|
Inferior Ramus Of The Ischium
The ischium () forms the lower and back region of the (''os coxae''). Situated below the ilium and behind the pubis, it is one of three regions whose fusion creates the . The superior portion of this region forms approximately one-third of the |
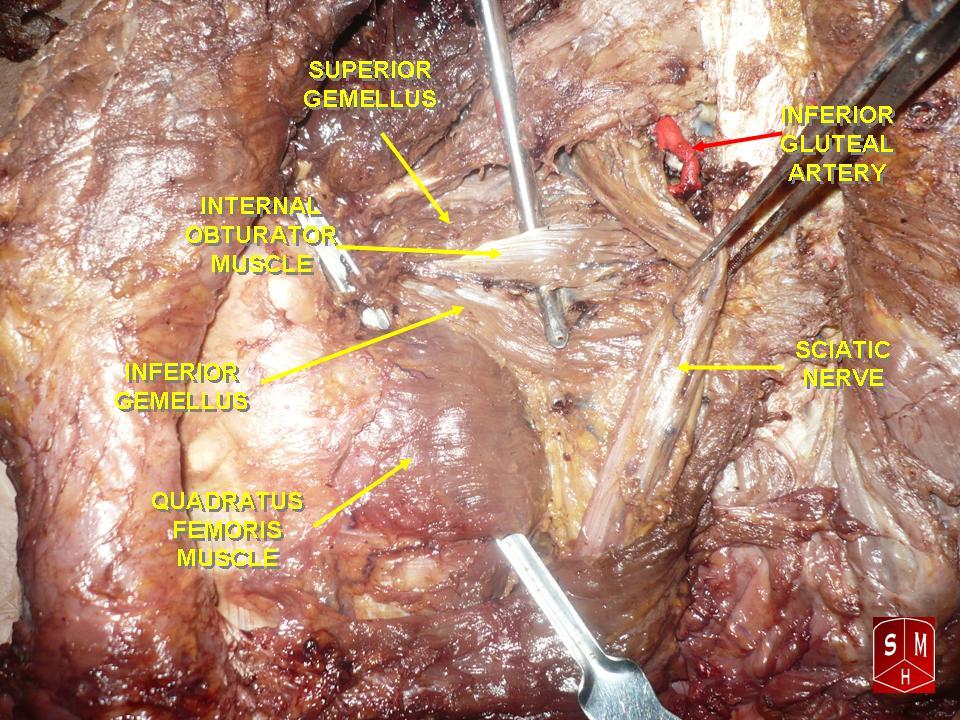
Superior Gemellus Muscle
The gemelli muscles are the inferior gemellus muscle and the superior gemellus muscle, two small accessory fasciculi to the tendon of the internal obturator muscle. The gemelli muscles belong to the lateral rotator group of six muscles of the hip that rotate the femur in the hip joint. Superior gemellus muscle The gemelli muscles are two small muscular fasciculi, accessories to the tendon of the internal obturator muscle which is received into a groove between them. The superior gemellus muscle is the higher placed gemellus muscle that arises from the outer (gluteal) surface of the ischial spine, and blends with the upper part of the tendon of the internal obturator. It is smaller than the inferior gemellus. In some people, the fibres of the gemellus superior extend further than average, and are prolonged onto the medial surface of the greater trochanter of the femur. The superior and inferior gemelli are supplied by the inferior gluteal artery. Nerve supply to the superior geme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetabular Fossa
The acetabular fossa is a fossa located at the centre of the acetabulum. It is occupied by the ligament of head of femur. In contrast to the thick and smooth surrounding lunate surface, the pelvis' articulation with the head of the femur, the acetabular fossa is rough and thin, often transparent, and continuous with the acetabular notch The acetabular notch is a deep notch in the acetabulum of the hip bone. The acetabular notch is continuous with a circular non-articular depression, the acetabular fossa, at the bottom of the cavity: this depression is perforated by numerous aper ... below. Additional Images File:Slide2DADA.JPG, Hip joint. Lateral view. Fat in acetabular fossa. References Pelvis {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberosity Of The Ischium
The ischial tuberosity (or tuberosity of the ischium, tuber ischiadicum), also known colloquially as the sit bones or sitz bones, or as a pair the sitting bones, is a large swelling posteriorly on the superior ramus of the ischium. It marks the lateral boundary of the pelvic outlet. When sitting, the weight is frequently placed upon the ischial tuberosity. The gluteus maximus provides cover in the upright posture, but leaves it free in the seated position.Platzer (2004), p 236 The distance between a cyclist's ischial tuberosities is one of the factors in the choice of a bicycle saddle. Divisions The tuberosity is divided into two portions: a lower, rough, somewhat triangular part, and an upper, smooth, quadrilateral portion. * The ''lower portion'' is subdivided by a prominent longitudinal ridge, passing from base to apex, into two parts: ** The outer gives attachment to the adductor magnus ** The inner to the sacrotuberous ligament * The ''upper portion'' is subdivided into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischiocavernosus
The ischiocavernosus muscle (erectores penis ''or'' erector clitoridis in older texts) is a muscle just below the surface of the perineum, present in both men and women. Structure It arises by tendinous and fleshy fibers from the inner surface of the tuberosity of the ischium, behind the crus penis; and from the inferior pubic rami and ischium on either side of the crus. From these points fleshy fibers succeed, and end in an aponeurosis which is inserted into the sides and under surface of the crus penis. Function In females, the ischiocavernosus muscle assists with clitoral erection. In males, it helps to stabilize the erect penis by compressing the crus penis For their anterior three-fourths the corpora cavernosa penis lie in intimate apposition with one another, but behind they diverge in the form of two tapering processes, known as the crura, which are firmly connected to the ischial rami. Traced ... and retarding the return of blood through the veins. Additional i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superficial Transverse Perineal Muscle
The transverse perineal muscles (transversus perinei) are the superficial and the deep transverse perineal muscles. Superficial transverse perineal The superficial transverse perineal muscle (transversus superficialis perinei or Lloyd-Beanie muscle) is a narrow muscular slip, which passes more or less transversely across the perineal space in front of the anus. It arises by tendinous fibers from the inner and forepart of the ischial tuberosity and, running medially, is inserted into the central tendinous point of the perineum (perineal body), joining in this situation with the muscle of the opposite side, with the external anal sphincter muscle behind, and with the bulbospongiosus muscle in front. In some cases, the fibers of the deeper layer of the external anal sphincter cross over in front of the anus and are continued into this mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrotuberous Ligament
The sacrotuberous ligament (great or posterior sacrosciatic ligament) is situated at the lower and back part of the pelvis. It is flat, and triangular in form; narrower in the middle than at the ends. Structure It runs from the sacrum (the lower transverse sacral tubercles, the inferior margins sacrum and the upper coccyx) to the tuberosity of the ischium. It is a remnant of part of Biceps femoris muscle. The sacrotuberous ligament is attached by its broad base to the posterior superior iliac spine, the posterior sacroiliac ligaments (with which it is partly blended), to the lower transverse sacral tubercles and the lateral margins of the lower sacrum and upper coccyx. Its oblique fibres descend laterally, converging to form a thick, narrow band that widens again below and is attached to the medial margin of the ischial tuberosity. It then spreads along the ischial ramus as the falciform process, whose concave edge blends with the fascial sheath of the internal pudendal vessels and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falciform
The ''falx'' was a weapon with a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge used by the Thracians and Dacians. The name was later applied to a siege hook used by the Romans. Etymology ''Falx'' is a Latin word originally meaning 'sickle' but was later used to mean any of a number of tools that had a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge like a sickle. ''Falx'' was thus also used to mean the weapon of the Thracians and Dacians, and the Roman siege hook. Dacian ''falx'' In Latin texts, the weapon was described as an ' (whence ''falcata'') by Ovid in ''Metamorphose'' and as a ' by Juvenal in ''Satiriae''. The Dacian ''falx'' came in two sizes: one-handed and two-handed. The shorter variant was called ''sica'' (sickle) in the Dacian language (Valerius Maximus, III, 2.12) with a blade length that varied but was usually around long with a handle 1/3 longer than the blade. The two-handed ''falx'' was a polearm. It consisted of a long wooden shaft with a long curved i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adductor Magnus
Adductor may refer to: * One of the anatomical terms of motion * Adductor muscle (other) * Adductor canal The adductor canal, also known as the subsartorial canal or Hunter’s canal, is an aponeurotic tunnel in the middle third of the thigh. It extends from the apex of the femoral triangle to the adductor hiatus. Structure The adductor canal extends ... {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadratus Femoris
The quadratus femoris is a flat, quadrilateral skeletal muscle. Located on the posterior side of the hip joint, it is a strong external rotator and adductor of the thigh, but also acts to stabilize the femoral head in the acetabulum. Quadratus femoris use in the Meyer's muscle pedicle grafting to prevent avascular necrosis of femur head. Course It originates on the lateral border of the ischial tuberosity of the ischium of the pelvis. From there, it passes laterally to its insertion on the posterior side of the head of the femur: the quadrate tubercle on the intertrochanteric crest and along the quadrate line, the vertical line which runs downward to bisect the lesser trochanter on the medial side of the femur. Along its course, quadratus is aligned edge to edge with the inferior gemellus above and the adductor magnus below, so that its upper and lower borders run horizontal and parallel. At its origin, the upper margin of the adductor magnus is separated from it by the te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obturator Foramen
The obturator foramen (Latin foramen obturatum) is the large opening created by the ischium and pubis (bone), pubis bones of the pelvis through which nerves and blood vessels pass. Structure It is bounded by a thin, uneven margin, to which a strong membrane is attached, and presents, superiorly, a deep groove, the obturator groove, which runs from the pelvis obliquely medialward and downward. This groove is converted into the obturator canal by a ligamentous band, a specialized part of the obturator membrane, attached to two tubercles: * one, the posterior obturator tubercle, on the medial border of the ischium, just in front of the acetabular notch * the other, the anterior obturator tubercle, on the obturator crest of the superior pubic ramus, superior ramus of the pubis (bone), pubis Variation Reflecting the overall sex differences in human physiology, sex differences between male and female pelvises, the obturator foramina are oval in the male and wider and more triangular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Sciatic Notch
The greater sciatic notch is a notch in the ilium (bone), ilium, one of the bones that make up the human pelvis. It lies between the posterior inferior iliac spine (above), and the ischial spine (below). The sacrospinous ligament changes this notch into an opening, the greater sciatic foramen. The notch holds the piriformis, the superior gluteal vein and superior gluteal artery, artery, and the superior gluteal nerve; the inferior gluteal vein and inferior gluteal artery, artery and the inferior gluteal nerve; the sciatic and posterior femoral cutaneous nerves; the internal pudendal artery and internal pudendal veins, veins, and the nerves to the internal obturator and quadratus femoris muscles. Of these, the superior gluteal vessels and nerve pass out above the piriformis, and the other structures below it. The greater sciatic notch is wider in women (about 74.4 Degree symbol, degrees on average) than in men (about 50.4 degrees). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemellus Superior Muscle
The gemelli muscles are the inferior gemellus muscle and the superior gemellus muscle, two small accessory fasciculi to the tendon of the internal obturator muscle. The gemelli muscles belong to the lateral rotator group of six muscles of the hip that rotate the femur in the hip joint. Superior gemellus muscle The gemelli muscles are two small muscular fasciculi, accessories to the tendon of the internal obturator muscle which is received into a groove between them. The superior gemellus muscle is the higher placed gemellus muscle that arises from the outer (gluteal) surface of the ischial spine, and blends with the upper part of the tendon of the internal obturator. It is smaller than the inferior gemellus. In some people, the fibres of the gemellus superior extend further than average, and are prolonged onto the medial surface of the greater trochanter of the femur. The superior and inferior gemelli are supplied by the inferior gluteal artery. Nerve supply to the superior geme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |