|
Indigenat (other)
Indigénat was a set of laws creating, in practice, an inferior legal status for natives of French Colonies. Indigenat or indigenate, literally meaning "the right by the place of birth", may refer to: * Ius indigenatus * Indygenat ''Indygenat'' or 'naturalization' in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was the grant of nobility to foreign nobles. To grant ''indygenat'', a foreign noble had to submit proof of their service to the Republic, together with proof of nobility is ... * ''Indigenat'' (Hungary) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigénat
The ''Code de l'indigénat'' ( "native code"), called ''régime de l'indigénat'' or simply ''indigénat'' by modern French historians, were diverse and fluctuating sets of laws and regulations characterized by arbitrariness which created in practice an inferior legal status for natives of French colonies from 1881 until 1944–1947. The ''indigénat'' was introduced by decree, in various forms and degrees of severity, to Algeria and Cochinchina in 1881, New Caledonia and Senegal in 1887, Annam-Tonkin and Polynesia in 1897, Cambodia in 1898, Mayotte and Madagascar in 1901, French West Africa in 1904, French Equatorial Africa in 1910, French Somaliland in 1912, and the Mandates of Togo and Cameroun in 1923 and 1924. Under the term ''indigénat'' are often grouped other oppressive measures that were applied to the native population of the French empire, such as forced labor, requisitions, capitation (head tax), etc. Introduction in Algeria The ''Indigénat'' was created first to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
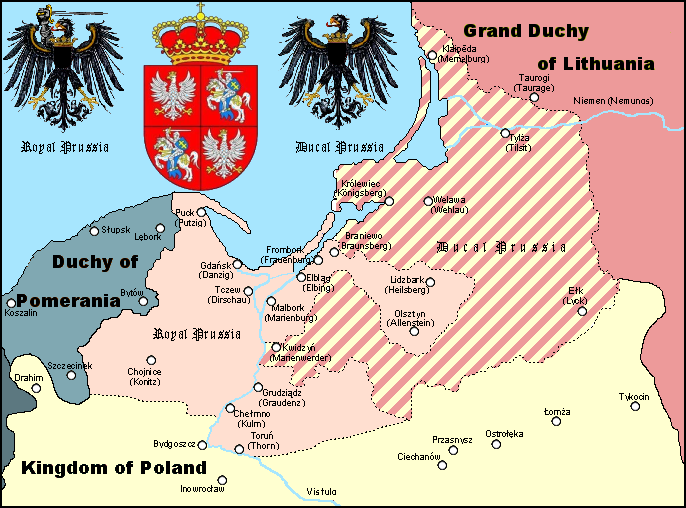
Ius Indigenatus
''Ius indigenatus'' (Latin for "right of local birth") is a right which was from the 15th to the 18th century a requirement for people to hold royal office in Royal Prussia, a Polish province. It limited offices and land ownership to local Prussian natives. It was confirmed in 1466 by the Second Peace of Thorn which secured a large decree of autonomy for Royal Prussia. The Prussian Ius indigenatus was valid for both parts of Prussia separated in 1466, the western part, later called Royal Prussia, and the eastern part, from 1525 the Duchy of Prussia, later East Prussia. See also *Jus soli *Jus sanguinis *Indygenat References * Karin Friedrich Karin Friedrich (born 12 June 1963, in Munich) is a German historian, a professor in history at the University of Aberdeen King's College. Friedrich received an M.A. in history and political science from Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich i ..., ''The Other Prussia. Royal Prussia, Poland and Liberty, 1569–1772'', Cambridge, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indygenat
''Indygenat'' or 'naturalization' in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was the grant of nobility to foreign nobles. To grant ''indygenat'', a foreign noble had to submit proof of their service to the Republic, together with proof of nobility issued by a foreign court, swear an oath of allegiance, and buy land. Grants of ''indygenat'' were limited in the history of Poland to just over 400 foreign nobles. It was granted by the King; after 1641 it was only valid with approval of the General sejm (parliament). Bibliography * Norman Davies, God's Playground A History of Poland: The Origins to 1795 (Vol. I), Oxford 2005, pp. 183-184 See also * Indigenat (other) * Nobilitation * Adopcja herbowa * Skartabellat Skartabellat (lat. ''scartabellat'') was a specific form of nobilitation in Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Introduced by pacta conventa of 1669, ennoblement into a sort of lower nobility. Skartabels could not hold public offices or be members ... External links ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |