|
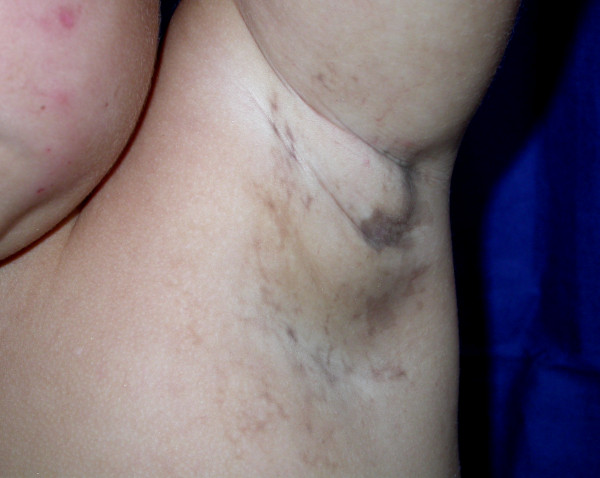
Incontinentia Pigmenti
Incontinentia pigmenti (IP) is a rare X-linked dominant genetic disorder that affects the skin, hair, teeth, nails and central nervous system. It is named from its appearance under a microscope. The disease is characterized by skin abnormalities that begin in childhood, usually a blistering rash which heals, followed by the development of harder skin growths. The skin may develop grey or brown patches which fade with time. Other symptoms can include hair loss, dental abnormalities, eye abnormalities that can lead to vision loss and lined or pitted fingernails and toenails. Associated problems can include delayed development, intellectual disability, seizures and other neurological problems. Most males with the disease do not survive to childbirth. Incontinentia pigmenti is caused by a mutation in the ''IKBKG'' gene, which encodes the NEMO protein, which serves to protect cells against TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis. A lack of IKBKG therefore makes cells more prone to apoptosis. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-linked Dominant
X-linked dominant inheritance, sometimes referred to as X-linked dominance, is a mode of genetic inheritance by which a dominant gene is carried on the X chromosome. As an inheritance pattern, it is less common than the X-linked recessive type. In medicine, X-linked dominant inheritance indicates that a gene responsible for a genetic disorder is located on the X chromosome, and only one copy of the allele is sufficient to cause the disorder when inherited from a parent who has the disorder. In this case, someone who expresses an X-linked dominant allele will exhibit the disorder and be considered affected. X-linked dominant traits do not necessarily affect males more than females (unlike X-linked recessive traits). The exact pattern of inheritance varies, depending on whether the father or the mother has the trait of interest. All fathers that are affected by an X-linked dominant disorder will have affected daughters but not affected sons. However, if the mother is also affected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limb (anatomy)
A limb (from the Old English ''lim'', meaning "body part") or leg is a jointed, muscled appendage that tetrapod vertebrates use for weight-bearing and terrestrial locomotion such as walking, running and jumping, for paddle-swimming, or for grasping and climbing. The distalmost portion of a limb is known as its extremity. The limbs' bony endoskeleton, known as the appendicular skeleton, is homologous among all tetrapods. All tetrapods have four limbs that are organized into two bilaterally symmetrical pairs, with one pair at each end of the torso. The cranial pair are known as the forelimbs or ''front legs'', and the caudal pair the hindlimbs or ''back legs''. In animals with more upright posture (mainly hominid primates, particularly humans), the forelimbs and hindlimbs are often called upper and lower limbs, respectively. The fore-/upper limbs are connected to the thoracic cage via the shoulder girdles, and the hind-/lower limbs are connected to the pelvis via the hip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spina Bifida
Spina bifida (Latin for 'split spine'; SB) is a birth defect in which there is incomplete closing of the spine and the membranes around the spinal cord during early development in pregnancy. There are three main types: spina bifida occulta, meningocele and myelomeningocele. Meningocele and myelomeningocele may be grouped as spina bifida cystica. The most common location is the lower back, but in rare cases it may be in the middle back or neck. Occulta has no or only mild signs, which may include a hairy patch, dimple, dark spot or swelling on the back at the site of the gap in the spine. Meningocele typically causes mild problems, with a sac of fluid present at the gap in the spine. Myelomeningocele, also known as open spina bifida, is the most severe form. Problems associated with this form include poor ability to walk, impaired bladder or bowel control, accumulation of fluid in the brain (hydrocephalus), a tethered spinal cord and latex allergy. Learning problems are rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
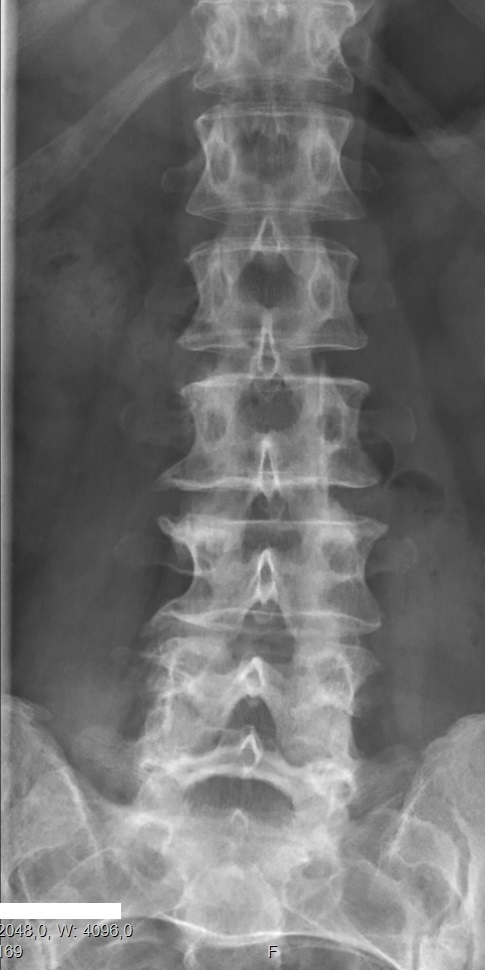
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition in which a person's spine has a sideways curve. The curve is usually "S"- or "C"-shaped over three dimensions. In some, the degree of curve is stable, while in others, it increases over time. Mild scoliosis does not typically cause problems, but more severe cases can affect breathing and movement. Pain is usually present in adults, and can worsen with age. The cause of most cases is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Risk factors include other affected family members. It can also occur due to another condition such as muscle spasms, cerebral palsy, Marfan syndrome, and tumors such as neurofibromatosis. Diagnosis is confirmed with X-rays. Scoliosis is typically classified as either structural in which the curve is fixed, or functional in which the underlying spine is normal. Treatment depends on the degree of curve, location, and cause. Minor curves may simply be watched periodically. Treatme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemivertebrae
Congenital vertebral anomalies are a collection of malformations of the spine. Most, around 85%, are not clinically significant, but they can cause compression of the spinal cord by deforming the vertebral canal or causing instability. This condition occurs in the womb. Congenital vertebral anomalies include alterations of the shape and number of vertebrae. Lumbarization and sacralization ''Lumbarization'' is an anomaly in the spine. It is defined by the nonfusion of the first and second segments of the sacrum. The lumbar spine subsequently appears to have six vertebrae or segments, not five. This sixth lumbar vertebra is known as a transitional vertebra. Conversely the sacrum appears to have only four segments instead of its designated five segments. Lumbosacral transitional vertebrae consist of the process of the last lumbar vertebra fusing with the first sacral segment. While only around 10 percent of adults have a spinal abnormality due to genetics, a sixth lumbar vertebra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernumerary Nipple
A supernumerary nipple is an additional instance of nipple occurring in mammals, including humans. They are often mistaken for moles. Studies variously report the prevalence of supernumerary nipples as approximately 1 in 18 and 1 in 40. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s004310050944 Supernumerary nipples: prevalence, size, sex and side predilection – a prospective clinical study, H. Schmidt, European Journal of Pediatrics volume 157, pages 821–823 (1998). https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/article-abstract/511138 Occurrence of Supernumerary Nipples in Newborns Francis Mimouni, MD; Paul Merlob, MD; Salomon H. Reisner, MB, ChB, Am J Dis Child. 1983;137(10):952-953. The nipples appear along the two vertical "milk lines", which start in the armpit on each side, run down through the typical nipples and end at the groin. They are classified into eight levels of completeness from a simple patch of hair to a milk-bearing breast in miniature. Types ''Polyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoplasia
Hypoplasia (from Ancient Greek ὑπo- ''hypo-'' 'under' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'; adjective form ''hypoplastic'') is underdevelopment or incomplete development of a tissue or organ. Dictionary of Cell and Molecular Biology (11 March 2008) Although the term is not always used precisely, it properly refers to an inadequate or below-normal number of cells.Hypoplasia Stedman's Medical Dictionary. lww.com Hypoplasia is similar to |
Tooth Eruption
Tooth eruption is a process in tooth development in which the teeth enter the mouth and become visible. It is currently believed that the periodontal ligament plays an important role in tooth eruption. The first human teeth to appear, the deciduous (primary) teeth (also known as baby or milk teeth), erupt into the mouth from around 6 months until 2 years of age, in a process known as "teething". These teeth are the only ones in the mouth until a person is about 6 years old creating the primary dentition stage. At that time, the first permanent tooth erupts and begins a time in which there is a combination of primary and permanent teeth, known as the mixed dentition stage, which lasts until the last primary tooth is lost. Then, the remaining permanent teeth erupt into the mouth during the permanent dentition stage. Theories Although researchers agree that tooth eruption is a complex process, there is little agreement on the identity of the mechanism that controls eruption. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypodontia
Hypodontia is defined as the developmental absence of one or more teeth excluding the third molars. It is one of the most common dental anomalies, and can have a negative impact on function, and also appearance. It rarely occurs in primary teeth (also known as deciduous, milk, first and baby teeth) and the most commonly affected are the adult second premolars and the upper lateral incisors. It usually occurs as part of a syndrome that involves other abnormalities and requires multidisciplinary treatment. The phenomenon can be subdivided into the following according to the number of teeth concerned: #Hypodontia: one to six missing teeth excluding the third molars #Oligodontia: six or more missing permanent teeth excluding the third molars #Anodontia: complete absence of teeth Signs and symptoms Typically, all baby teeth will be present by the age of three. As for all adult teeth, they erupt between the ages 6 to 14, with the exception of the third molar, also known as the wisd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cataracts
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and trouble seeing at night. This may result in trouble driving, reading, or recognizing faces. Poor vision caused by cataracts may also result in an increased risk of falling and depression. Cataracts cause 51% of all cases of blindness and 33% of visual impairment worldwide. Cataracts are most commonly due to aging but may also occur due to trauma or radiation exposure, be present from birth, or occur following eye surgery for other problems. Risk factors include diabetes, longstanding use of corticosteroid medication, smoking tobacco, prolonged exposure to sunlight, and alcohol. The underlying mechanism involves accumulation of clumps of protein or yellow-brown pigment in the lens that reduces transmission of li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossed Eyes
Strabismus is a vision disorder in which the eyes do not properly align with each other when looking at an object. The eye that is focused on an object can alternate. The condition may be present occasionally or constantly. If present during a large part of childhood, it may result in amblyopia, or lazy eyes, and loss of depth perception. If onset is during adulthood, it is more likely to result in double vision. Strabismus can occur due to muscle dysfunction, farsightedness, problems in the brain, trauma or infections. Risk factors include premature birth, cerebral palsy and a family history of the condition. Types include esotropia, where the eyes are crossed ("cross eyed"); exotropia, where the eyes diverge ("lazy eyed" or "wall eyed"); and hypertropia or hypotropia where they are vertically misaligned. They can also be classified by whether the problem is present in all directions a person looks (comitant) or varies by direction (incomitant). Diagnosis may be made by obser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Development
A motor neuron (or motoneuron or efferent neuron) is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or indirectly control effector organs, mainly muscles and glands. There are two types of motor neuron – upper motor neurons and lower motor neurons. Axons from upper motor neurons synapse onto interneurons in the spinal cord and occasionally directly onto lower motor neurons. The axons from the lower motor neurons are efferent nerve fibers that carry signals from the spinal cord to the effectors. Types of lower motor neurons are alpha motor neurons, beta motor neurons, and gamma motor neurons. A single motor neuron may innervate many muscle fibres and a muscle fibre can undergo many action potentials in the time taken for a single muscle twitch. Innervation takes place at a neuromuscular junction and twitches can become superimposed as a result of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_PHIL_4284_lores.jpg)
