|
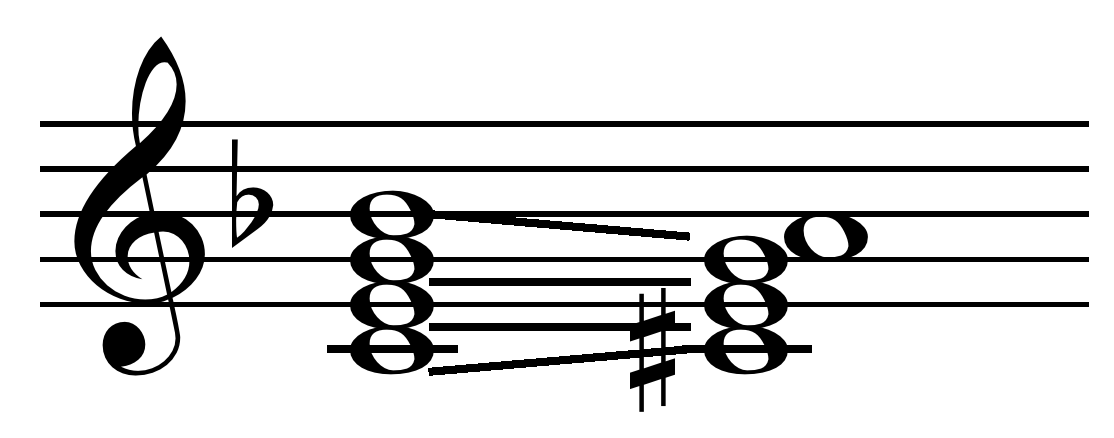
Irregular Resolution
In music, an irregular resolution is resolution by a dominant seventh chord or diminished seventh chord to a chord other than the tonic. Regarding the dominant seventh, there are many irregular resolutions including to a chord with which it has tones in common or if the parts move only a whole or half step. Chadwick, George Whitefield (2008). ''Harmony, a Course of Study'', p.160. . Consecutive fifths and octaves, augmented intervals, and false relations should still be avoided. Voice leading may cause the seventh to ascend, to be prolonged into the next chord, or to be unresolved.Foote, Arthur (2007). ''Modern Harmony in its Theory and Practice'', p.93ff. . The following resolutions to a chord with tones in common have been identified: *Type I, in which the root motion descends by minor third. C, E, G, B would resolve to C, E, G, A; two tones are common, two voices move by half-step in contrary motion. *Type II, in which the root motion rises by minor third. C, E, G, B would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irregular Resolution I
Irregular, irregulars or irregularity may refer to any of the following: Astronomy * Irregular galaxy * Irregular moon * Irregular variable, a kind of star Language * Irregular inflection, the formation of derived forms such as plurals in unpredictable ways ** Irregular verb Law * Against regulations * In canon law, an irregularity is an impediment for the Catholic priesthood or for exercising orders already received Mathematics * Irregularity of a surface * Irregularity of distributions * Irregularity index Medicine * Irregular bone * Arrhythmia, also known as an irregular heartbeat * Constipation, also called "irregularity" Other * ''The Irregulars'', a 2021 Netflix series * Accounting irregularity * Irregular military * Irregular chess opening See also * Anomaly (other) * Baker Street Irregulars * Regular (other) The term regular can mean normal or in accordance with rules. It may refer to: People * Moses Regular (born 1971), America f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Third
In music theory, a minor third is a musical interval that encompasses three half steps, or semitones. Staff notation represents the minor third as encompassing three staff positions (see: interval number). The minor third is one of two commonly occurring thirds. It is called ''minor'' because it is the smaller of the two: the major third spans an additional semitone. For example, the interval from A to C is a minor third, as the note C lies three semitones above A. Coincidentally, there are three staff positions from A to C. Diminished and augmented thirds span the same number of staff positions, but consist of a different number of semitones (two and five). The minor third is a skip melodically. Notable examples of ascending minor thirds include the opening two notes of " Greensleeves" and of " Light My Fire". The minor third may be derived from the harmonic series as the interval between the fifth and sixth harmonics, or from the 19th harmonic. The minor third is co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neapolitan Chord
In Classical music theory, a Neapolitan chord (or simply a "Neapolitan") is a major chord built on the lowered ( flatted) second (supertonic) scale degree. In Schenkerian analysis, it is known as a Phrygian II, since in minor scales the chord is built on the notes of the corresponding Phrygian mode. Although it is sometimes indicated by an "N" rather than a "II", some analysts prefer the latter because it indicates the relation of this chord to the supertonic. The Neapolitan chord does not fall into the categories of mixture or tonicization. Moreover, even Schenkerians like Carl Schachter do not consider this chord as a sign for a shift to the Phrygian mode. Therefore, like the augmented sixth chords it should be assigned to a separate category of chromatic alteration. In European Classical music, the Neapolitan most commonly occurs in first inversion so that it is notated either as II6 or N6 and normally referred to as a Neapolitan sixth chord. In C major or C minor, for exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enharmonic Equivalence
In modern musical notation and tuning, an enharmonic equivalent is a note, interval, or key signature that is equivalent to some other note, interval, or key signature but "spelled", or named differently. The enharmonic spelling of a written note, interval, or chord is an alternative way to write that note, interval, or chord. The term is derived from Latin ''enharmonicus'', from Late Latin ''enarmonius'', from Ancient Greek ἐναρμόνιος (''enarmónios''), from ἐν (''en'') and ἁρμονία (''harmonía''). Definition For example, in any twelve-tone equal temperament (the predominant system of musical tuning in Western music), the notes C and D are ''enharmonic'' (or ''enharmonically equivalent'') notes. Namely, they are the same key on a keyboard, and thus they are identical in pitch, although they have different names and different roles in harmony and chord progressions. Arbitrary amounts of accidentals can produce further enharmonic equivalents, such as B (mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Sixth
In music theory, an augmented sixth chord contains the interval of an augmented sixth, usually above its bass tone. This chord has its origins in the Renaissance, was further developed in the Baroque, and became a distinctive part of the musical style of the Classical and Romantic periods. Conventionally used with a predominant function ( resolving to the dominant), the three most common types of augmented sixth chords are usually called the ''Italian sixth'', the ''French sixth'', and the ''German sixth''. Augmented sixth interval The augmented sixth interval is typically between the sixth degree of the minor scale, , and the raised fourth degree, . With standard voice leading, the chord is followed directly or indirectly by some form of the dominant chord, in which both and have resolved to the fifth scale degree, . This tendency to resolve outwards to is why the interval is spelled as an augmented sixth, rather than enharmonically as a minor seventh ( and ). Alth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augmented Sixth Chord
In music theory, an augmented sixth chord contains the interval of an augmented sixth, usually above its bass tone. This chord has its origins in the Renaissance, was further developed in the Baroque, and became a distinctive part of the musical style of the Classical and Romantic periods. Conventionally used with a predominant function ( resolving to the dominant), the three most common types of augmented sixth chords are usually called the ''Italian sixth'', the ''French sixth'', and the ''German sixth''. Augmented sixth interval The augmented sixth interval is typically between the sixth degree of the minor scale, , and the raised fourth degree, . With standard voice leading, the chord is followed directly or indirectly by some form of the dominant chord, in which both and have resolved to the fifth scale degree, . This tendency to resolve outwards to is why the interval is spelled as an augmented sixth, rather than enharmonically as a minor seventh ( and ). Alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deceptive Cadence
In Western musical theory, a cadence (Latin ''cadentia'', "a falling") is the end of a phrase in which the melody or harmony creates a sense of full or partial resolution, especially in music of the 16th century onwards.Don Michael Randel (1999). ''The Harvard Concise Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', pp. 105-106. . A harmonic cadence is a progression of two or more chords that concludes a phrase, section, or piece of music. A rhythmic cadence is a characteristic rhythmic pattern that indicates the end of a phrase. A cadence can be labeled "weak" or "strong" depending on the impression of finality it gives. While cadences are usually classified by specific chord or melodic progressions, the use of such progressions does not necessarily constitute a cadence—there must be a sense of closure, as at the end of a phrase. Harmonic rhythm plays an important part in determining where a cadence occurs. Cadences are strong indicators of the tonic or central pitch of a passage o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Edward Wilson
Richard Edward Wilson (born May 15, 1941) is an American composer and pianist. Rejecting serialism, to some extent Wilson engages in tonality, though often with the use of considerable chromaticism. His ''oeuvre'' includes orchestral, operatic, instrumental, and chamber music among other genres. Life and career Wilson was born in Cleveland, Ohio, where he was at a young age drawn to the concerts of George Szell and the Cleveland Orchestra. In 1963, Wilson graduated ''magna cum laude'' and Phi Beta Kappa from Harvard University, where he studied with Robert Moevs and Randall Thompson. He later received an MA from Rutgers University. From 1966 to 2016, he taught at Vassar College, where he was Mary Conover Mellon Professor of Music. Since 1992 he has been composer-in-residence with the American Symphony Orchestra. Music Richard Wilson's compositions are marked by a stringent yet lyrical atonality which often sets him apart from the established schools of modern American mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Resolution
The term regular can mean normal or in accordance with rules. It may refer to: People * Moses Regular (born 1971), America football player Arts, entertainment, and media Music * "Regular" (Badfinger song) * Regular tunings of stringed instruments, tunings with equal intervals between the paired notes of successive open strings Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * Regular character, a main character who appears more frequently and/or prominently than a recurring character * Regular division of the plane, a series of drawings by the Dutch artist M. C. Escher which began in 1936 * ''Regular Show'', an animated television sitcom * ''The Regular Guys'', a radio morning show Language * Regular inflection, the formation of derived forms such as plurals in ways that are typical for the language ** Regular verb * Regular script, the newest of the Chinese script styles Mathematics There are an extremely large number of unrelated notions of "regularity" in mathematics. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tritone
In music theory, the tritone is defined as a musical interval composed of three adjacent whole tones (six semitones). For instance, the interval from F up to the B above it (in short, F–B) is a tritone as it can be decomposed into the three adjacent whole tones F–G, G–A, and A–B. Narrowly defined, each of these whole tones must be a step in the scale, so by this definition, within a diatonic scale there is only one tritone for each octave. For instance, the above-mentioned interval F–B is the only tritone formed from the notes of the C major scale. More broadly, a tritone is also commonly defined as any interval with a width of three whole tones (spanning six semitones in the chromatic scale), regardless of scale degrees. According to this definition, a diatonic scale contains two tritones for each octave. For instance, the above-mentioned C major scale contains the tritones F–B (from F to the B above it, also called augmented fourth) and B–F (from B to the F abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contrapuntal Motion
In music theory, contrapuntal motion is the general movement of two melodic lines with respect to each other. In traditional four-part harmony, it is important that lines maintain their independence, an effect which can be achieved by the judicious use of the four types of contrapuntal motion: parallel motion, similar motion, contrary motion, and oblique motion.Free-Ed.NeTraditional Harmony: Voice Motion Retrieved 2011-09-15. Parallel motion Parallel motion is motion in the same direction, keeping the same interval between them. For example : : Parallel motion at an interval of a perfect fifth is known as parallel or consecutive fifths, and at an interval of an octave is known as parallel or consecutive octaves. These motions are generally avoided in traditional counterpoint because they offer the lines so little independence from each other. Similar motion Similar motion is motion in the same direction, but with the interval between them changing. In other words, both lines mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semitone
A semitone, also called a half step or a half tone, is the smallest musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most dissonant when sounded harmonically. It is defined as the interval between two adjacent notes in a 12-tone scale. For example, C is adjacent to C; the interval between them is a semitone. In a 12-note approximately equally divided scale, any interval can be defined in terms of an appropriate number of semitones (e.g. a whole tone or major second is 2 semitones wide, a major third 4 semitones, and a perfect fifth 7 semitones. In music theory, a distinction is made between a diatonic semitone, or minor second (an interval encompassing two different staff positions, e.g. from C to D) and a chromatic semitone or augmented unison (an interval between two notes at the same staff position, e.g. from C to C). These are enharmonically equivalent when twelve-tone equal temperament is used, but are not the same thing in meantone temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |