|
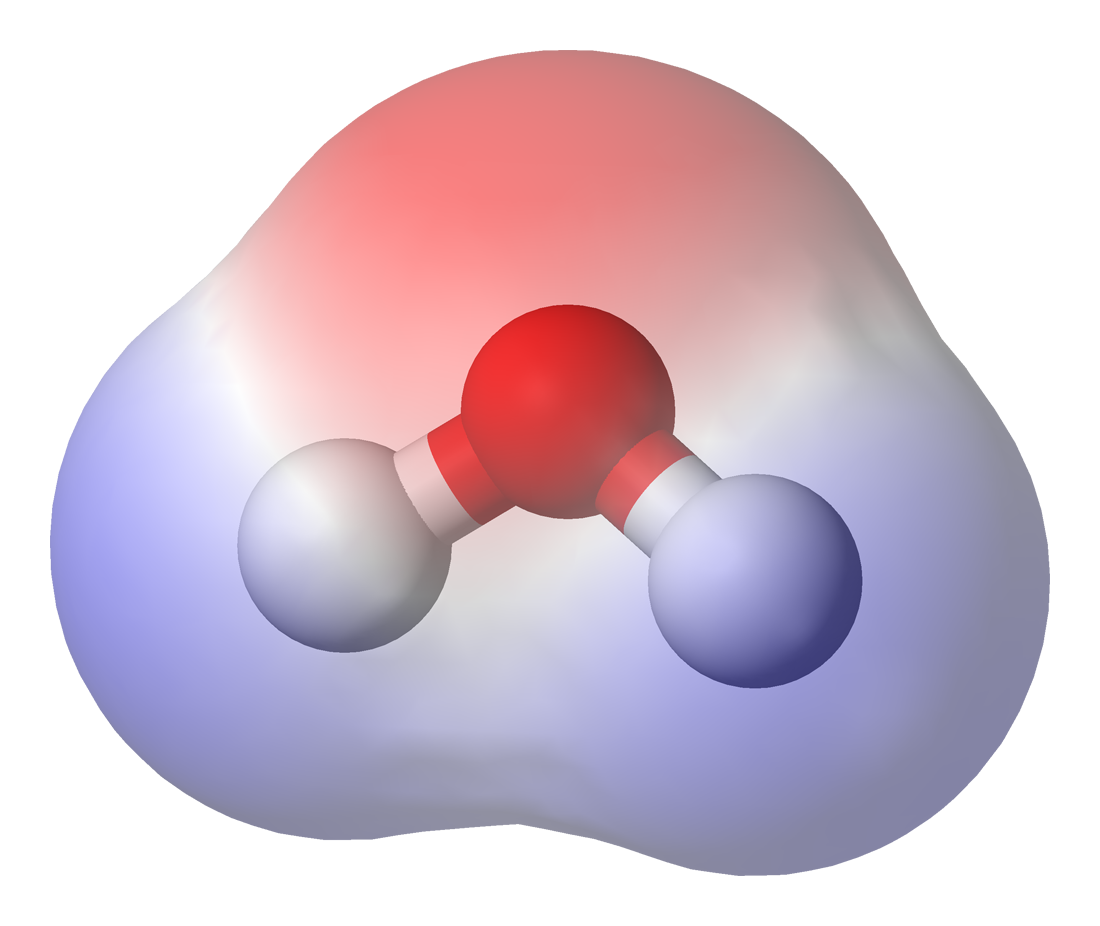
Iodine Monochloride
Iodine monochloride is an interhalogen compound with the formula . It is a red-brown chemical compound that melts near room temperature. Because of the difference in the electronegativity of iodine and chlorine, this molecule is highly polar and behaves as a source of I+. Preparation Iodine monochloride is produced simply by combining the halogens in a 1:1 molar ratio, according to the equation : When chlorine gas is passed through iodine crystals, one observes the brown vapor of iodine monochloride. Dark brown iodine monochloride liquid is collected. Excess chlorine converts iodine monochloride into iodine trichloride in a reversible reaction: : Polymorphs has two polymorphs; α-ICl, which exists as black needles (red by transmitted light) with a melting point of 27.2 °C, and β-ICl, which exists as black platelets (red-brown by transmitted light) with a melting point 13.9 °C.Brisbois, R. G.; Wanke, R. A.; Stubbs, K. A.; Stick, R. V. "Iodine Monochloride" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the substance and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine Monobromide
Iodine monobromide is an interhalogen compound with the chemical symbol IBr. It is a dark red solid that melts near room temperature. Like iodine monochloride, IBr is used in some types of iodometry. It serves as a source of I+. Its Lewis acid properties are compared with those of ICl and I2 in the ECW model. It can form CT adducts with Lewis donors. Synthesis Iodine monobromide is formed when iodine and bromine Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table ( halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a simi ... are combined in a chemical reaction: :I2 + Br2 → 2 IBr : References Iodine compounds Interhalogen compounds Diatomic molecules Bromides {{inorganic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Group
In mathematics, physics and chemistry, a space group is the symmetry group of an object in space, usually in three dimensions. The elements of a space group (its symmetry operations) are the rigid transformations of an object that leave it unchanged. In three dimensions, space groups are classified into 219 distinct types, or 230 types if chiral copies are considered distinct. Space groups are discrete cocompact groups of isometries of an oriented Euclidean space in any number of dimensions. In dimensions other than 3, they are sometimes called Bieberbach groups. In crystallography, space groups are also called the crystallographic or Fedorov groups, and represent a description of the symmetry of the crystal. A definitive source regarding 3-dimensional space groups is the ''International Tables for Crystallography'' . History Space groups in 2 dimensions are the 17 wallpaper groups which have been known for several centuries, though the proof that the list was complete was only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melting Point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at a standard pressure such as 1 atmosphere or 100 kPa. When considered as the temperature of the reverse change from liquid to solid, it is referred to as the freezing point or crystallization point. Because of the ability of substances to supercool, the freezing point can easily appear to be below its actual value. When the "characteristic freezing point" of a substance is determined, in fact, the actual methodology is almost always "the principle of observing the disappearance rather than the formation of ice, that is, the melting point." Examples For most substances, melting and freezing points are approximately equal. For example, the melting point ''and'' freezing point of mercury is . How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymorphism (materials Science)
In materials science, polymorphism describes the existence of a solid material in more than one form or crystal structure. Polymorphism is a form of isomerism. Any crystalline material can exhibit the phenomenon. Allotropy refers to polymorphism for chemical elements. Polymorphism is of practical relevance to pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, pigments, dyestuffs, foods, and explosives. According to IUPAC, a polymorphic transition is "A reversible transition of a solid crystalline phase at a certain temperature and pressure (the inversion point) to another phase of the same chemical composition with a different crystal structure." According to McCrone, polymorphs are "different in crystal structure but identical in the liquid or vapor states." Materials with two polymorphs are called dimorphic, with three polymorphs, trimorphic, etc. Examples Many compounds exhibit polymorphism. It has been claimed that "every compound has different polymorphic forms, and that, in general, the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine Trichloride
Iodine trichloride is an interhalogen compound of iodine and chlorine. It is bright yellow but upon time and exposure to light it turns red due to the presence of elemental iodine. In the solid state is present as a planar dimer I2Cl6, with two bridging Cl atoms. It can be prepared by reacting iodine with an excess of liquid chlorine at −70 °C. In the molten state it is conductive, which may indicate dissociation: :I2Cl6 + Iodine trichloride can be created by heating a mixture of liquid iodine and chlorine gas to 105 °C. It is an oxidizing agent An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or "Electron acceptor, accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ). In ot ..., capable of causing fire on contact with organic materials. References Iodine compounds Chlorides Interhalogen compounds Oxidizing agents {{inorganic-compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Polarity
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end. Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Molecules containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond dipoles cancel each other out by symmetry. Polar molecules interact through dipole–dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting and boiling points. Polarity of bonds Not all atoms attract electrons with the same force. The amount of "pull" an atom exerts on its electrons is called its electronegativity. Atoms with high electronegativitiessuch as fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogenexert a greater pull on electrons than atoms with lower electronegativities such as alkali metals and alkaline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Electronegativity#Pauling electronegativity, Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine. Chlorine played an important role in the experiments conducted by medieval Alchemy, alchemists, which commonly involved the heating of chloride Salt (chemistry), salts like ammonium chloride (sal ammoniac) and sodium chloride (common salt), producing various chemical substances containing chlorine such as hydrogen chloride, mercury(II) chloride (corrosive sublimate), and hydrochloric acid (in the form of ). However ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a violet gas at . The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek 'violet-coloured'. Iodine occurs in many oxidation states, including iodide (I−), iodate (), and the various periodate anions. It is the least abundant of the stable halogens, being the sixty-first most abundant element. As the heaviest essential mineral nutrient, iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities. The dominant producers of iodine today are Chile and Japan. Due to its high atomic number and ease of attachment to organic compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity, the more an atom or a substituent group attracts electrons. Electronegativity serves as a simple way to quantitatively estimate the bond energy, and the sign and magnitude of a bond's chemical polarity, which characterizes a bond along the continuous scale from covalent to ionic bonding. The loosely defined term electropositivity is the opposite of electronegativity: it characterizes an element's tendency to donate valence electrons. On the most basic level, electronegativity is determined by factors like the nuclear charge (the more protons an atom has, the more "pull" it will have on electrons) and the number and location ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Room Temperature
Colloquially, "room temperature" is a range of air temperatures that most people prefer for indoor settings. It feels comfortable to a person when they are wearing typical indoor clothing. Human comfort can extend beyond this range depending on humidity, air circulation and other factors. Food or beverages may be served at ''room temperature'', meaning neither heated nor cooled. In certain fields, like science and engineering, and within a particular context, ''room temperature'' can mean different agreed-upon ranges. In contrast, ''ambient temperature'' is the actual temperature, as measured by a thermometer, of the air (or other medium and surroundings) in any particular place. The ambient temperature (e.g. an unheated room in winter) may be very different from an ideal ''room temperature''. Comfort temperatures ''The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language'' identifies room temperature as around , while the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' states that it is "conv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melting
Melting, or fusion, is a physical process that results in the phase transition of a substance from a solid to a liquid. This occurs when the internal energy of the solid increases, typically by the application of heat or pressure, which increases the substance's temperature to the melting point. At the melting point, the ordering of ions or molecules in the solid breaks down to a less ordered state, and the solid "melts" to become a liquid. Substances in the molten state generally have reduced viscosity as the temperature increases. An exception to this principle is the element sulfur, whose viscosity increases in the range of 160 °C to 180 °C due to polymerization. Some organic compounds melt through mesophases, states of partial order between solid and liquid. First order phase transition From a thermodynamics point of view, at the melting point the change in Gibbs free energy ''∆G'' of the substances is zero, but there are non-zero changes in the enthalpy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |