|
Internet In The United Kingdom
The United Kingdom has been involved with the Internet throughout its origins and development. The telecommunications infrastructure in the United Kingdom provides Internet access to businesses and home users in various forms, including fibre, cable, DSL, wireless and mobile. The share of households with Internet access in the United Kingdom grew from 9 percent in 1998 to 93 percent in 2019. Virtually all adults aged 16 to 44 years in the UK were recent internet users (99%) in 2019, compared with 47% of adults aged 75 years and over; in aggregate, the third-highest in Europe. Online shoppers in the UK spend more per household than consumers in any other country. Internet bandwidth per Internet user was the seventh highest in the world in 2016, and average and peak internet connection speeds were top-quartile in 2017. Internet use in the United Kingdom doubled in 2020. The Internet country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for the United Kingdom is .uk and is run by Nominet. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as Computer program, programs. These programs enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. A computer system is a nominally complete computer that includes the Computer hardware, hardware, operating system (main software), and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation. This term may also refer to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of Programmable logic controller, industrial and Consumer electronics, consumer products use computers as control systems. Simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls are included, as are factory devices like industrial robots and computer-aided design, as well as general-purpose devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Datagram
A datagram is a basic transfer unit associated with a packet-switched network. Datagrams are typically structured in header and payload sections. Datagrams provide a connectionless communication service across a packet-switched network. The delivery, arrival time, and order of arrival of datagrams need not be guaranteed by the network. History In the early 1970s, the term ''datagram'' was created by combining the words ''data'' and ''telegram'' by the CCITT rapporteur on packet switching, Halvor Bothner-By. While the word was new, the concept had already a long history. In 1962, Paul Baran described, in a RAND Corporation report, a hypothetical military network having to resist a nuclear attack. Small standardized "message blocks", bearing source and destination addresses, were stored and forwarded in computer nodes of a highly redundant meshed computer network. "The network user who has called up a "virtual connection" to an end station and has transmitted messages ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger Scantlebury
Roger Anthony Scantlebury (born August 1936) is a British computer scientist who worked at the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) and later at Logica. Scantlebury participated in pioneering work to develop packet switching and associated communication protocols at the NPL in the late 1960s. He proposed the use of the technology in the ARPANET, the forerunner of the Internet, at the inaugural Symposium on Operating Systems Principles in 1967. During the 1970s, he was an active member of international working groups that developed concepts for the interconnection of computer networks. Early life Roger Scantlebury was born in Ealing in 1936. Career National Physical Laboratory Scantlebury worked at the National Physical Laboratory in south-west London, in collaboration with the National Research Development Corporation (NRDC). His early work was on the Automatic Computing Engine and English Electric DEUCE computers. Following this he worked with Donald Davies on his pioneering p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
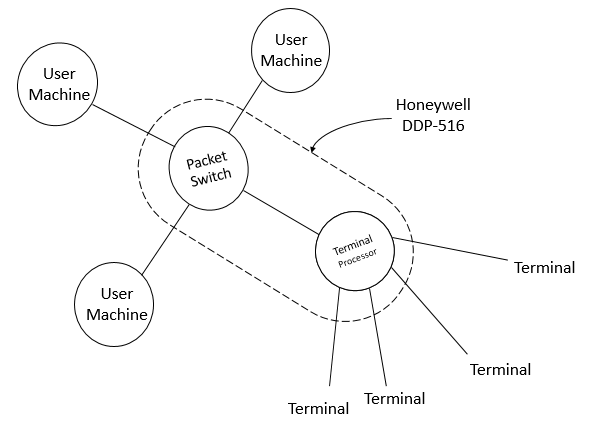
NPL Network
The NPL network, or NPL Data Communications Network, was a local area computer network operated by a team from the National Physical Laboratory in London that pioneered the concept of packet switching. Based on designs first conceived by Donald Davies in 1965, development work began in 1968. Elements of the first version of the network, the Mark I, became operational during 1969 then fully operational in January 1970, and the Mark II version operated from 1973 until 1986. The NPL network and the ARPANET in the United States were the first two computer networks that implemented packet switching and the NPL network was the first to use high-speed links. Origins In 1965, Donald Davies, who was later appointed to head of the NPL Division of Computer Science, proposed a commercial national data network based on packet switching in ''Proposal for the Development of a National Communications Service for On-line Data Processing''. After the proposal was not taken up nationally, during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Federation For Information Processing
The International Federation for Information Processing (IFIP) is a global organisation for researchers and professionals working in the field of computing to conduct research, develop standards and promote information sharing. Established in 1960 under the auspices of UNESCO, IFIP is recognised by the United Nations and links some 50 national and international societies and academies of science with a total membership of over half a million professionals. IFIP is based in Laxenburg, Austria and is an international, non-governmental organisation that operates on a non-profit basis. Overview IFIP activities are coordinated by 13 Technical Committees (TCs) which are organised into more than 100 Working Groups (WGs), bringing together over 3,500 ICT professionals and researchers from around the world to conduct research, develop standards and promote information sharing. Each TC covers a particular aspect of computing and related disciplines, as detailed below. IFIP actively prom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time-sharing
In computing, time-sharing is the sharing of a computing resource among many users at the same time by means of multiprogramming and multi-tasking.DEC Timesharing (1965), by Peter Clark, The DEC Professional, Volume 1, Number 1 Its emergence as the prominent model of computing in the 1970s represented a major technological shift in the history of computing. By allowing many users to interact concurrently with a single computer, time-sharing dramatically lowered the cost of providing computing capability, made it possible for individuals and organizations to use a computer without owning one, and promoted the interactive use of computers and the development of new interactive applications. History Batch processing The earliest computers were extremely expensive devices, and very slow in comparison to later models. Machines were typically dedicated to a particular set of tasks and operated by control panels, the operator manually entering small programs via switches in order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Strachey
Christopher S. Strachey (; 16 November 1916 – 18 May 1975) was a British computer scientist. He was one of the founders of denotational semantics, and a pioneer in programming language design and computer time-sharing.F. J. Corbató, et al., The Compatible Time-Sharing System A Programmer's Guide' (MIT Press, 1963) . "the first paper on time-shared computers by C. Strachey at the June 1959 UNESCO Information Processing conference" He has also been credited as possibly being the first developer of a video game. He was a member of the Strachey family, prominent in government, arts, administration, and academia. Early life and education Christopher Strachey was born on 16 November 1916 to Oliver Strachey and Rachel (Ray) Costelloe in Hampstead, England. Oliver Strachey was the son of Richard Strachey and the great grandson of Sir Henry Strachey, 1st Baronet. His elder sister was the writer Barbara Strachey. In 1919, the family moved to 51 Gordon Square. The Stracheys belonge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biographical Memoirs Of Fellows Of The Royal Society
The ''Biographical Memoirs of Fellows of the Royal Society'' is an academic journal on the history of science published annually by the Royal Society. It publishes obituaries of Fellows of the Royal Society. It was established in 1932 as ''Obituary Notices of Fellows of the Royal Society'' and obtained its current title in 1955, with volume numbering restarting at 1. Prior to 1932, obituaries were published in the ''Proceedings of the Royal Society''. The memoirs are a significant historical record and most include a full bibliography of works by the subjects. The memoirs are often written by a scientist of the next generation, often one of the subject's own former students, or a close colleague. In many cases the author is also a Fellow. Notable biographies published in this journal include Albert Einstein, Alan Turing, Bertrand Russell, Claude Shannon, Clement Attlee, Ernst Mayr, and Erwin Schrödinger. Each year around 40 to 50 memoirs of deceased Fellows of the Royal Soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald Davies
Donald Watts Davies, (7 June 1924 – 28 May 2000) was a Welsh computer scientist who was employed at the UK National Physical Laboratory (NPL). In 1965 he conceived of packet switching, which is today the dominant basis for data communications in computer networks worldwide. Davies proposed a commercial national data network in the United Kingdom and designed and built the local-area NPL network to demonstrate the technology. Many of the wide-area packet-switched networks built in the 1970s were similar "in nearly all respects" to his original 1965 design. The ARPANET project credited Davies for his influence, which was key to the development of the Internet. Davies' work was independent of the work of Paul Baran in the United States who had a similar idea in the early 1960s, and who also provided input to the ARPANET project, after his work was highlighted by Davies' team. Early life Davies was born in Treorchy in the Rhondda Valley, Wales. His father, a clerk at a coal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher, and theoretical biologist. Turing was highly influential in the development of theoretical computer science, providing a formalisation of the concepts of algorithm and computation with the Turing machine, which can be considered a model of a general-purpose computer. He is widely considered to be the father of theoretical computer science and artificial intelligence. Born in Maida Vale, London, Turing was raised in southern England. He graduated at King's College, Cambridge, with a degree in mathematics. Whilst he was a fellow at Cambridge, he published a proof demonstrating that some purely mathematical yes–no questions can never be answered by computation and defined a Turing machine, and went on to prove that the halting problem for Turing machines is undecidable. In 1938, he obtained his PhD from the Department of Mathemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Physical Laboratory (United Kingdom)
The National Physical Laboratory (NPL) is the national measurement standards laboratory of the United Kingdom. It is one of the most extensive government laboratories in the UK and has a prestigious reputation for its role in setting and maintaining physical standards for British industry. Founded in 1900, it is one of the oldest metrology institutes in the world. Research and development work at NPL has contributed to the advancement of many disciplines of science, including the development early computers in the late 1940s and 1950s, construction of the first accurate atomic clock in 1955, and the invention and pioneering implementation of packet switching in the 1960s, which is today one of the fundamental technologies of the Internet. The former heads of NPL include many individuals who were pillars of the British scientific establishment. NPL is based at Bushy Park in Teddington, west London. It is under the management of the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |