|
Ioann (Archbishop Of Novgorod)
Ioann (Russian: Иоанн) was Archbishop of Novgorod the Great and Pskov from 1388 until his retirement in 1415. He is not to be confused with Archbishop Ilya, who ruled in the twelfth century, and who is often referred to as ''Ioann'' in hagiographic literature but was apparently called ''Ilya'' during his archiepiscopate. Ioann was elected by the veche with the blessings of his predecessor, Archbishop Aleksei in 1388 (Aleksei had retired to the Dereviatinskii Monastery north of Novgorod where he died in 1390). The main crisis Ioann faced during his archiepiscopate was the drawn-out dispute between Novgorod and Metropolitan Kiprian that dated to 1376. Kiprian was named the successor to Metropolitan Aleksei (d. 1378) but when he tried to gain recognition from Novgorod as the rightful successor in 1376, he was rebuffed. When he was finally accepted as the Metropolitan of Kiev and All Rus' by Moscow in 1390, he was still not allowed to hear appeals to the archbishop's court ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishop Of Novgorod
The Diocese of Novgorod (russian: Новгородская епархия) is one of the oldest offices in the Russian Orthodox Church. The medieval archbishops of Novgorod were among the most important figures in medieval Russian history and culture and their successors (as bishops, archbishops, or metropolitans) have continued to play significant roles in Russian history up to the present day. They patronized a significant number of churches in and around the city, (several of which can still be seen today), and their artistic and architectural embellishments influenced later Russian art and architecture; they also patronized chronicle-writing, a crucial source on medieval Russian history. The Republican period The office of bishop of Novgorod was created around the time of the Christianization of Rus' (988), although the chronicles give conflicting dates for its establishment ranging anywhere from 989 to 992. The first bishop, Ioakim Korsunianin (ca. 989-1030), built the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Sophia Cathedral In Novgorod
The Cathedral of Holy Wisdom (the Holy Wisdom, Holy Wisdom of God) in Veliky Novgorod is the cathedral church of the Archbishop of Novgorod, Metropolitan of Novgorod and the mother church of the Novgorodian Eparchy. History The 38-metre-high, five-domed, stone cathedral was built by Vladimir of Novgorod and Bishop Luka Zhidiata between 1045 and 1050 to replace an oaken cathedral built by Bishop Ioakim Korsunianin in the late tenth century (making it the oldest church building in Russia proper and, with the exception of the Zelenchuk churches, Arkhyz and Shoana Church, Shoana churches, the oldest building of any kind still in use in the country). It was consecrated by Bishop Luka Zhidiata (1035–1060) on September 14, in 1050 or 1052, the feast of the Feast of the Cross, Exaltation of the Cross. (A fresco just inside the south entrance depicts Sts. Constantine and Helena, who found the true cross in the fourth century; it is one of the oldest works of art in the cathedral and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishops And Metropolitans Of Novgorod
In Christian denomination A Christian denomination is a distinct religious body within Christianity that comprises all church congregations of the same kind, identifiable by traits such as a name, particular history, organization, leadership, theological doctrine, worsh ...s, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdiocese (#Non-metropolitan_archiepiscopal_sees, with some exceptions), or are otherwise granted a Titular bishop, titular archbishopric. In others, such as the Lutheranism, Lutheran Church of Sweden and the Church of England, the title is borne by the leader of the denomination. Etymology The word archbishop () comes via the Latin ''archiepiscopus.'' This in turn comes from the Greek language, Greek , which has as components the etymons -, meaning 'chief', , 'over', and , 'seer'. Early hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valaam
Valaam (Russian: Валаам or Валаамский архипелаг, also known by the Finnish name Valamo) is an archipelago in the northern portion of Lake Ladoga, lying within the Republic of Karelia, Russian Federation. The total area of its more than 50 islands is 36 km². The largest island is also called Valaam. Other known islands are: Skitsky (second by size), Lembos, Sviatoy, Bayonny, Moskovsky, Predtechensky, Nikonovsky, Divny, Emelyanov, Oboronny, Goly, Savvaty's, Zosima's, Skalisty, Lukovy, Ovsiany, Rzhanoi, Nikolsky. It is best known as the site of the 14th century Valaam Monastery on Valaam Island and for its natural environment.Selby p. 175 In the 12th century, the islands were a part of the Novgorod Republic. In the 17th century, they were captured by Sweden during the Time of Troubles, but Russia reconquered them less than a century later. When the Grand Duchy of Finland was set up in the early 19th century as an autonomous part of the Russian Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karelians
Karelians ( krl, karjalaižet, karjalazet, karjalaiset, Finnish: , sv, kareler, karelare, russian: Карелы) are a Finnic ethnic group who are indigenous to the historical region of Karelia, which is today split between Finland and Russia. Karelians living in Russian Karelia are considered a distinct ethnic group closely related to Finnish Karelians, who are considered a subset of Finns. This distinction historically arose from Karelia having been fought over and eventually split between Sweden and Novgorod, resulting in Karelians being under different cultural spheres. In Russia, Karelians mostly live in the Republic of Karelia, where they are the designated ethnic group, and in other adjacent north-western parts of the country. They traditionally speak the Karelian language and are Eastern Orthodox Christians. There are also significant Karelian enclaves in the Tver and Novgorod oblasts, as some Karelians migrated to those areas after the Russo-Swedish War of 1656-16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valaam Monastery
The Valaam Monastery (russian: Валаамский монастырь; Finnish version: ''Valamo Monastery'') is a stauropegic Orthodox monastery in Russian Karelia, located on Valaam, the largest island in Lake Ladoga, the largest lake in Europe. History It is not clear when the monastery was founded, as the cloister is not mentioned in documents before the 16th century. Dates from the 10th to the 15th centuries having been suggested. According to one tradition, the monastery was founded by a 10th-century Greek monk, Sergius of Valaam, and his Karelian companion, Herman of Valaam. Heikki Kirkinen inclines to date the foundation of the monastery to the 12th century. Contemporary historians consider even this date too early. According to the scholarly consensus, the monastery was founded at some point towards the end of the 14th century. John H. Lind and Michael C. Paul date the founding to between 1389 and 1393 based on various sources, including the "Tale of the Valaamo Monas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vyborg
Vyborg (; rus, Вы́борг, links=1, r=Výborg, p=ˈvɨbərk; fi, Viipuri ; sv, Viborg ; german: Wiborg ) is a town in, and the administrative center of, Vyborgsky District in Leningrad Oblast, Russia. It lies on the Karelian Isthmus near the head of the Vyborg Bay, to the northwest of St. Petersburg, east of the Finnish capital Helsinki, and south of Russia's border with Finland, where the Saimaa Canal enters the Gulf of Finland. The population of Vyborg is as follows: Located in the boundary zone between the East Slavic/Russian and Finnish worlds, formerly well known as one of the few medieval towns in Finland, Vyborg has changed hands several times in history, most recently in 1944 when the Soviet Union captured it from Finland during World War II. Finland evacuated the entire population of the city and resettled them within the rest of the country. On March 25, 2010, Dmitry Medvedev named Vyborg the "City of Military Glory". In Russia, a city can be award ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Dvina
, image = dvina.jpg , image_size = , image_caption = Northern Dvina starts as the confluence of Yug River (on left) and Sukhona River (on top) near Veliky Ustyug (photo 2001) , source1 = Confluence of Yug and Sukhona , source1_location = , mouth_location = Dvina Bay , subdivision_type1 = Country , subdivision_name1 = Russia , length = , source1_elevation = , mouth_elevation = , discharge1_avg = , basin_size = The Northern Dvina (russian: Се́верная Двина́, ; kv, Вы́нва / Výnva) is a river in northern Russia flowing through the Vologda Oblast and Arkhangelsk Oblast into the Dvina Bay of the White Sea. Along with the Pechora River to the east, it drains most of Northwest Russia into the Arctic Ocean. It should not be confused with Western Dvina. The principal tributaries of the Northern Dvina are the Vychegda (right), the Vaga (left), and the Pinega ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilya (Archbishop Of Novgorod)
Ilya of Novgorod, also known as Ioann (John) of Novgorod (russian: Иоанн Новгородский, his name upon entering the Great Schema and the name by which he is known in Russian Orthodox hagiography), was Archbishop of Novgorod from 1165 to his death in 1186. Life The son of a priest, Ilya was himself priest of the Church of St. Blaise, south of the Novgorod Kremlin. The church was destroyed, rebuilt in 1407, destroyed during the Second World War and rebuilt again. Ilya was probably his first monastic name, and his baptismal name is not known. Ilya was appointed bishop of Novgorod by Metropolitan Ioann of Kiev in 1165. He was the first to hold the title of archbishop in Novgorod after the office was elevated to the archiepiscopal dignity a few months later. Niphont held the title as a personal honor. Ilya carried out a number of construction projects in Novgorod along with his brother, Gavril (also known as Grigorii), who succeeded him as archbishop (1186–119 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boyar
A boyar or bolyar was a member of the highest rank of the Feudalism, feudal nobility in many Eastern European states, including Kievan Rus', Bulgarian Empire, Bulgaria, Russian nobility, Russia, Boyars of Moldavia and Wallachia, Wallachia and Moldavia, and later Romania, Lithuanian nobility, Lithuania and among Baltic German nobility, Baltic Germans. Boyars were second only to the ruling knyaz, princes (in Bulgaria, tsars) from the 10th century to the 17th century. The rank has lived on as a surname in Russia, Finland, Lithuania and Latvia where it is spelled ''Pajari'' or ''Bajārs/-e''. Etymology Also known as bolyar; variants in other languages include bg, боляр or ; rus, боя́рин, r=boyarin, p=bɐˈjærʲɪn; ; ro, boier, ; and el, βογιάρος. The title Boila is predecessor or old form of the title Bolyar (the Bulgarian language, Bulgarian word for Boyar). Boila was a title worn by some of the Bulgars, Bulgar aristocrats (mostly of regional governors a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
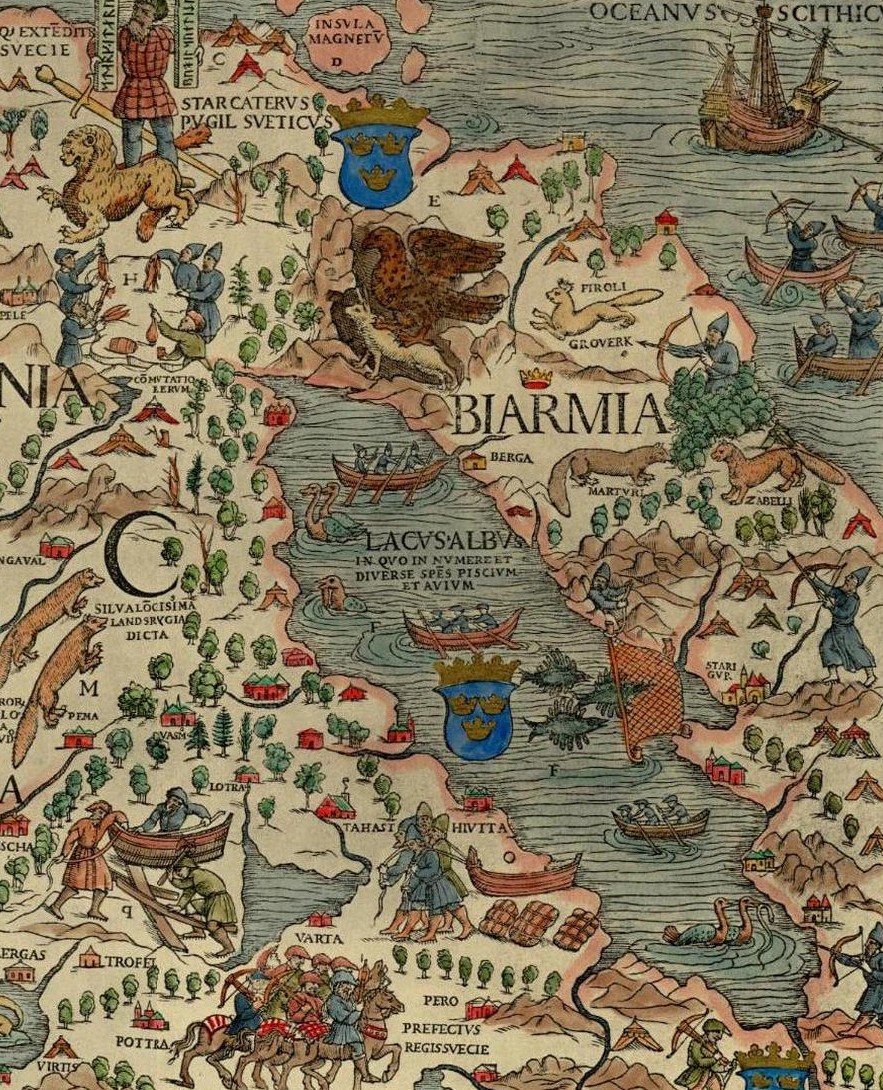
Dvina Land
Bjarmaland (also spelt ''Bjarmland'' and ''Bjarmia''; Latin: ''Biarmia''; Old English: ''Beormaland,'' Komi: Биармия ''Biarmia,'' Old Permic: 𐍑𐍙𐍐𐍒𐍜𐍙𐍐) was a territory mentioned in Norse sagas since the Viking Age and in geographical accounts until the 16th century. The term is usually seen to have referred to the southern shores of the White Sea and the basin of the Northern Dvina River (''Vienanjoki'' in Finnish) as well as, presumably, some of the surrounding areas. Today, those territories comprise a part of the Arkhangelsk Oblast of Russia, as well as the Kola Peninsula. Norse voyagers in Bjarmaland According to the '' Voyage of Ohthere'' (c. 890 CE), the Norwegian merchant Ottar (Ohthere) reported to king Alfred the Great that he had sailed for 15 days along the northern coast and then southwards, finally arriving at a great river, probably the Northern Dvina. At the estuary of the river dwelt the ''Beormas'', who unlike the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

_-_contrast.jpg)