica-rich) rock. Another example is the peralkaline granite that forms the islet of Rockall in the North Atlantic Ocean. Peralkaline rocks are indicative of continental rift-related volcanicity (e.g. the peralkaline rhyolites of the East African Rift in central Kenya) as well as continental and oceanic hotspot volcanicity (e.g. the peralkaline rhyolites of the Glass House Mountains in eastern Australia and the Canary Islands in the Atlantic Ocean). Peralkaline rocks related to subduction zone volcanicity have also been reported (e.g. Sardinia in Italy). Peralkaline magmas likely form when fractional crys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mafic
A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks include basalt, diabase and gabbro. Mafic rocks often also contain calcium-rich varieties of plagioclase feldspar. Mafic materials can also be described as ferromagnesian. History The term ''mafic'' is a portmanteau of "magnesium" and "ferric" and was coined by Charles Whitman Cross, Joseph P. Iddings, Louis Valentine Pirsson, and Henry Stephens Washington in 1912. Cross' group had previously divided the major rock-forming minerals found in igneous rocks into ''salic'' minerals, such as quartz, feldspars, or feldspathoids, and ''femic'' minerals, such as olivine and pyroxene. However, micas and aluminium-rich amphiboles were excluded, while some calcium minerals containing little iron or magnesium, such as wollastonite or apatite, were included ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Volcano (British Columbia)
The Volcano, also known as Lava Fork volcano, is a small cinder cone in the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains in northwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is located approximately northwest of the small community of Stewart near the head of Lava Fork. With a summit elevation of and a topographic prominence of , it rises above the surrounding rugged landscape on a remote mountain ridge that represents the northern flank of a glaciated U-shaped valley. Lava Fork volcano is associated with a small group of volcanoes called the Iskut volcanic field. This forms part of the much larger Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province, which extends from the Alaska–Yukon border to near the port city of Prince Rupert, British Columbia. Eruptive activity at The Volcano is relatively young compared to most other volcanoes in the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province. Geologic studies have shown that The Volcano and its eruptive products were emplaced in the last 400 years; this is w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
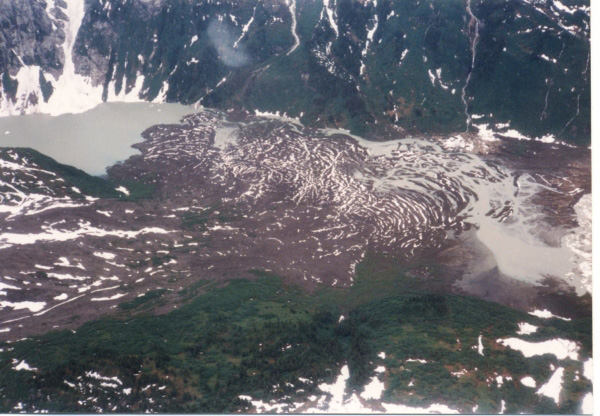
Cone Glacier Volcano
Cone Glacier Volcano is a cinder cone in the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains in northwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is part of the Iskut-Unuk River Cones group and last erupted during the Holocene period. Cone Glacier contains two arms that surround the volcano. See also *List of volcanoes in Canada *List of Northern Cordilleran volcanoes *Volcanic history of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province *Volcanism of Canada *Volcanism of Western Canada Volcanism of Western Canada has produced lava flows, lava plateaus, lava domes, cinder cones, stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes, greenstone belts, submarine volcanoes, calderas, diatremes and maars, along with examples of more less common volcanic ... References Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province Cinder cones of British Columbia {{BritishColumbiaInterior-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iskut Canyon Cone
Iskut Canyon Cone, also known as Iskut River Cone, is a cinder cone of the Iskut-Unuk River Cones group in northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located on the steep southern flank of the Iskut valley near its junction with Forrest Kerr Creek. It last erupted during the Holocene epoch. See also *List of volcanoes in Canada *List of Northern Cordilleran volcanoes *Volcanism of Canada *Volcanism of Western Canada Volcanism of Western Canada has produced lava flows, lava plateaus, lava domes, cinder cones, stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes, greenstone belts, submarine volcanoes, calderas, diatremes and maars, along with examples of more less common volcanic ... References Cinder cones of British Columbia Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province Polygenetic volcanoes Boundary Ranges {{BritishColumbiaInterior-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snippaker Creek Cone
Snippaker Creek Cone is a cinder cone of the Iskut-Unuk River Cones group in northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located near the western flank of Cinder Mountain. It last erupted during the Holocene epoch. See also * * * |
Tom MacKay Creek Cone
Tom MacKay Creek Cone is a basalt subglacial mound in northwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is part of the Iskut-Unuk River Cones group and last erupted during the Pleistocene epoch. There is a single vent and a single flow of weathered, fragmented pillow basalt that has a maximum thickness of .Petrography, Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of the Iskut-Unuk Rivers Volcanic Centres, Northwestern British Columbia, by Steinunn Hauksdottir, 1994 See also *List of volcanoes in Canada *List of Northern Cordilleran volcanoes *Volcanism of Canada *Volcanism of Western Canada Volcanism of Western Canada has produced lava flows, lava plateaus, lava domes, cinder cones, stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes, greenstone belts, submarine volcanoes, calderas, diatremes and maars, along with examples of more less common volcanic ... References Volcanoes of British Columbia Mountains of British Columbia Subglacial mounds of Canada Pleistocene volcanoes {{BritishColumbiaInterior-geo-stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |