|
Indori River
The Indori river (Hindi: इन्दोरी नदी), is a rain-fed river originates from Aravalli Range from Sikar district and flows through Alwar district of Rajasthan to Rewari district of Haryana and it is the longest tributary of Sahibi River which stretches to 50 km. In Delhi, it is called the Najafgarh drain or Najafgarh Nallah. Archaeological findings Archaeological findings on the Sahibi River have confirmed habitations on its banks before the Harappan and pre-Mahabharata periods. Both handmade and wheel-made earthenware dated from 3309–2709 BCE and 2879–2384 BCE has been found on the banks of the Sahibi River at Jodhpura. INTACH-Rewari found pottery on the Sahibi riverbed at Hansaka in the Rewari district. A red stone statue of Vamana Dev was found in the Sahibi riverbed near Bawal in 2002; the statue is now displayed at the Shri Krishna Museum, Kurukshetra. Other artifacts discovered in the Sahibi River include arrowheads, fishhooks, appearheads, awls, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
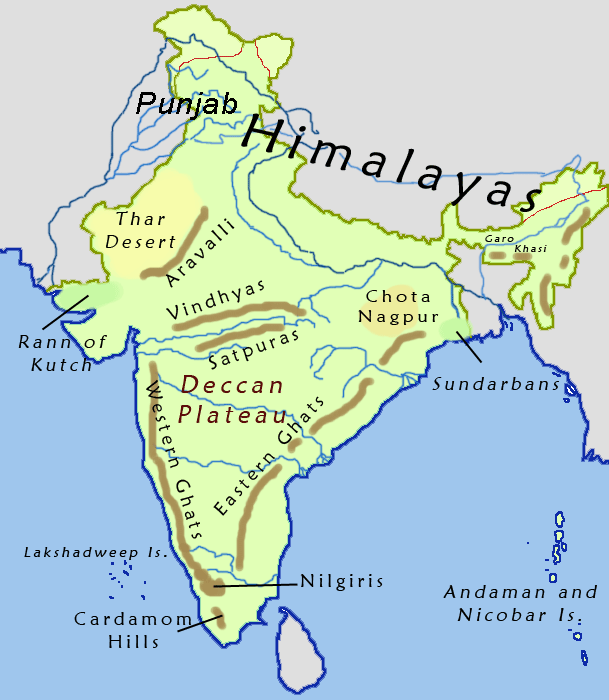
Aravalli Range
The Aravalli Range (also spelled ''Aravali'') is a mountain range in Northern-Western India, running approximately in a south-west direction, starting near Delhi, passing through southern Haryana, Rajasthan, and ending in Ahmedabad Gujarat. The highest peak is Guru Shikhar on Mount Abu at . The Aravalli Range is arguably the oldest geological feature on Earth, having its origin in the Proterozoic era. The Aravalli Range is rich in natural resources and serves as check to the growth of the western desert. Etymology Aravalli, a composite Sanskrit word from the roots ''"ara"'' and ''"vali"'', literally means the ''"line of peaks"''. Natural history Geology The Aravalli Range, an eroded stub of ancient mountains, is believed to be the oldest range of fold mountains in India.Roy, A. B. (1990). Evolution of the Precambrian crust of the Aravalli Range. Developments in Precambrian Geology, 8, 327–347. The natural history of the Aravalli Range dates back to times when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurukshetra
Kurukshetra (, ) is a city and administrative headquarter of Kurukshetra district in the Indian state of Haryana. It is also known as Dharmakshetra ("Realm of duty ") and as the "Land of the Bhagavad Gita". Legends According to the Puranas, Kurukshetra is a region named after King Kuru, the ancestor of Kauravas and Pandavas in the Kuru kingdom, as depicted in epic ''Mahabharata''. The Kurukshetra War of the ''Mahabharata'' is believed to have taken place here. Thaneswar whose urban area is merged with Kurukshetra is a pilgrimage site with many locations attributed to ''Mahabharata''. In the Vedas Kurukshetra is described not as a city but as a region ("kshetra" means "region" in Sanskrit). The boundaries of Kurukshetra correspond roughly to the central and western parts of the state of Haryana and southern Punjab. According to the Taittiriya Aranyaka 5.1.1., the Kurukshetra region is south of Turghna (Srughna/Sugh in Sirhind, Punjab), north of Khandava (Delhi and Mewa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dangri
The Tangri River, also called the Dangri River, which originates in the Shivalik Hills, is a tributary of the Ghaggar River in the Haryana state of India. Origin and route The Tangri river originates in the Shivalik hills on the border of Haryana and Himachal Pradesh State, and flows along the Haryana and Punjab border before meeting with the Ghaggar river at the confluence. The basin is classified in two parts, Khadir and Bangar, the higher area that is not flooded in rainy season is called ''Bangar'' and the lower flood-prone area is called ''Khadar''. The Dangri or Tangri is a stream that rises in the Morni Hills of the Siwalik Hills of south-eastern Himachal Pradesh in India, and flows for 70 km in Haryana.Haryana rivers profile South Asia Network on Dams, Rivers and People. It confluences with the < ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krishnavati River
The Krishnavati river ( hi, कृष्णावती नदी), also called Kasaunti ( hi, कसौंती नदी), is a rain-fed river originates from Aravalli Range near Dariba copper mines in Rajsamand district of Rajasthan, and flows through Patan in Dausa district and Mothooka in Alwar district and then disappears in Mahendragarh district in Haryana where it use to be a tributary of Sahibi River, which in turn still is a tributary of Yamuna.Minerals and Metals in Ancient India: Archaeological evidence Arun Kumar Biswas, Sulekha Biswas, University of Michigan. 1996. . Several sites (also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manusmriti
The ''Manusmṛiti'' ( sa, मनुस्मृति), also known as the ''Mānava-Dharmaśāstra'' or Laws of Manu, is one of the many legal texts and constitution among the many ' of Hinduism. In ancient India, the sages often wrote their ideas on how society should run in the manuscripts. It is believed that the original form of ''Manusmriti'' was changed as many things written in the manuscript contradict each other. Over fifty manuscripts of the ''Manusmriti'' are now known, but the earliest discovered, most translated and presumed authentic version since the 18th century has been the "Kolkata (formerly Calcutta) manuscript with Kulluka Bhatta commentary". Modern scholarship states this presumed authenticity is false, and the various manuscripts of ''Manusmriti'' discovered in India are inconsistent with each other, and within themselves, raising concerns of its authenticity, insertions and interpolations made into the text in later times. The metrical text is in Sansk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts (''śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one Shakha of the many survive today, namely the Śakalya Shakha. Much of the contents contained in the remaining Shakhas are now lost or are not available in the public forum. The ''Rigveda'' is the oldest known Vedic Sanskrit text. Its early layers are among the oldest extant texts in any Indo-European language. The sounds and texts of the ''Rigveda'' have been orally transmitted since the 2nd millennium BCE. Philological and linguistic evidence indicates that the bulk of the ''Rigveda'' Samhita was composed in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent (see) Rigvedic rivers), most likely between 1500 and 1000 BCE, although a wider approximation of 19001200 BCE has also been given. The text is layered, consisting of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmavarta
The Hindu religious text ''Manusmriti'' describes Brahmavarta as the region between the rivers Saraswati and Drishadwati in India. The text defines the area as the place where the "good" people are born with "goodness" being dependent on location rather than behaviour. The name has been translated in various ways, including "holy land", "sacred land", "abode of gods", and "the scene of creation". The precise location and size of the region has been the subject of academic uncertainty. Some scholars, such as the archaeologists Bridget and Raymond Allchin, believe the term ''Brahmavarta'' to be synonymous with the Aryavarta region. According to ''Manusmriti'', the purity of a place and its inhabitants decreased the further it was from Brahmavarta. Aryan (noble) people were believed to inhabit the "good" area and the proportion of Mleccha (barbarian) people in the population rose as the distance from it increased. This implies a series of concentric circles of decreasing purity as one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vedic
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''. The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the oldest layer of Sanskrit literature and the oldest scriptures of Hinduism. There are four Vedas: the Rigveda, the Yajurveda, the Samaveda and the Atharvaveda. Each Veda has four subdivisions – the Samhitas (mantras and benedictions), the Aranyakas (text on rituals, ceremonies, sacrifices and symbolic-sacrifices), the Brahmanas (commentaries on rituals, ceremonies and sacrifices), and the Upanishads (texts discussing meditation, philosophy and spiritual knowledge).Gavin Flood (1996), ''An Introduction to Hinduism'', Cambridge University Press, , pp. 35–39A Bhattacharya (2006), ''Hindu Dharma: Introduction to Scriptures and Theology'', , pp. 8–14; George M. Williams (2003), Handbook of Hindu Mythology, Oxford University Press, , p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drishadwati
The Drishadvati river (IAST:, "She with many stones") is a river hypothesized by Indologists to identify the route of the Vedic river Saraswati and the state of ''Brahmavarta''. According to ''Manusmriti'', the ''Brahmavarta'', where the Rishis composed the Vedas and other Sanskrit texts of the Vedic religion, was at the confluence of the Saraswati and Drishadvati rivers during the Vedic period. Location Although the Drishadvati is mentioned several times in Sanskrit Granthas, a detailed description of the river is not found in other ancient literature and this has generated speculation about its source and route. The ''Latyayana Srautasutra'' (10.17) describes it as a seasonal river, with the Saraswati a perennial river until its ''vinasana'' (10.15-19). The Drishadvati is mentioned in Brahmanas written primarily in the state of Brahmavarta. According to these texts, the river originated in the pot of Brahma: Pushkar Lake, near Ajmer. The Sarasvati, with four branches flowing i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurukshetra University
Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra (KUK) is a university established on 11January 1956 in Kurukshetra, in the Indian state of Haryana, from the capital, Delhi. It is a member of Association of Commonwealth Universities. History The university was in 1956 as a unitary residential University. The Department of Sanskrit was the first and the only department in the university when it was inaugurated by Bharat Ratna Dr. Rajendra Prasad, the first President of the Indian Republic. The idea of establishing university was conceived by then governor of Punjab, Chandeshwar Prasad Narayan Singh, a Sanskrit scholar. In 2012, the Department of philosophy introduced an academic course on Gita. Campus Spread over , the KUK campus is located on the western bank of Brahma Sarovar in the Hindu holy city of Kurukshetra. Academics Grading The university follows a weighted average pattern to calculate grades, with the 1st and 2nd semester contributing 20% to the aggregate marks and ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indus Valley Civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900 BCE. Together with ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, it was one of three early civilisations of the Near East and South Asia, and of the three, the most widespread. Its sites spanned an area from much of Pakistan, to northeast Afghanistan, and northwestern India. The civilisation flourished both in the alluvial plain of the Indus River, which flows through the length of Pakistan, and along a system of perennial monsoon-fed rivers that once coursed in the vicinity of the Ghaggar-Hakra River, Ghaggar-Hakra, a seasonal river in northwest India and eastern Pakistan. The term ''Harappan'' is sometimes applied to the Indus civilisation after its type site Harappa, the first to be excavated early in the 20th century in what was then the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vedic Period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (ca. 1300–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, between the end of the urban Indus Valley civilisation and a second urbanisation, which began in the central Indo-Gangetic Plain BCE. The Vedas are liturgical texts which formed the basis of the influential Brahmanical ideology, which developed in the Kuru Kingdom, a tribal union of several Indo-Aryan tribes. The Vedas contain details of life during this period that have been interpreted to be historical and constitute the primary sources for understanding the period. These documents, alongside the corresponding archaeological record, allow for the evolution of the Indo-Aryan and Vedic culture to be traced and inferred. The Vedas were composed and orally transmitted with precision by speakers of an Old Indo-Aryan language who had migrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)



