|
Iprazochrome
Iprazochrome is an antimigraine agent used for prophylaxis of the attacks. It is also indicated for diabetic retinopathy (both treatment and prevention in people with type-2 diabetes). Chemically, it is a derivative of adrenochrome, which is a product of adrenaline oxidation. And it is a derivative of carbazochrome as well. Mechanism of action It is a serotonin antagonist A serotonin antagonist, or serotonin receptor antagonist, is a drug used to inhibit the action at serotonin (5-HT) receptors. Types 5-HT2A antagonists Antagonists of the 5-HT2A receptor are sometimes used as atypical antipsychotics (contrast wi ... both ''in vitro'' and ''in vivo'' (it is a 5-HT2D receptor antagonist). It also neutralises other vasoactive compounds such as bradykinin, histamine, and others. This drug decreases the permeability and fragility of blood vessels, which reduces the number of migraine days and attenuates the symptoms associated with this condition, but it does not elimina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimigraine
Antimigraine drugs are medications intended to reduce the effects or intensity of migraine headache. They include drugs for the treatment of acute migraine symptoms as well as drugs for the prevention of migraine attacks. Treatment of acute symptoms Examples of specific antimigraine drug classes include triptans (first line option), ergot alkaloids, ditans and gepants. Migraines can also be treated with unspecific analgesics such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ... (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen. Opioids are not recommended for treatment of migraines. Triptans The triptan drug class includes 1st generation sumatriptan (which has poor bioavailability), and second generation zolmitriptan. Due to their safety, efficacy and selectiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
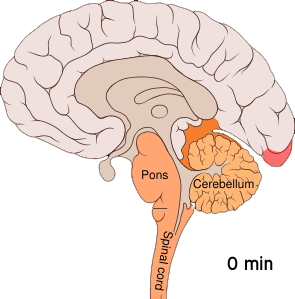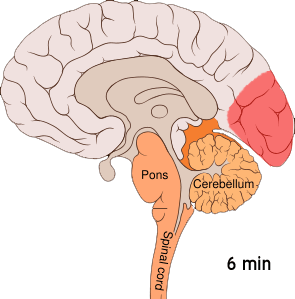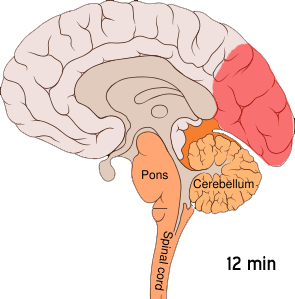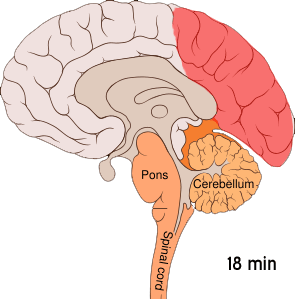
Cortical Spreading Depression
] Cortical spreading depression (CSD) or spreading depolarization (SD) is a wave of Electrophysiology, electrophysiological hyperactivity followed by a wave of inhibition. Spreading depolarization describes a phenomenon characterized by the appearance of depolarization waves of the neurons and neuroglia that propagates across the cerebral cortex, cortex at a velocity of 1.5–9.5 mm/min. CSD can be induced by hypoxia (medical), hypoxic conditions and facilitates neuronal death in energy-compromised tissue. CSD has also been implicated in migraine aura (symptom), aura, where CSD is assumed to ascend in well-nourished tissue and is typically benign in most of the cases, although it may increase the probability in migraine patients to develop a stroke. Spreading depolarization within brainstem tissues regulating functions crucial for life has been implicated in sudden unexpected death in epilepsy, by way of ion channel mutations such as those seen in Dravet syndrome, a particul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semicarbazones
In organic chemistry, a semicarbazone is a derivative of imines formed by a condensation reaction between a ketone or aldehyde and semicarbazide. They are classified as imine derivatives because they are formed from the reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with the terminal -NH2 group of semicarbazide, which behaves very similarly to primary amines. Formation ;For ketones :H2NNHC(=O)NH2 + RC(=O)R → R2C=NNHC(=O)NH2 ;For aldehydes :H2NNHC(=O)NH2 + RCHO → RCH=NNHC(=O)NH2 For example, the semicarbazone of acetone would have the structure (CH3)2C=NNHC(=O)NH2. Properties and uses Some semicarbazones, such as nitrofurazone, and thiosemicarbazones are known to have anti-viral and anti-cancer activity, usually mediated through binding to copper or iron in cells. Many semicarbazones are crystalline solids, useful for the identification of the parent aldehydes/ketones by melting point analysis. A ''thiosemicarbazone'' is an analog of a semicarbazone which contains a sulfur atom in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimigraine Drugs
Antimigraine drugs are medications intended to reduce the effects or intensity of migraine headache. They include drugs for the treatment of acute migraine symptoms as well as drugs for the prevention of migraine attacks. Treatment of acute symptoms Examples of specific antimigraine drug classes include triptans (first line option), ergot alkaloids, ditans and gepants. Migraines can also be treated with unspecific analgesics such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ... (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen. Opioids are not recommended for treatment of migraines. Triptans The triptan drug class includes 1st generation sumatriptan (which has poor bioavailability), and second generation zolmitriptan. Due to their safety, efficacy and selectiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indole
Indole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound with the formula C8 H7 N. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered pyrrole ring. Indole is widely distributed in the natural environment and can be produced by a variety of bacteria. As an intercellular signal molecule, indole regulates various aspects of bacterial physiology, including spore formation, plasmid stability, resistance to drugs, biofilm formation, and virulence. The amino acid tryptophan is an indole derivative and the precursor of the neurotransmitter serotonin. General properties and occurrence Indole is a solid at room temperature. It occurs naturally in human feces and has an intense fecal odor. At very low concentrations, however, it has a flowery smell, and is a constituent of many perfumes. It also occurs in coal tar. The corresponding substituent is called indolyl. Indole undergoes electrophilic substitution, mainly at position 3 (see diagra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable atoms survive. The term is also used more generally to characterize any type of exponential (or, rarely, non-exponential) decay. For example, the medical sciences refer to the biological half-life of drugs and other chemicals in the human body. The converse of half-life (in exponential growth) is doubling time. The original term, ''half-life period'', dating to Ernest Rutherford's discovery of the principle in 1907, was shortened to ''half-life'' in the early 1950s. Rutherford applied the principle of a radioactive element's half-life in studies of age determination of rocks by measuring the decay period of radium to lead-206. Half-life is constant over the lifetime of an exponentially decaying quantity, and it is a characteristic unit for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cmax (pharmacology)
Cmax is the maximum (or peak) serum concentration that a drug achieves in a specified compartment or test area of the body after the drug has been administered and before the administration of a second dose. It is a standard measurement in pharmacokinetics. Description Cmax is the opposite of Cmin, which is the minimum (or trough) concentration that a drug achieves after dosing. The related pharmacokinetic parameter tmax is the time at which the Cmax is observed. After an intravenous administration, Cmax and tmax are closely dependent on the experimental protocol, since the concentrations are always decreasing after the dose. But after oral administration, Cmax and tmax are dependent on the extent, and the rate of drug absorption and the disposition profile of the drug. They could be used to characterize the properties of different formulations in the same subject. Short term drug side effects are most likely to occur at or near the Cmax, whereas the therapeutic effect of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Since histamine was discovered in 1910, it has been considered a local hormone (autocoid) because it lacks the classic endocrine glands to secrete it; however, in recent years, histamine has been recognized as a central neurotransmitter. Histamine is involved in the inflammatory response and has a central role as a mediator of itching. As part of an immune response to foreign pathogens, histamine is produced by basophils and by mast cells found in nearby connective tissues. Histamine increases the permeability of the capillaries to white blood cells and some proteins, to allow them to engage pathogens in the infected tissues. It consists of an imidazole ring attached to an ethylamine chain; under physiological conditions, the amino group of the side-chain is protonate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy (also known as diabetic eye disease), is a medical condition in which damage occurs to the retina due to diabetes mellitus. It is a leading cause of blindness in developed countries. Diabetic retinopathy affects up to 80 percent of those who have had both type 1 and type 2 diabetes for 20 years or more. In at least 90% of new cases, progression to more aggressive forms of sight threatening retinopathy and maculopathy could be reduced with proper treatment and monitoring of the eyes The longer a person has diabetes, the higher his or her chances of developing diabetic retinopathy. Each year in the United States, diabetic retinopathy accounts for 12% of all new cases of blindness. It is also the leading cause of blindness in people aged 20 to 64. Signs and symptoms Nearly all people with diabetes develop some degree of retina damage ("retinopathy") over several decades with the disease. For many, that damage can only be detected by a retinal exam, and has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bradykinin
Bradykinin (BK) (Greek brady-, slow; -kinin, kīn(eîn) to move) is a peptide that promotes inflammation. It causes arterioles to dilate (enlarge) via the release of prostacyclin, nitric oxide, and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor and makes veins constrict, via prostaglandin F2, thereby leading to leakage into capillary beds, due to the increased pressure in the capillaries. Bradykinin is a physiologically and pharmacologically active peptide of the kinin group of proteins, consisting of nine amino acids. A class of drugs called angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors) increase bradykinin levels by inhibiting its degradation, thereby increasing its blood pressure lowering effect. ACE inhibitors are FDA approved for the treatment of hypertension and heart failure. Structure Bradykinin, sometimes referred to as BK, is a 9-amino acid peptide chain. The amino acid sequence of bradykinin is: Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly- Phe-Ser-Pro- Phe- Arg (RPPGFSPFR). Its empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT2D
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. Approximately 90% of the serotonin that the body produces is in the intestinal tract. Biochemically, the indoleamine molecule derives from the amino acid tryptophan, via the (rate-limiting) hydroxylation of the 5 position on the ring (forming the intermediate 5-hydroxytryptophan), and then decarboxylation to produce serotonin. Serotonin is primarily found in the enteric nervous system located in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). However, it is also produced in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically in the raphe nuclei located in the brainstem, Merkel cells located in the skin, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells and taste receptor cells in the tongue. Additionally, serotonin is stored in blood platelets an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |