|
Innovations In Theoretical Computer Science
The Conference on Innovations in Theoretical Computer Science is an academic conference about theoretical computer science. The conference was initiated by Andrew Yao in 2010, and was originally called ''Innovations in Computer Science''. The proceedings were hosted online in 2010 and 2011, were published in the ACM Digital Library from 2012 to 2016, and were published as open access in the LIPIcs collection from 2017 onwards. As of 2022, the conference is listed by Google Scholar as the 8th venue in theoretical computer science according to the h5-index Journal ranking is widely used in academic circles in the evaluation of an academic journal's impact and quality. Journal rankings are intended to reflect the place of a journal within its field, the relative difficulty of being published in that ... metric.{{Cite web, title=Theoretical Computer Science – Google Scholar Metrics, url=https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=top_venues&hl=en&vq=eng_theoreticalcomputersci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theoretical Computer Science
Theoretical computer science (TCS) is a subset of general computer science and mathematics that focuses on mathematical aspects of computer science such as the theory of computation, lambda calculus, and type theory. It is difficult to circumscribe the theoretical areas precisely. The Association for Computing Machinery, ACM's ACM SIGACT, Special Interest Group on Algorithms and Computation Theory (SIGACT) provides the following description: History While logical inference and mathematical proof had existed previously, in 1931 Kurt Gödel proved with his incompleteness theorem that there are fundamental limitations on what statements could be proved or disproved. Information theory was added to the field with a 1948 mathematical theory of communication by Claude Shannon. In the same decade, Donald Hebb introduced a mathematical model of Hebbian learning, learning in the brain. With mounting biological data supporting this hypothesis with some modification, the fields of n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
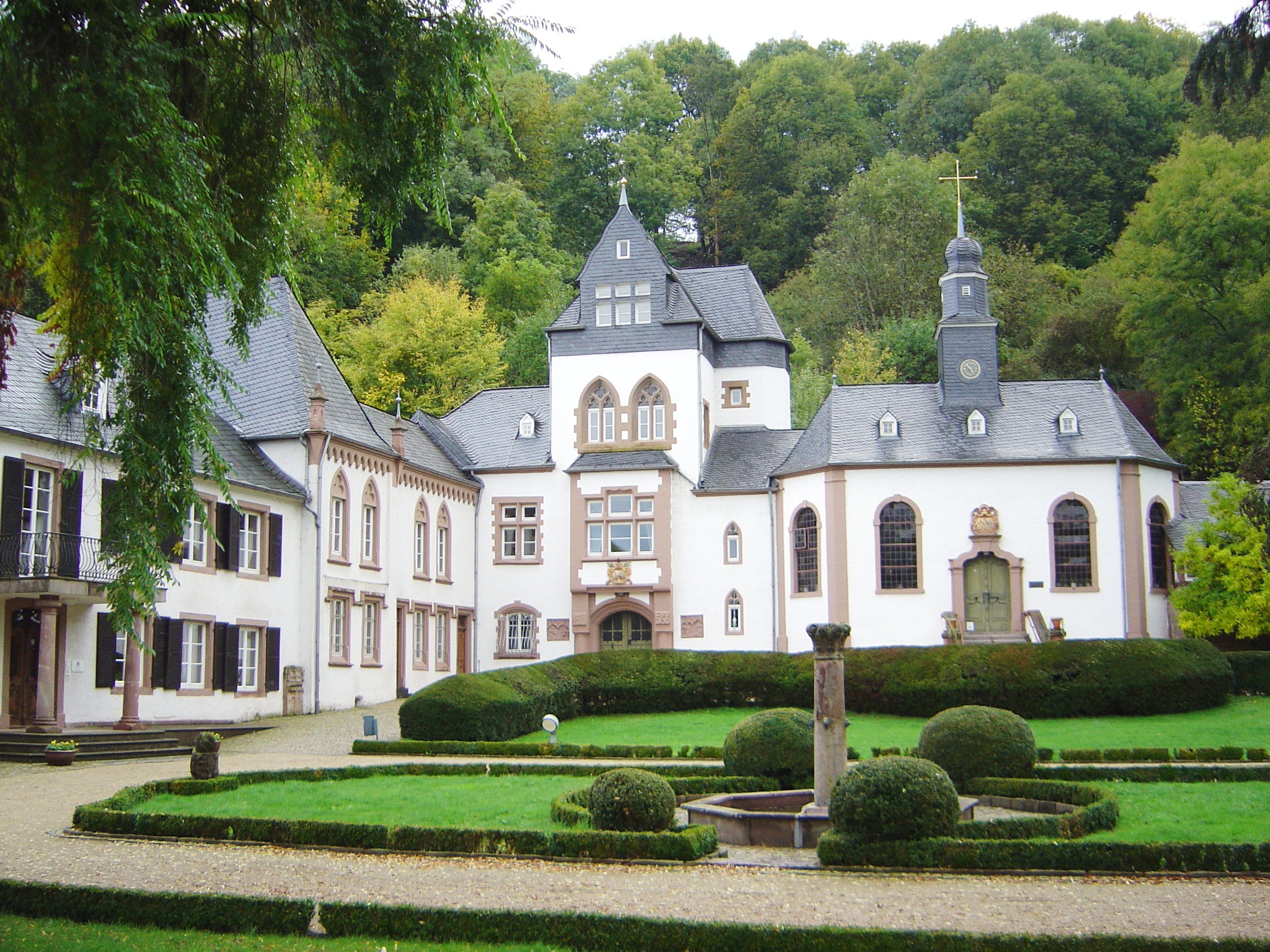
Leibniz Center For Informatics
Dagstuhl is a computer science research center in Germany, located in and named after a district of the town of Wadern, Merzig-Wadern, Saarland. Location Following the model of the mathematical center at Oberwolfach, the center is installed in a very remote and relaxed location in the countryside. The Leibniz Center is located in a historic country house, Schloss Dagstuhl (Dagstuhl Castle), together with modern purpose-built buildings connected by an enclosed footbridge. The ruins of the 13th-century Dagstuhl Castle are nearby, a short walk up a hill from the Schloss. History The Leibniz-Zentrum für Informatik (LZI, ''Leibniz Center for Informatics'') was established at Dagstuhl in 1990. In 1993, the over 200-year-old building received a modern extension with other guest rooms, conference rooms and a library. The center is managed as a non-profit organization, and financed by national funds. It receives scientific support by a variety of German and foreign research institutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theoretical Computer Science
Theoretical computer science (TCS) is a subset of general computer science and mathematics that focuses on mathematical aspects of computer science such as the theory of computation, lambda calculus, and type theory. It is difficult to circumscribe the theoretical areas precisely. The Association for Computing Machinery, ACM's ACM SIGACT, Special Interest Group on Algorithms and Computation Theory (SIGACT) provides the following description: History While logical inference and mathematical proof had existed previously, in 1931 Kurt Gödel proved with his incompleteness theorem that there are fundamental limitations on what statements could be proved or disproved. Information theory was added to the field with a 1948 mathematical theory of communication by Claude Shannon. In the same decade, Donald Hebb introduced a mathematical model of Hebbian learning, learning in the brain. With mounting biological data supporting this hypothesis with some modification, the fields of n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Yao
Andrew Chi-Chih Yao (; born December 24, 1946) is a Chinese computer scientist and computational theorist. He is currently a professor and the dean of Institute for Interdisciplinary Information Sciences (IIIS) at Tsinghua University. Yao used the minimax theorem to prove what is now known as Yao's Principle. Yao was a naturalized U.S. citizen, and worked for many years in the U.S. In 2015, together with Yang Chen-Ning, he renounced his U.S. citizenship and became an academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Early life Yao was born in Shanghai, China. He completed his undergraduate education in physics at the National Taiwan University, before completing a Doctor of Philosophy in physics at Harvard University in 1972, and then a second PhD in computer science from the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign in 1975. Academic career Yao was an assistant professor at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (1975–1976), assistant professor at Stanford University ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ACM Digital Library
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) is a US-based international learned society for computing. It was founded in 1947 and is the world's largest scientific and educational computing society. The ACM is a non-profit professional membership group, claiming nearly 110,000 student and professional members . Its headquarters are in New York City. The ACM is an umbrella organization for academic and scholarly interests in computer science (informatics). Its motto is "Advancing Computing as a Science & Profession". History In 1947, a notice was sent to various people: On January 10, 1947, at the Symposium on Large-Scale Digital Calculating Machinery at the Harvard computation Laboratory, Professor Samuel H. Caldwell of Massachusetts Institute of Technology spoke of the need for an association of those interested in computing machinery, and of the need for communication between them. ..After making some inquiries during May and June, we believe there is ample interest to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Access
Open access (OA) is a set of principles and a range of practices through which research outputs are distributed online, free of access charges or other barriers. With open access strictly defined (according to the 2001 definition), or libre open access, barriers to copying or reuse are also reduced or removed by applying an open license for copyright. The main focus of the open access movement is "peer reviewed research literature". Historically, this has centered mainly on print-based academic journals. Whereas non-open access journals cover publishing costs through access tolls such as subscriptions, site licenses or pay-per-view charges, open-access journals are characterised by funding models which do not require the reader to pay to read the journal's contents, relying instead on author fees or on public funding, subsidies and sponsorships. Open access can be applied to all forms of published research output, including peer-reviewed and non peer-reviewed academic journa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LIPIcs
Dagstuhl is a computer science research center in Germany, located in and named after a district of the town of Wadern, Merzig-Wadern, Saarland. Location Following the model of the mathematical center at Oberwolfach, the center is installed in a very remote and relaxed location in the countryside. The Leibniz Center is located in a historic country house, Schloss Dagstuhl (Dagstuhl Castle), together with modern purpose-built buildings connected by an enclosed footbridge. The ruins of the 13th-century Dagstuhl Castle are nearby, a short walk up a hill from the Schloss. History The Leibniz-Zentrum für Informatik (LZI, ''Leibniz Center for Informatics'') was established at Dagstuhl in 1990. In 1993, the over 200-year-old building received a modern extension with other guest rooms, conference rooms and a library. The center is managed as a non-profit organization, and financed by national funds. It receives scientific support by a variety of German and foreign research institutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google Scholar
Google Scholar is a freely accessible web search engine that indexes the full text or metadata of scholarly literature across an array of publishing formats and disciplines. Released in beta in November 2004, the Google Scholar index includes peer-reviewed online academic journals and books, conference papers, theses and dissertations, preprints, abstracts, technical reports, and other scholarly literature, including court opinions and patents. Google Scholar uses a web crawler, or web robot, to identify files for inclusion in the search results. For content to be indexed in Google Scholar, it must meet certain specified criteria. An earlier statistical estimate published in PLOS One using a mark and recapture method estimated approximately 80–90% coverage of all articles published in English with an estimate of 100 million.''Trend Watch'' (2014) Nature 509(7501), 405 – discussing Madian Khabsa and C Lee Giles (2014''The Number of Scholarly Documents on the Public Web'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H5-index
Journal ranking is widely used in academic circles in the evaluation of an academic journal's impact and quality. Journal rankings are intended to reflect the place of a journal within its field, the relative difficulty of being published in that journal, and the prestige associated with it. They have been introduced as official research evaluation tools in several countries. Measures Traditionally, journal ranking "measures" or evaluations have been provided simply through institutional lists established by academic leaders or through a committee vote. These approaches have been notoriously politicized and inaccurate reflections of actual prestige and quality, as they would often reflect the biases and personal career objectives of those involved in ranking the journals; also causing the problem of highly disparate evaluations across institutions. Also, see YouTube video narrative of this paper at: Consequently, many institutions have required external sources of evaluation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DBLP
DBLP is a computer science bibliography website. Starting in 1993 at Universität Trier in Germany, it grew from a small collection of HTML files and became an organization hosting a database and logic programming bibliography site. Since November 2018, DBLP is a branch of Schloss Dagstuhl – Leibniz-Zentrum für Informatik (LZI). DBLP listed more than 5.4 million journal articles, conference papers, and other publications on computer science in December 2020, up from about 14,000 in 1995 and 3.66 million in July 2016. All important journals on computer science are tracked. Proceedings papers of many conferences are also tracked. It is mirrored at three sites across the Internet. For his work on maintaining DBLP, Michael Ley received an award from the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) and the VLDB Endowment Special Recognition Award in 1997. Furthermore, he was awarded the ACM Distinguished Service Award for "creating, developing, and curating DBLP" in 2019. ''DBLP' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theoretical Computer Science Conferences
A theory is a rational type of abstract thinking about a phenomenon, or the results of such thinking. The process of contemplative and rational thinking is often associated with such processes as observational study or research. Theories may be scientific, belong to a non-scientific discipline, or no discipline at all. Depending on the context, a theory's assertions might, for example, include generalized explanations of how nature works. The word has its roots in ancient Greek, but in modern use it has taken on several related meanings. In modern science, the term "theory" refers to scientific theories, a well-confirmed type of explanation of nature, made in a way consistent with the scientific method, and fulfilling the criteria required by modern science. Such theories are described in such a way that scientific tests should be able to provide empirical support for it, or empirical contradiction ("falsify") of it. Scientific theories are the most reliable, rigorous, and compre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |