|
Ion Transport Number
In chemistry, ion transport number, also called the transference number, is the fraction of the total electric current carried in an electrolyte by a given ionic species : :t_i = \frac Differences in transport number arise from differences in electrical mobility. For example, in an aqueous solution of sodium chloride, less than half of the current is carried by the positively charged sodium ions (cations) and more than half is carried by the negatively charged chloride ions (anions) because the chloride ions are able to move faster, i.e., chloride ions have higher mobility than sodium ions. The sum of the transport numbers for all of the ions in solution always equals unity: :\sum_i t_i = 1 The concept and measurement of transport number were introduced by Johann Wilhelm Hittorf in the year 1853. Liquid junction potential can arise from ions in a solution having different ion transport numbers. At zero concentration, the limiting ion transport numbers may be expressed in terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during a Chemical reaction, reaction with other Chemical substance, substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both Basic research, basic and Applied science, applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the properties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faraday Constant
In physical chemistry, the Faraday constant, denoted by the symbol and sometimes stylized as ℱ, is the electric charge per mole of elementary charges. It is named after the English scientist Michael Faraday. Since the 2019 redefinition of SI base units, which took effect on 20 May 2019, the Faraday constant has the exactly defined value given by the product of the elementary charge ''e'' and Avogadro constant ''N''A: : : :. Derivation The Faraday constant can be thought of as the conversion factor between the mole (used in chemistry) and the coulomb (used in physics and in practical electrical measurements), and is therefore of particular use in electrochemistry. Because 1 mole contains exactly entities, and 1 coulomb contains exactly elementary charges, the Faraday constant is given by the quotient of these two quantities: :. One common use of the Faraday constant is in electrolysis calculations. One can divide the amount of charge (the current integrated over time) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrochemical Kinetics
Electrochemical kinetics is the field of electrochemistry that studies the rate of electrochemical processes. This includes the study of how process conditions, such as concentration and electric potential, influence the rate of oxidation and reduction (redox) reactions that occur at the surface of an electrode, as well as an investigation into electrochemical reaction mechanisms. Two accompanying processes are involved in the electrochemical reaction and influence the overall reaction rate: * electron transfer at the interface between the electrode and the electrolyte * transport of the redox species from the interior of the solution to the surface of the electrode; the transport can occur by diffusion, convection and migration. Contributors to this field include Alexander Frumkin, John Alfred Valentine Butler, Max Volmer, and Julius Tafel. Butler-Volmer equation An elementary charge transfer step can be described by the Butler–Volmer model proposed by John Alfred Valenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debye Length
In plasmas and electrolytes, the Debye length \lambda_ (also called Debye radius), is a measure of a charge carrier's net electrostatic effect in a solution and how far its electrostatic effect persists. With each Debye length the charges are increasingly electrically screened and the electric potential decreases in magnitude by 1/ e. A Debye sphere is a volume whose radius is the Debye length. Debye length is an important parameter in plasma physics, electrolytes, and colloids (DLVO theory). The corresponding Debye screening wave vector k_=1/\lambda_ for particles of density n, charge q at a temperature T is given by k_^2=4\pi n q^2/(k_T) in Gaussian units. Expressions in MKS units will be given below. The analogous quantities at very low temperatures (T \to 0) are known as the Thomas–Fermi length and the Thomas–Fermi wave vector. They are of interest in describing the behaviour of electrons in metals at room temperature. The Debye length is named after the Dutch-America ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Born Equation
The Born equation can be used for estimating the electrostatic component of Gibbs free energy of solvation of an ion. It is an electrostatic model that treats the solvent as a continuous dielectric medium (it is thus one member of a class of methods known as continuum solvation methods). It was derived by Max Born. \Delta G =- \frac\left(1-\frac\right) where: *''N''A = Avogadro constant *''z'' = charge of ion *''e'' = elementary charge The elementary charge, usually denoted by is the electric charge carried by a single proton or, equivalently, the magnitude of the negative electric charge carried by a single electron, which has charge −1 . This elementary charge is a fundame ..., 1.6022 C *''ε''0 = permittivity of free space *''r''0 = effective radius of ion *''ε''r = dielectric constant of the solvent Derivation The energy U stored in an electrostatic field distribution is:U=\frac \varepsilon_0 \varepsilon_r \int , , ^2 dVKnowing the magnitude of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
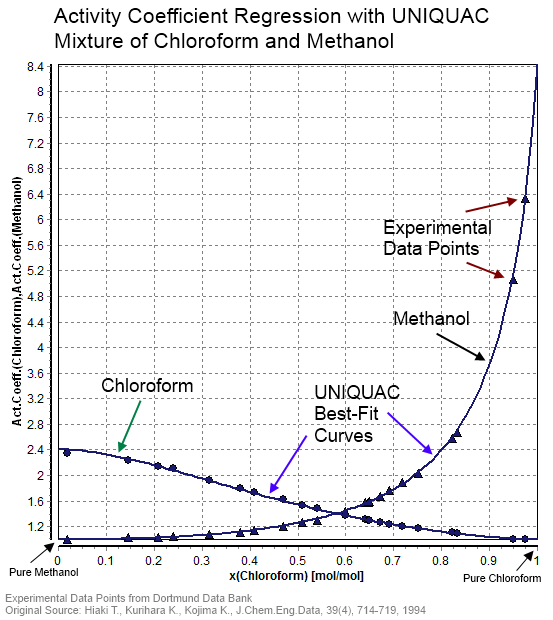
Activity Coefficient
In thermodynamics, an activity coefficient is a factor used to account for deviation of a mixture of chemical substances from ideal behaviour. In an ideal mixture, the microscopic interactions between each pair of chemical species are the same (or macroscopically equivalent, the enthalpy change of solution and volume variation in mixing is zero) and, as a result, properties of the mixtures can be expressed directly in terms of simple concentrations or partial pressures of the substances present e.g. Raoult's law. Deviations from ideality are accommodated by modifying the concentration by an ''activity coefficient''. Analogously, expressions involving gases can be adjusted for non-ideality by scaling partial pressures by a fugacity coefficient. The concept of activity coefficient is closely linked to that of activity in chemistry. Thermodynamic definition The chemical potential, \mu_\mathrm, of a substance B in an ideal mixture of liquids or an ideal solution is given by :\mu_ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from CT and PET scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft-tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, though "Open" MRI designs mostly relieve this. Additionally, implants and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentration Cell
In battery technology, a concentration cell is a limited form of a galvanic cell that has two equivalent half-cells of the same composition differing only in concentrations. One can calculate the potential developed by such a cell using the Nernst equation.Almost any textbook on physical chemistry, e.g. by I. N. Levine or P. W. Atkins, and also many general chemistry texts. A concentration cell produces a small voltage as it attempts to reach chemical equilibrium, which occurs when the concentration of reactant in both half-cells are equal. Because an order of magnitude concentration difference produces less than 60 millivolts at room temperature, concentration cells are not typically used for energy storage. A concentration cell generates electricity from the reduction in the thermodynamic free energy of the electrochemical system as the difference in the chemical concentrations in the two half-cells is reduced. The same reaction occurs in the half-cells but in opposite direction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromophenol Blue
Bromophenol blue (3′,3″,5′,5″-tetrabromophenolsulfonphthalein, BPB), albutest is used as a pH indicator, an electrophoretic color marker, and a dye. It can be prepared by slowly adding excess bromine to a hot solution of phenolsulfonphthalein in glacial acetic acid. Acid–base indicator As an acid–base indicator, its useful range lies between pH 3.0 and 4.6. It changes from yellow at pH 3.0 to blue at pH 4.6; this reaction is reversible. Bromophenol blue is structurally related to phenolphthalein (a popular indicator). Color marker Bromophenol is also used as a colour marker to monitor the process of agarose gel electrophoresis and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Since bromophenol blue carries a slight negative charge at moderate pH, it will migrate in the same direction as DNA or protein in a gel; the rate at which it migrates varies according to gel density and buffer composition, but in a typical 1% agarose gel in a 1X TAE buffer or TBE buff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid-base Indicator
A pH indicator is a halochromic chemical compound added in small amounts to a solution so the pH (acidity or basicity) of the solution can be determined visually or spectroscopically by changes in absorption and/or emission properties. Hence, a pH indicator is a chemical detector for hydronium ions (H3O+) or hydrogen ions (H+) in the Arrhenius model. Normally, the indicator causes the color of the solution to change depending on the pH. Indicators can also show change in other physical properties; for example, olfactory indicators show change in their odor. The pH value of a neutral solution is 7.0 at 25°C ( standard laboratory conditions). Solutions with a pH value below 7.0 are considered acidic and solutions with pH value above 7.0 are basic. Since most naturally occurring organic compounds are weak electrolytes, such as carboxylic acids and amines, pH indicators find many applications in biology and analytical chemistry. Moreover, pH indicators form one of the three main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadmium Chloride
Cadmium chloride is a white crystalline compound of cadmium and chloride, with the formula CdCl2. This salt is a hygroscopic solid that is highly soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol. The crystal structure of cadmium chloride (described below), is a reference for describing other crystal structures. Also known are CdCl2•H2O and CdCl2•5H2O. Structure Cadmium chloride forms a layered structure consisting of octahedral Cd2+ centers linked with chloride ligands. Cadmium iodide, CdI2, has a similar structure, but the iodide ions are arranged in a HCP lattice, whereas in CdCl2 the chloride ions are arranged in a CCP lattice.N. N. Greenwood, A. Earnshaw, ''Chemistry of the Elements'', 2nd ed., Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, UK, 1997. Chemical properties Cadmium chloride dissolves well in water and other polar solvents. It is a mild Lewis acid. :CdCl2 + 2 Cl− → dCl4sup>2− Solutions of equimolar cadmium chloride and potassium chloride give potassium cadmium trichlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula HA, to dissociate into a proton, H+, and an anion, A-. The dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions .... It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical. History In the early tenth century, the Persian physician and alchemist Abu Bakr al-Razi ( 865–925, Latin: Rhazes) conducted experiments with sal ammoniac (ammonium chloride) and vitriol (hydrated sulfates of various metals), which he distilled together, thus producing the gas hydrogen chloride. In doing so, al-Razi may have stumbled upon a primitive method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)