|
Ionic Transfer
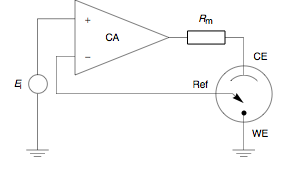
Ionic transfer is the transfer of ions from one liquid phase to another. This is related to the phase transfer catalysts which are a special type of liquid-liquid extraction which is used in synthetic chemistry. For instance nitrate anions can be transferred between water and nitrobenzene. One way to observe this is to use a cyclic voltammetry experiment where the liquid-liquid interface is the working electrode. This can be done by placing secondary electrodes in each phase and close to interface each phase has a reference electrode. One phase is attached to a potentiostat which is set to zero volts, while the other |
Phase Transfer Catalyst
In chemistry, a phase-transfer catalyst or PTC is a catalyst that facilitates the transition of a reactant from one phase into another phase where reaction occurs. Phase-transfer catalysis is a special form of heterogeneous catalysis. Ionic reactants are often soluble in an aqueous phase but insoluble in an organic phase in the absence of the phase-transfer catalyst. The catalyst functions like a detergent for solubilizing the salts into the organic phase. Phase-transfer catalysis refers to the acceleration of the reaction upon the addition of the phase-transfer catalyst. By using a PTC process, one can achieve faster reactions, obtain higher conversions or yields, make fewer byproducts, eliminate the need for expensive or dangerous solvents that will dissolve all the reactants in one phase, eliminate the need for expensive raw materials and/or minimize waste problems. Phase-transfer catalysts are especially useful in green chemistry—by allowing the use of water, the nee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Synthesis
As a topic of chemistry, chemical synthesis (or combination) is the artificial execution of chemical reactions to obtain one or several products. This occurs by physical and chemical manipulations usually involving one or more reactions. In modern laboratory uses, the process is reproducible and reliable. A chemical synthesis involves one or more compounds (known as '' reagents'' or ''reactants'') that will experience a transformation when subjected to certain conditions. Various reaction types can be applied to formulate a desired product. This requires mixing the compounds in a reaction vessel, such as a chemical reactor or a simple round-bottom flask. Many reactions require some form of processing (" work-up") or purification procedure to isolate the final product. The amount produced by chemical synthesis is known as the ''reaction yield''. Typically, yields are expressed as a mass in grams (in a laboratory setting) or as a percentage of the total theoretical quantity that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during a Chemical reaction, reaction with other Chemical substance, substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both Basic research, basic and Applied science, applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the properties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion A polyatomic ion, also known as a molecular ion, is a covalent bonded set of two or more atoms, or of a metal complex, that can be considered to behave as a single unit and that has a net charge that is not zero. The term molecule may or may no ... with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in water. An example of an insoluble nitrate is bismuth oxynitrate. Structure The ion is the conjugate acid, conjugate base of nitric acid, consisting of one central nitrogen atom surrounded by three identically bonded oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement. The nitrate ion carries a formal charge of −1. This charge results from a combination formal charge in which each of the three oxygens carries a − charge, whereas the nitrogen carries a +1 charge, all these adding up to formal c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons. Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed atomic or monatomic ions, while two or more atoms form molecular ions or polyatomic ions. In the case of physical ionization in a fluid (gas or liquid), "ion pairs" are created by spontaneous molecule collisions, where each generated pair consists of a free electron and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrobenzene
Nitrobenzene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5 NO2. It is a water-insoluble pale yellow oil with an almond-like odor. It freezes to give greenish-yellow crystals. It is produced on a large scale from benzene as a precursor to aniline. In the laboratory, it is occasionally used as a solvent, especially for electrophilic reagents. Production Nitrobenzene is prepared by nitration of benzene with a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid, water, and nitric acid. This mixture is sometimes called "mixed acid." The production of nitrobenzene is one of the most dangerous processes conducted in the chemical industry because of the exothermicity of the reaction (Δ''H'' = −117 kJ/mol). World capacity for nitrobenzene in 1985 was about 1,700,000 tonnes. The nitration process involves formation of the nitronium ion (NO2+), followed by an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction of it with benzene. The nitronium ion is generated by the reaction of nitric aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Voltammetry
Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is a type of potentiodynamic electrochemical measurement. In a cyclic voltammetry experiment, the working electrode potential is ramped linearly versus time. Unlike in linear sweep voltammetry, after the set potential is reached in a CV experiment, the working electrode's potential is ramped in the opposite direction to return to the initial potential. These cycles of ramps in potential may be repeated as many times as needed. The current at the working electrode is plotted versus the applied voltage (that is, the working electrode's potential) to give the cyclic voltammogram trace. Cyclic voltammetry is generally used to study the electrochemical properties of an analyte in solution or of a molecule that is adsorbed onto the electrode. Experimental method In cyclic voltammetry (CV), the electrode potential ramps linearly versus time in cyclical phases (Figure 2). The rate of voltage change over time during each of these phases is known as the experiment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials depending on the type of battery. The electrophore, invented by Johan Wilcke, was an early version of an electrode used to study static electricity. Anode and cathode in electrochemical cells Electrodes are an essential part of any battery. The first electrochemical battery made was devised by Alessandro Volta and was aptly named the Voltaic cell. This battery consisted of a stack of copper and zinc electrodes separated by brine-soaked paper disks. Due to fluctuation in the voltage provided by the voltaic cell it wasn't very practical. The first practical battery was invented in 1839 and named the Daniell cell after John Frederic Daniell. Still making use of the zinc–copper electrode combination. Since then many more batteries have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reference Electrode
A reference electrode is an electrode which has a stable and well-known electrode potential. The high stability of the electrode potential is usually reached by employing a redox system with constant (buffered or saturated) concentrations of each participant of the redox reaction. There are many ways reference electrodes are used. The simplest is when the reference electrode is used as a half-cell to build an electrochemical cell. This allows the reduction potential, potential of the other half cell to be determined. An accurate and practical method to measure an electrode's potential in isolation (absolute electrode potential) has yet to be developed. Aqueous reference electrodes Common reference electrodes and potential with respect to the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE): * Standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) (E = 0.000 V) activity of H+ = 1 Molar * Normal hydrogen electrode (NHE) (E ≈ 0.000 V) concentration H+ = 1 Molar * Reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE) (E = 0.000 V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potentiostat
A potentiostat is the electronic hardware required to control a three electrode cell and run most electroanalytical experiments. A ''Bipotentiostat'' and ''polypotentiostat'' are potentiostats capable of controlling two working electrodes and more than two working electrodes, respectively. The system functions by maintaining the potential of the working electrode at a constant level with respect to the reference electrode by adjusting the current at an auxiliary electrode. The heart of the different potentiostatic electronic circuits is an operational amplifier (op amp). It consists of an electric circuit which is usually described in terms of simple op amps. Primary use This equipment is fundamental to modern electrochemical studies using three electrode systems for investigations of reaction mechanisms related to redox chemistry and other chemical phenomena. The dimensions of the resulting data depend on the experiment. In voltammetry, electric current in amps is pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITIES
In electrochemistry, ITIES (interface between two immiscible electrolyte solutions) is an electrochemical interface that is either polarisable or polarised. An ITIES is polarisable if one can change the Galvani potential difference, or in other words the difference of inner potentials between the two adjacent phases, without noticeably changing the chemical composition of the respective phases (i.e. without noticeable electrochemical reactions taking place at the interface). An ITIES system is polarised if the distribution of the different charges and redox species between the two phases determines the Galvani potential difference. Usually, one electrolyte is an aqueous electrolyte composed of hydrophilic ions such as NaCl dissolved in water and the other electrolyte is a lipophilic salt such as tetrabutylammonium tetraphenylborate dissolved in an organic solvent immiscible with water such as nitrobenzene, or 1,2-dichloroethane. Charge transfer reactions of an ITIES Three major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |