|
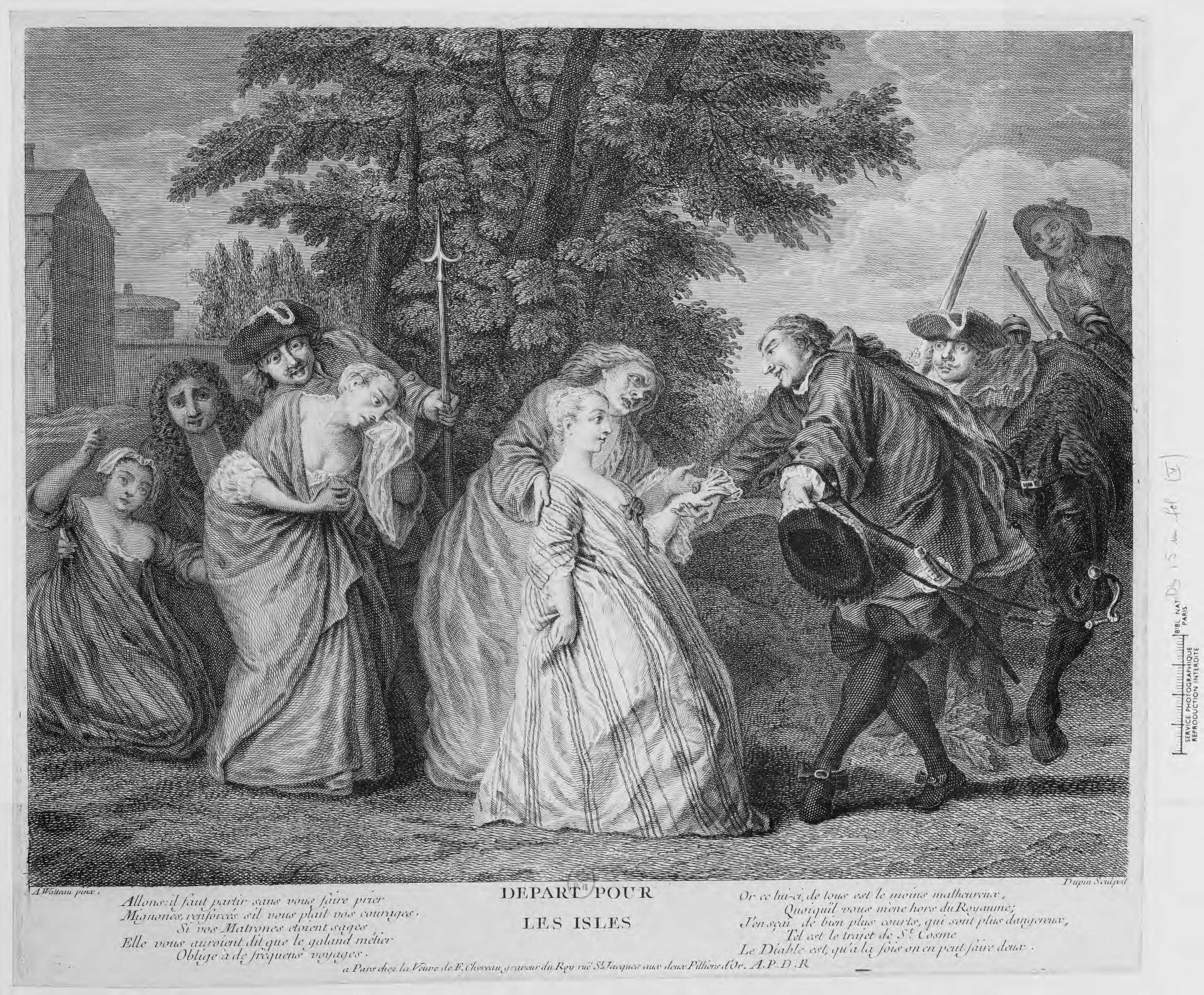
International Marriage Agency
A mail-order bride is a woman who lists herself in catalogs and is selected by a man for marriage. In the twentieth century, the trend was primarily towards women living in developing countries seeking men in more developed nations. The majority of the women making use of these services in the late twentieth-century and early twenty-first-century are from East and Southeast Asia, the countries of the former Eastern Bloc, and to a lesser extent Latin America. Since the collapse of the Soviet Union, large numbers of eastern European women have advertised themselves in such a way, primarily from Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, Lithuania, Latvia, Georgia and Moldova. Men who list themselves in such publications are referred to as "mail-order husbands", although this is much less common. The term ''mail-order bride'' is both criticized by owners (and customers) of international marriage agencies and used by them as an easily recognizable term. International marriage agency An international ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developing Country
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreement on which countries fit this category. The term low and middle-income country (LMIC) is often used interchangeably but refers only to the economy of the countries. The World Bank classifies the world's economies into four groups, based on gross national income per capita: high, upper-middle, lower-middle, and low income countries. Least developed countries, landlocked developing countries and small island developing states are all sub-groupings of developing countries. Countries on the other end of the spectrum are usually referred to as high-income countries or developed countries. There are controversies over this term's use, which some feel it perpetuates an outdated concept of "us" and "them". In 2015, the World Bank declared that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virginia Company
The Virginia Company was an English trading company chartered by King James I on 10 April 1606 with the object of colonizing the eastern coast of America. The coast was named Virginia, after Elizabeth I, and it stretched from present-day Maine to the Carolinas. The company's shareholders were Londoners, and it was distinguished from the Plymouth Company, which was chartered at the same time and composed largely of gentlemen from Plymouth, England. The biggest trade breakthrough resulted after adventurer and colonist John Rolfe introduced several sweeter strains of tobacco from the Caribbean. These yielded a more appealing product than the harsh-tasting tobacco native to Virginia. Cultivation of Rolfe's new tobacco strains produced a strong commodity crop for export for the London Company and other early English colonies and helped to balance a national trade deficit with Spain. The company failed in 1624, following the widespread destruction of the Great Massacre of 1622 by in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coolie
A coolie (also spelled koelie, kuli, khuli, khulie, cooli, cooly, or quli) is a term for a low-wage labourer, typically of South Asian or East Asian descent. The word ''coolie'' was first popularized in the 16th century by European traders across Asia, and by the 18th century would refer to migrant Indian indentured labourers, and by the 19th century during the British colonial era, would gain a new definition of the systematic transportation and employment of Asian laborers via employment contracts on sugar plantations that had been formerly worked by enslaved Africans. The word has had a variety of other implications and is sometimes regarded as offensive or a pejorative, depending upon the historical and geographical context; in India, its country of origin, it is still considered a derogatory slur. It is similar, in many respects, to the Spanish term peón, although both terms are used in some countries with different implications. The word originated in the 17th-centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Frontier
The American frontier, also known as the Old West or the Wild West, encompasses the geography, history, folklore, and culture associated with the forward wave of United States territorial acquisitions, American expansion in mainland North America that began with European colonization of the Americas, European colonial settlements in the early 17th century and ended with the admission of the last few western territories as states in 1912 (except Alaska, which was not Alaska Statehood Act, admitted into the Union until 1959). This era of massive migration and settlement was particularly encouraged by President Thomas Jefferson following the Louisiana Purchase, giving rise to the Expansionism, expansionist attitude known as "Manifest destiny, Manifest Destiny" and the historians' "Frontier thesis, Frontier Thesis". The legends, historical events and folklore of the American frontier have embedded themselves into United States culture so much so that the Old West, and the Western ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonial Brazil
Colonial Brazil ( pt, Brasil Colonial) comprises the period from 1500, with the arrival of the Portuguese, until 1815, when Brazil was elevated to a kingdom in union with Portugal as the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. During the early 300 years of Brazilian colonial history, the economic exploitation of the territory was based first on brazilwood (''pau brazil'') extraction (16th century), which gave the territory its name; sugar production (16th–18th centuries); and finally on gold and diamond mining (18th century). Slaves, especially those brought from Africa, provided most of the work force of the Brazilian export economy after a brief period of Indian slavery to cut brazilwood. In contrast to the neighboring Spanish possessions, which had several viceroyalties with jurisdiction initially over New Spain (Mexico) and Peru, and in the eighteenth century expanded to viceroyalties of the Río de la Plata and New Granada, the Portuguese colony of Brazil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire ( pt, Império Português), also known as the Portuguese Overseas (''Ultramar Português'') or the Portuguese Colonial Empire (''Império Colonial Português''), was composed of the overseas colonies, factories, and the later overseas territories governed by Portugal. It was one of the longest-lived empires in European history, lasting almost six centuries from the conquest of Ceuta in North Africa, in 1415, to the transfer of sovereignty over Macau to China in 1999. The empire began in the 15th century, and from the early 16th century it stretched across the globe, with bases in North and South America, Africa, and various regions of Asia and Oceania. The Portuguese Empire originated at the beginning of the Age of Discovery, and the power and influence of the Kingdom of Portugal would eventually expand across the globe. In the wake of the Reconquista, Portuguese sailors began exploring the coast of Africa and the Atlantic archipelagos in 1418–1419, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Órfãs Do Rei
The Órfãs do Rei (, ''orphans of the king'') were Portuguese girl orphans who were sent from Portugal to overseas colonies during the Portuguese Empire as part of Portugal's colonization efforts. The orphans were married to native rulers or Portuguese settlers. Purpose and practicalities Orfãs do Rei translates to "Orphans of the King", and they were all girls. Their fathers were Portuguese men who died in battle for the king. They were sent to the colonies of the Portuguese Empire. The Asian colonies contained more Portuguese females than was previously thought. Bernard Sta Maria wrote that "From 1545, King John III began to send to India (and the Far East) with all pomp and distinction many young Portuguese women known as 'Orphans of the Queen' to be married with local young men." Both noble and non-noble girls were in the ''órfãs do rei''. Since these girls were specifically designated as the "King's", the Portuguese government paid for their care and upbringing before and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Ship Pélican (1702)
''Pélican'' was a ship in French service for colonial duty in the transport of colonists to French North America. History In January 1704, the ship left Loire, France for La Mobile, La Louisiane, New France. The ship that brought additional pioneers and yellow fever to the French colony of the original Mobile site, arriving in August 1704. The ship brought filles à la casquette to help found the colony with womenfolk for the menfolk; also called Pelican Girls, after the ship they were transported on; and Casket Girls or Cassettes, for the boxes, called casquettes, used to carry their belongings. The yellow fever had been acquired in a stopover in Cuba on the way to Mobile. References See also * French ship Pélican (1693) Pelican Pelicans (genus ''Pelecanus'') are a genus of large water birds that make up the family Pelecanidae. They are characterized by a long beak and a large throat pouch used for catching prey and draining water from the scooped-up contents bef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casquette Girl
A casquette girl (french: fille à la cassette) but also known historically as a casket girl or a Pelican girl, was a woman brought from France to the French colonies of Louisiana to marry. The name derives from the small chests, known as casquettes, in which they carried their clothes.Higginbotham, Jay. ''Old Mobile: Fort Louis de la Louisiane, 1702-1711'', pp.106–07. Museum of the City of Mobile, 1977. . History The French policy of sending young women known as King's Daughters (french: filles du roi) to their colonies for marriage goes back to the 17th-century. Young women were sent to Canada, Louisiana and the French West Indies. Later women, called correction girls, were supplied to the colonists by raking the streets of Paris for ''undesirables'', or by emptying the houses of correction. France also sent women convicted along with their debtor husbands, and in 1719, deported 209 women felons "who were of a character to be sent to the French settlement in Louisiana.". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louisiana (New France)
Louisiana (french: La Louisiane; ''La Louisiane Française'') or French Louisiana was an administrative district of New France. Under French control from 1682 to 1769 and 1801 (nominally) to 1803, the area was named in honor of King Louis XIV, by French explorer René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de la Salle. It originally covered an expansive territory that included most of the drainage basin of the Mississippi River and stretched from the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico and from the Appalachian Mountains to the Rocky Mountains. Louisiana included two regions, now known as Upper Louisiana (), which began north of the Arkansas River, and ''Lower Louisiana'' (). The U.S. state of Louisiana is named for the historical region, although it is only a small part of the vast lands claimed by France.La Louisiane française 1682-1803 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Canadians
French Canadians (referred to as Canadiens mainly before the twentieth century; french: Canadiens français, ; feminine form: , ), or Franco-Canadians (french: Franco-Canadiens), refers to either an ethnic group who trace their ancestry to French people, French colonists who settled in Canada (New France), Canada beginning in the 17th century or to French-speaking or Francophone Canadians of any ethnic origin. During the 17th century, French settlers originating mainly from the west and north of France settled Canada (New France), Canada. It is from them that the French Canadian ethnicity was born. During the 17th to 18th centuries, French Canadians expanded across North America and colonized various regions, cities, and towns. As a result people of French Canadian descent can be found across North America. Between 1840 and 1930, many French Canadians immigrated to New England, an event known as the Grande Hémorragie. Etymology French Canadians get their name from ''Canada, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Livre
The livre (abbreviation: £ or ₶., French for (pound)) was the currency of Kingdom of France and its predecessor state of West Francia from 781 to 1794. Several different livres existed, some concurrently. The livre was the name of coins and of units of account. History Origin and etymology The livre was established by Charlemagne as a unit of account equal to one pound of silver. It was subdivided into 20 ''sous'' (also ''sols''), each of 12 '' deniers''. The word ''livre'' came from the Latin word ''libra'', a Roman unit of weight and still the name of a pound in modern French, and the denier comes from the Roman denarius. This system and the denier itself served as the model for many of Europe's currencies, including the British pound, Italian lira, Spanish dinero and the Portuguese dinheiro. This first livre is known as the . Only deniers were initially minted, but debasement led to larger denominations being issued. Different mints in different regions used diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





