|
Inequality In The United States (other)
{{dab ...
Inequality in the United States may refer to: * Educational inequality in the United States * Gender inequality in the United States * Health inequality in the United States * Racial inequality in the United States Economic *Income inequality in the United States ** Causes of income inequality in the United States * Tax policy and economic inequality in the United States * Wealth inequality in the United States See also * Socioeconomic mobility in the United States Socioeconomic mobility in the United States refers to the upward or downward movement of Americans from one social class or economic level to another, through job changes, inheritance, marriage, connections, tax changes, innovation, illegal ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Inequality In The United States
Unequal access to education in the United States results in unequal outcomes for students. Disparities in academic access among students in the United States are the result of several factors including: government policies, school choice, family wealth, parenting style, implicit bias towards the race or ethnicity of the student, and the resources available to the student and their school. Educational inequality contributes to a number of broader problems in the United States, including income inequality and increasing prison populations. Educational inequalities in the United States are wide-ranging, and many potential solutions have been proposed to mitigate their impacts on students. History Colonial era The earliest forms of education in the U.S. were primarily religiously motivated. The main purpose of education in the 17th and 18th was to teach children how to read the bible and abide by Puritan values. These values were espoused by religious white colonists, who would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
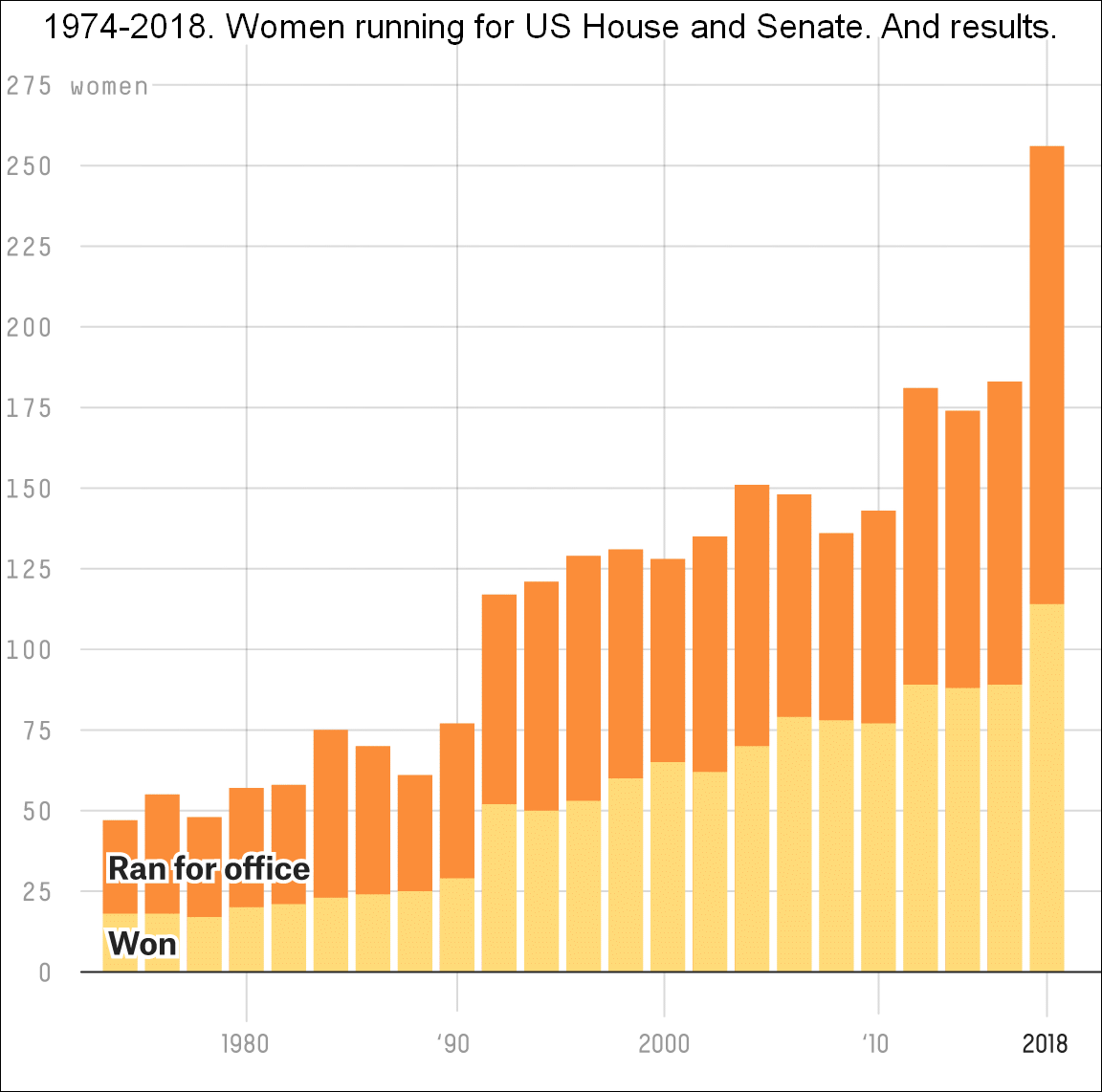
Gender Inequality In The United States
Gender inequality in the United States has been diminishing throughout its history and significant advancements towards equality have been made beginning mostly in the early 1900s. However, despite this progress, gender inequality in the United States continues to persist in many forms, including the disparity in women's political representation and participation, occupational segregation, and the unequal distribution of household labor. The alleviation of gender inequality has been the goal of several major pieces of legislation since 1920 and continues to the present day. As of 2021, the World Economic Forum ranks the United States 30th in terms of gender equality out of 149 countries. In addition to the inequality faced by women, inequality, prejudice, and violence against transgender men and women, as well as gender nonconforming individuals and non-binary individuals, are also prevalent in the United States. Transgender individuals suffer from prejudices in the workforce and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Inequality In The United States
The United States far outspends any other nation on health care, measured both in ''per capita'' spending and as a percentage of GDP. Despite this, the country has significantly worse healthcare outcomes when compared to peer nations. The United States is the only developed nation without a system of universal health care, with a large proportion of its population not carrying health insurance, a substantial factor in the country's excess mortality. Healthcare is provided by many distinct organizations, made up of insurance companies, healthcare providers, hospital systems, and independent providers. Health care facilities are largely owned and operated by private sector businesses. 58% of community hospitals in the United States are non-profit, 21% are government-owned, and 21% are for-profit. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the United States spent $9,403 on health care per capita, and 17.9% on health care as percentage of its GDP in 2014. Healthcare cove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racial Inequality In The United States
Racial inequality in the United States identifies the social inequality and advantages and disparities that affect different races within the United States. These can also be seen as a result of historic oppression, inequality of inheritance, or racism and prejudice, especially against minority groups. There are vast differences in wealth across racial groups in the United States. The wealth gap between Caucasian and African-American families nearly tripled from $85,000 in 1984 to $236,500 in 2009. There are many causes, including years of home ownership, household income, unemployment, education, and inheritance. Under slavery in the United States, African Americans were treated as property. After the American Civil War, Black sharecroppers became trapped in debt. African Americans were rarely able to homestead. The Freedman's Bank failed, losing many Black assets. Exclusions from Social Security disproportionately affected African Americans. Savings were spent for retirement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
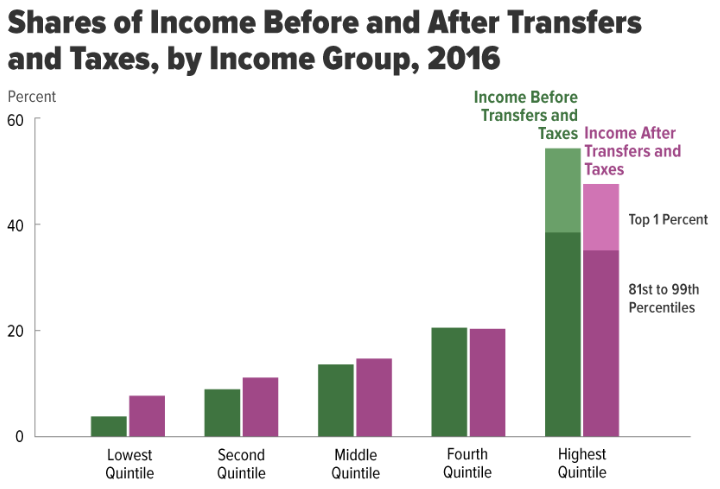
Income Inequality In The United States
Income inequality in the United States is the extent to which income is distributed in differing amounts among the American population. It has fluctuated considerably since measurements began around 1915, moving in an arc between peaks in the 1920s and 2000s, with a 30-year period of relatively lower inequality between 1950 and 1980. The U.S. has the highest level of income inequality among its (post-)industrialized peers.United Press International (UPI), June 22, 2018"U.N. Report: With 40M in Poverty, U.S. Most Unequal Developed Nation"/ref> When measured for all households, U.S. income inequality is comparable to other developed countries before taxes and transfers, but is among the highest after taxes and transfers, meaning the U.S. shifts relatively less income from higher income households to lower income households. In 2016, average market income was $15,600 for the lowest quintile and $280,300 for the highest quintile. The degree of inequality accelerated within the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causes Of Income Inequality In The United States
Causes of income inequality in the United States describes the reasons for the unequal distribution of income in the US and the factors that cause it to change over time. This topic is subject to extensive ongoing research, media attention, and political interest. Income inequality in the United States grew significantly beginning in the early 1970s, after several decades of stability. The US consistently exhibits higher rates of income inequality than most developed nations, arguably due to the nation's relatively less regulated markets.Weeks, J. (2007)Inequality Trends in Some Developed OECD countries In J. K. S. & J. Baudot (Ed.), ''Flat World, Big Gaps'' (159–74). New York: ZED Books (published in association with the United Nations).Income distribution and poverty – OECD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Policy And Economic Inequality In The United States
Tax policy and economic inequality in the United States discusses how tax policy affects the distribution of income and wealth in the United States. Income inequality can be measured before- and after-tax; this article focuses on the after-tax aspects. Income tax rates applied to various income levels and tax expenditures (i.e., deductions, exemptions, and preferential rates that modify the outcome of the rate structure) primarily drive how market results are redistributed to impact the after-tax inequality. After-tax inequality has risen in the United States markedly since 1980, following a more egalitarian period following World War II. Overview Tax policy is the mechanism through which market results are redistributed, affecting after-tax inequality. The provisions of the United States Internal Revenue Code regarding income taxes and estate taxes have undergone significant changes under both Republican and Democratic administrations and Congresses since 1964. Since the Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
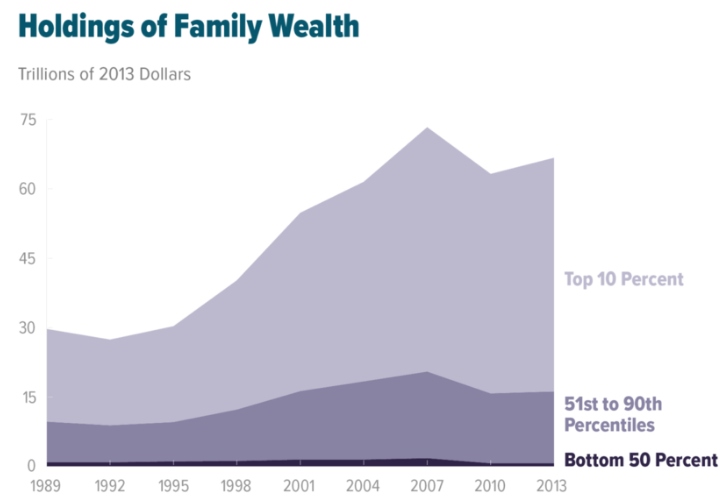
Wealth Inequality In The United States
Wealth inequality in the United States is the unequal distribution of assets among residents of the United States. Wealth commonly includes the values of any homes, automobiles, personal valuables, businesses, savings, and investments, as well as any associated debts. Although different from income inequality, the two are related. Wealth is usually not used for daily expenditures or factored into household budgets, but combined with income, it represents a family's total opportunity to secure stature and a meaningful standard of living, or to pass their class status down to their children. Moreover, wealth provides for both short- and long-term financial security, bestows social prestige, contributes to political power, and can be leveraged to obtain more wealth. Hence, wealth provides mobility and agency—the ability to act. The accumulation of wealth enables a variety of freedoms, and removes limits on life that one might otherwise face. Federal Reserve data indicates th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |