|
Inferential Theory Of Learning
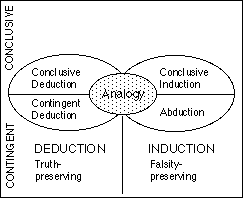
Inferential Theory of Learning (ITL) is an area of machine learning which describes inferential processes performed by learning agents. ITL has been continuously developed by Ryszard S. Michalski, starting in the 1980s. The first known publication of ITL was in 1983. In ITL learning process is viewed as a search (inference) through hypotheses space guided by a specific goal. Results of learning need to be stored. Stored information will later be used by the learner for future inferences. Inferences are split into multiple categories includinconclusive, deduction, and induction.In order for an inference to be considered complete it was required that all categories must be taken into account. This is how the ITL varies from other machine learning theories like Computational Learning Theory and Statistical Learning Theory Statistical learning theory is a framework for machine learning drawing from the fields of statistics and functional analysis. Statistical learning theory deal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferential Theory
Inferential may refer to: * Inferential statistics; see statistical inference * Inference (logic) * Inferential mood (grammar) * Inferential programming * Inferential role semantics * Inferential theory of learning Inferential Theory of Learning (ITL) is an area of machine learning which describes inferential processes performed by learning agents. ITL has been continuously developed by Ryszard S. Michalski, starting in the 1980s. The first known publication ... * Informal inferential reasoning * Simple non-inferential passage {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence. Machine learning algorithms build a model based on sample data, known as training data, in order to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms are used in a wide variety of applications, such as in medicine, email filtering, speech recognition, agriculture, and computer vision, where it is difficult or unfeasible to develop conventional algorithms to perform the needed tasks.Hu, J.; Niu, H.; Carrasco, J.; Lennox, B.; Arvin, F.,Voronoi-Based Multi-Robot Autonomous Exploration in Unknown Environments via Deep Reinforcement Learning IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020. A subset of machine learning is closely related to computational statistics, which focuses on making pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryszard S
Ryszard () is the Polish equivalent of "Richard", and may refer to: * Ryszard Andrzejewski (born 1976), Polish rap musician, songwriter and producer * Ryszard Bakst (1926–1999), Polish and British pianist and piano teacher of Jewish/Polish/Russian origin * Ryszard Bartel (1897–1982), Polish engineer, aircraft designer, pioneer and aviator * Ryszard Bender (born 1932), Polish politician and historian, specialist in the history of the January Uprising * Ryszard Wincenty Berwiński (1817–1879), Polish poet, translator, folklorist, and nationalist * Ryszard Białous (1914–1992), Polish scoutmaster (harcmistrz) captain of the AK-Szare Szeregi *Ryszard Bober (born 1956), Polish politician, Vice-Chairperson of Kuyavian-Pomeranian Regional Assembly * Ryszard Bogusz (born 1951), Lutheran theologian, bishop of the diocese Wroclaw of the Evangelical Augsburg Church in Poland * Ryszard Bolesławski (1889–1937), Polish film director, actor and teacher of acting *Ryszard Bosek (born 1950 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals, and some machines; there is also evidence for some kind of learning in certain plants. Some learning is immediate, induced by a single event (e.g. being burned by a hot stove), but much skill and knowledge accumulate from repeated experiences. The changes induced by learning often last a lifetime, and it is hard to distinguish learned material that seems to be "lost" from that which cannot be retrieved. Human learning starts at birth (it might even start before in terms of an embryo's need for both interaction with, and freedom within its environment within the womb.) and continues until death as a consequence of ongoing interactions between people and their environment. The nature and processes involved in learning are studied in many established fields (including educational psychology, neurop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inference
Inferences are steps in reasoning, moving from premises to logical consequences; etymologically, the word '' infer'' means to "carry forward". Inference is theoretically traditionally divided into deduction and induction, a distinction that in Europe dates at least to Aristotle (300s BCE). Deduction is inference deriving logical conclusions from premises known or assumed to be true, with the laws of valid inference being studied in logic. Induction is inference from particular evidence to a universal conclusion. A third type of inference is sometimes distinguished, notably by Charles Sanders Peirce, contradistinguishing abduction from induction. Various fields study how inference is done in practice. Human inference (i.e. how humans draw conclusions) is traditionally studied within the fields of logic, argumentation studies, and cognitive psychology; artificial intelligence researchers develop automated inference systems to emulate human inference. Statistical infer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Storage Device
Data storage is the recording (storing) of information (data) in a storage medium. Handwriting, phonographic recording, magnetic tape, and optical discs are all examples of storage media. Biological molecules such as RNA and DNA are considered by some as data storage. Recording may be accomplished with virtually any form of energy. Electronic data storage requires electrical power to store and retrieve data. Data storage in a digital, machine-readable medium is sometimes called ''digital data''. Computer data storage is one of the core functions of a general-purpose computer. Electronic documents can be stored in much less space than paper documents. Barcodes and magnetic ink character recognition (MICR) are two ways of recording machine-readable data on paper. Recording media A recording medium is a physical material that holds information. Newly created information is distributed and can be stored in four storage media–print, film, magnetic, and optical–and see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Learning Theory
In computer science, computational learning theory (or just learning theory) is a subfield of artificial intelligence devoted to studying the design and analysis of machine learning algorithms. Overview Theoretical results in machine learning mainly deal with a type of inductive learning called supervised learning. In supervised learning, an algorithm is given samples that are labeled in some useful way. For example, the samples might be descriptions of mushrooms, and the labels could be whether or not the mushrooms are edible. The algorithm takes these previously labeled samples and uses them to induce a classifier. This classifier is a function that assigns labels to samples, including samples that have not been seen previously by the algorithm. The goal of the supervised learning algorithm is to optimize some measure of performance such as minimizing the number of mistakes made on new samples. In addition to performance bounds, computational learning theory studies the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Learning Theory
Statistical learning theory is a framework for machine learning drawing from the fields of statistics and functional analysis. Statistical learning theory deals with the statistical inference problem of finding a predictive function based on data. Statistical learning theory has led to successful applications in fields such as computer vision, speech recognition, and bioinformatics. Introduction The goals of learning are understanding and prediction. Learning falls into many categories, including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, online learning, and reinforcement learning. From the perspective of statistical learning theory, supervised learning is best understood. Supervised learning involves learning from a training set of data. Every point in the training is an input-output pair, where the input maps to an output. The learning problem consists of inferring the function that maps between the input and the output, such that the learned function can be used to pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cybernetics
Cybernetics is a wide-ranging field concerned with circular causality, such as feedback, in regulatory and purposive systems. Cybernetics is named after an example of circular causal feedback, that of steering a ship, where the helmsperson maintains a steady course in a changing environment by adjusting their steering in continual response to the effect it is observed as having. Cybernetics is concerned with circular causal processes such as steering however they are embodied,Ashby, W. R. (1956). An introduction to cybernetics. London: Chapman & Hall, p. 1. including in ecological, technological, biological, cognitive, and social systems, and in the context of practical activities such as designing, learning, managing, conversation, and the practice of cybernetics itself. Cybernetics' transdisciplinary and "antidisciplinary" character has meant that it intersects with a number of other fields, leading to it having both wide influence and diverse interpretations. Cybernetics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |