|
Instrument Landing System Glide Path
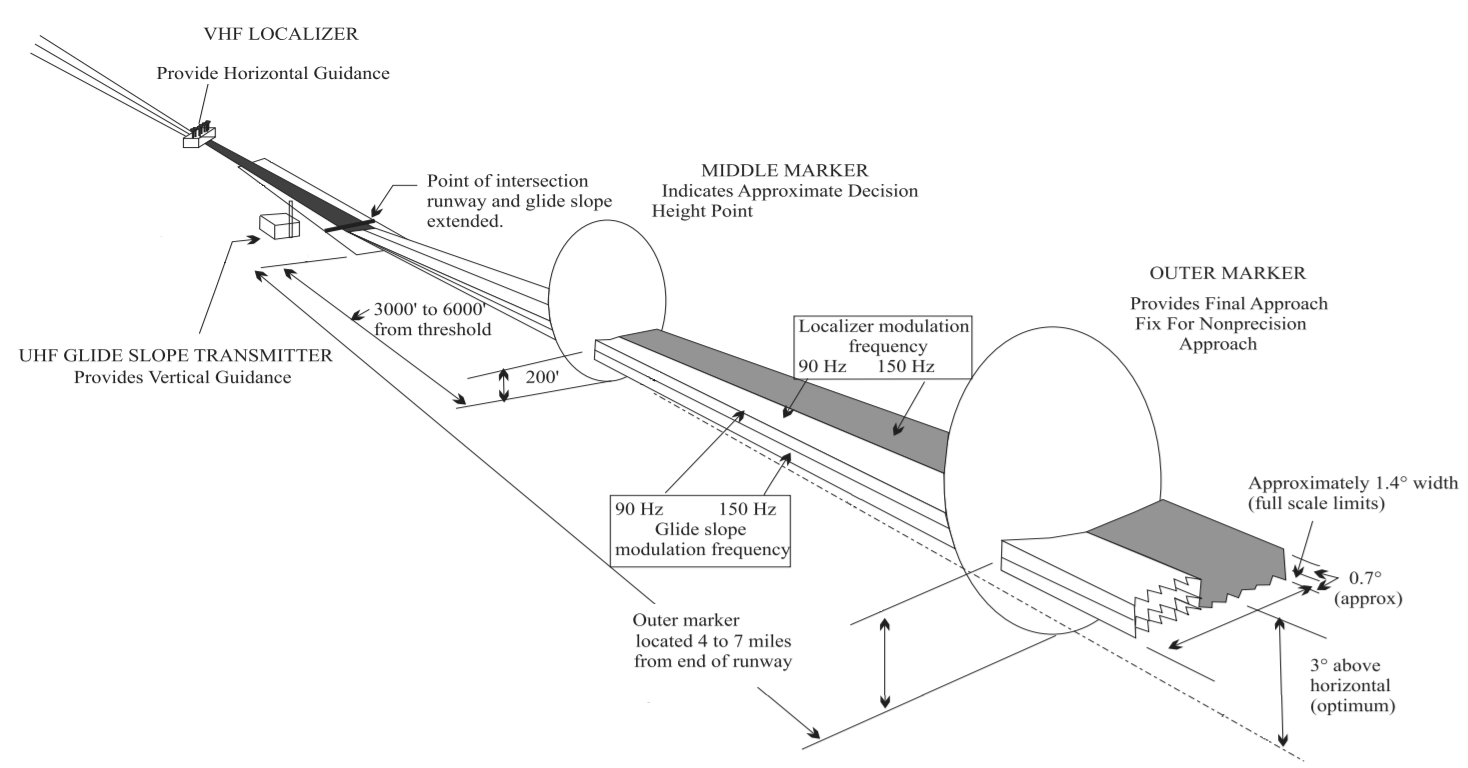
Instrument landing system glide path, commonly referred to as a glide path (G/P) or glide slope (G/S), is "a system of vertical guidance embodied in the instrument landing system which indicates the vertical deviation of the aircraft from its optimum path of descent", according to ''Article 1.106'' of the ITU Radio Regulations (ITU RR).ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Systems – Article 1.106, definition: ''instrument landing system (ILS)'' Principle of operation A glide slope station uses an antenna array sited to one side of the runway touchdown zone. The GS signal is transmitted on a carrier signal using a technique similar to that for the localizer. The centre of the glide slope signal is arranged to define a glide path of approximately 3° above horizontal (ground level). The beam is 1.4° deep (0.7° below the glide-path centre and 0.7° above). The pilot (or the autopilot, if using autoland) controls the aircraft so that the glide slope indicator r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ILS Localizer Illustration
ILS or ils may refer to: Organizations *ILS Law College, of the Indian Law Society *International Launch Services *International Life Saving Federation *International Lenin School Science and technology * Iterated local search, in computing * Instrument landing system, for aircraft * Integrated library system, an enterprise resource planning system for libraries * Internet Locator Server, for Microsoft NetMeeting Business and military * Integrated logistics support * Inventory Locator Service, LLC, a digital aviation warehouse company * ILS (company), a Finnish engineering company Finance * Insurance-Linked Securities (ILS) * Israeli new shekel, ISO 4217 currency code Other uses *''Inscriptiones Latinae Selectae'', a book of Latin inscriptions * Ils (musician) *Them (2006 film), ''Them'' (2006 film) (French: ''Ils''), a French horror film {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instrument Landing System
In aviation, the instrument landing system (ILS) is a precision radio navigation system that provides short-range guidance to aircraft to allow them to approach a runway at night or in bad weather. In its original form, it allows an aircraft to approach until it is over the ground, within a of the runway. At that point the runway should be visible to the pilot; if it is not, they perform a missed approach. Bringing the aircraft this close to the runway dramatically increases the range of weather conditions in which a safe landing can be made. Other versions of the system, or "categories", have further reduced the minimum altitudes, runway visual ranges (RVRs), and transmitter and monitoring configurations designed depending on the normal expected weather patterns and airport safety requirements. ILS uses two directional radio signals, the ''localizer'' (108 to 112 MHz frequency), which provides horizontal guidance, and the ''glideslope'' (329.15 to 335 MHz frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITU Radio Regulations
The ITU Radio Regulations (short: RR) is a basic document of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) that regulates on law of nations scale radiocommunication services and the utilisation of radio frequencies. It is the supplementation to the ITU Constitution and Convention and in line with the ITU International Telecommunication Regulations (ITR). The ITU RR comprise and regulate the part of the allocated electromagnetic spectrum (also: radio frequency spectrum) from 9 kHz to 275 GHz. Structure The current approved version of the ITU Radio Regulations (addition 2012) is structured as follows: Volume 1 – Articles * CHAPTER I – Terminology and technical characteristics **Section I – General terms (article 1.1-1.15) **Section II – Specific terms related to frequency management (article 1.16-1.18) **Section III – Radiocommunication services (article 1.19-1.60) **Section IV – Radio stations and systems (article 1.61-1.115) **Section V – Operationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrier Signal
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a waveform (usually sinusoidal) that is modulated (modified) with an information-bearing signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave usually has a much higher frequency than the input signal does. The purpose of the carrier is usually either to transmit the information through space as an electromagnetic wave (as in radio communication), or to allow several carriers at different frequencies to share a common physical transmission medium by frequency division multiplexing (as in a cable television system). The term originated in radio communication, where the carrier wave creates the waves which carry the information (modulation) through the air from the transmitter to the receiver. The term is also used for an unmodulated emission in the absence of any modulating signal. In music production, carrier signals can be controlled by a modulating signal to change the sound property of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instrument Landing System Localizer
An instrument landing system localizer, or simply localizer (LOC), is a system of horizontal guidance in the instrument landing system, which is used to guide aircraft along the axis of the runway. Principle of operation In aviation, a localizer is the lateral component of the ''instrument landing system'' (ILS) for the runway centerline when combined with the vertical glide slope, not to be confused with a locator, although both are parts of aviation navigation systems. A localizer (like a glideslope) requires both a transmitting airport runway system and receiving cockpit instruments. An older aircraft without an ILS receiver cannot take advantage of any ILS facilities at any runway, and much more importantly, the most modern aircraft have no use of their ILS instruments at runways which lack ILS facilities. In parts of Africa and Asia large airports may lack any kind of transmitting ILS system. Some runways have ILS only in one direction, this can however still be used for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoland
In aviation, autoland describes a system that fully automates the landing procedure of an aircraft's flight, with the flight crew supervising the process. Such systems enable airliners to land in weather conditions that would otherwise be dangerous or impossible to operate in. Description Autoland systems were designed to make landing possible in visibility too poor to permit any form of visual landing, although they can be used at any level of visibility. They are usually used when visibility is less than 600 meters runway visual range and/or in adverse weather conditions, although limitations do apply for most aircraft—for example, for a Boeing 747-400 the limitations are a maximum headwind of 25 kts, a maximum tailwind of 10 kts, a maximum crosswind component of 25 kts, and a maximum crosswind with one engine inoperative of five knots. They may also include automatic braking to a full stop once the aircraft is on the ground, in conjunction with the autobrake system, and some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrier Signal
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a waveform (usually sinusoidal) that is modulated (modified) with an information-bearing signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave usually has a much higher frequency than the input signal does. The purpose of the carrier is usually either to transmit the information through space as an electromagnetic wave (as in radio communication), or to allow several carriers at different frequencies to share a common physical transmission medium by frequency division multiplexing (as in a cable television system). The term originated in radio communication, where the carrier wave creates the waves which carry the information (modulation) through the air from the transmitter to the receiver. The term is also used for an unmodulated emission in the absence of any modulating signal. In music production, carrier signals can be controlled by a modulating signal to change the sound property of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplitude Modulation
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude (signal strength) of the wave is varied in proportion to that of the message signal, such as an audio signal. This technique contrasts with angle modulation, in which either the frequency of the carrier wave is varied, as in frequency modulation, or its phase, as in phase modulation. AM was the earliest modulation method used for transmitting audio in radio broadcasting. It was developed during the first quarter of the 20th century beginning with Roberto Landell de Moura and Reginald Fessenden's radiotelephone experiments in 1900. This original form of AM is sometimes called double-sideband amplitude modulation (DSBAM), because the standard method produces sidebands on either side of the carrier frequency. Single-sideband modulation uses bandpass filters to eliminate one of the sidebands and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Station
Radio broadcasting is transmission of audio (sound), sometimes with related metadata, by radio waves to radio receivers belonging to a public audience. In terrestrial radio broadcasting the radio waves are broadcast by a land-based radio station, while in satellite radio the radio waves are broadcast by a satellite in Earth orbit. To receive the content the listener must have a broadcast radio receiver (''radio''). Stations are often affiliated with a radio network which provides content in a common radio format, either in broadcast syndication or simulcast or both. Radio stations broadcast with several different types of modulation: AM radio stations transmit in AM ( amplitude modulation), FM radio stations transmit in FM (frequency modulation), which are older analog audio standards, while newer digital radio stations transmit in several digital audio standards: DAB (digital audio broadcasting), HD radio, DRM ( Digital Radio Mondiale). Television broadcasting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiocommunication Service
Radio communication service or radiocommunication service is according to Article 1.19 of the International Telecommunication Union's Radio Regulations (ITU RR),ITU Radio Regulations, Section III – Radio services, Article 1.19, definition: Radiocommunication service defined as “a service…involving the transmission, emission and/or reception of radio waves for specific telecommunication purposes”. Radiocommunication Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmit ... is sub-divided into space and terrestrial radiocommunication. Space radiocommunication is defined in RR Article 1 as “any radiocommunication involving the use of one or more space stations or the use of one or more reflecting satellites or other objects in space”. Terrestrial radiocommunication is defined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeronautical Navigation Systems
Aeronautics is the science or art involved with the study, design process, design, and manufacturing of air flight–capable machines, and the techniques of operating aircraft and rockets within the atmosphere. The British Royal Aeronautical Society identifies the aspects of "aeronautical Art, Science and Engineering" and "The profession of Aeronautics (which expression includes Astronautics)." While the term originally referred solely to ''operating'' the aircraft, it has since been expanded to include technology, business, and other aspects related to aircraft. The term "aviation" is sometimes used interchangeably with aeronautics, although "aeronautics" includes lighter-than-air craft such as airships, and includes ballistic vehicles while "aviation" technically does not. A significant part of aeronautical science is a branch of dynamics (mechanics), dynamics called aerodynamics, which deals with the motion of air and the way that it interacts with objects in motion, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |