|
Ilha Do Pico
Pico Island (''Ilha do Pico,'' ) is an island in the Central Group of the Portuguese Azores. The landscape features an eponymous volcano, Ponta do Pico, which is the highest mountain in Portugal, the Azores, and the highest elevation of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. In the tradition of the Portuguese poet, Raul Brandão, Pico is referred to as the ''Ilha Preta'' ("Black Island"), for its black volcanic soils, which nourish its UNESCO-designated vineyards that once allowed the development of the island's economy. Pico is the second largest and, geologically speaking, the most recently formed island of the Azores, being around 300,000 years old. History The exact date of the island's discovery is not known. However, in the 1375 Catalan Atlas, Pico is depicted along several other islands of the Azores, where it is labelled as ''li colunbj''. In Cristoforo Soligo's map from 1475, Pico is described both as Dom Diniz (or São Diniz) island and as ''Insula Columbi''. Although the Azores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madalena, Azores
Madalena () is a municipality along the western coast of the island of Pico, in the Portuguese Azores. It has 6,332 inhabitants as of 2021, in an area of 147.12 km². The municipality is fronted by the stratovolcano Pico in the eastern frontier, and the Faial Channel which divides Pico from the island of Faial seven kilometers away. It is made up of six freguesias (civil parishes) and is encircled almost entirely by the Atlantic Ocean except in the east, where it is bordered by the two remaining municipalities on the island: Lajes do Pico to the southeast, and São Roque do Pico to the northeast. History The settlement of the island of Pico occurred much later than most islands, partly due to greater interest shown in the other islands of the Central Group. For a time, only small herds, deposited by property-owners from Faial and Terceira, along with their caretakers (some of whom were slaves), were the only inhabitants of the island. It was not until the Infanta Beatri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igreja E Convento De São Pedro De Alcântara, São Roque, Ilha Do Pico, Açores, Portugal
"Igreja" ("Church") is a single by Brazilian rock band Titãs, released in 1986, part of their ''Cabeça Dinossauro'' album. Lyrics and composition According to songwriter and then bassist and vocalist Nando Reis, the song was written on the acoustic guitar at his mother's house in the district of Butantã, São Paulo: By the time of the album's release, Reis said: Reception within the band It was one of the last songs to be selected for the album and it stirred controversy among the members themselves - vocalist Arnaldo Antunes, at first, didn't want to record it and would even leave the stage sometimes when the song was performed live. When the members had a meeting at vocalist Branco Mello's apartment to discuss the album's repertoire, vocalist, bassist and saxophonist Paulo Miklos also opposed the song's inclusion, but soon changed his mind as the band performed it live. Antunes, on the other hand, said "the song is against the Church as the institution, but at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terceira
Terceira () is a volcanic island in the Azores archipelago, in the middle of the North Atlantic Ocean. It is one of the larger islands of the archipelago, with a population of 53,311 inhabitants in an area of approximately . It is the location of the Azores' oldest city, Angra do Heroísmo, the historical capital of the archipelago and UNESCO World Heritage Site; the seat of the judicial system (Supreme Court); and the main Air Force base, Base Aérea nº 4 at Lajes, with a United States Air Force detachment. The island has two main sea ports, one at Angra do Heroísmo and the other at Praia da Vitória, and a commercial airport integrated with the flight operations at Base Aérea nº 4. The Portuguese bullfight is popular on the island, coming in two variations: the traditional equestrian bullfight (in the ring) and the popular " touradas à corda" that occur in the streets. History In 1439, the first official discovery document appeared, attributing the discovery of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
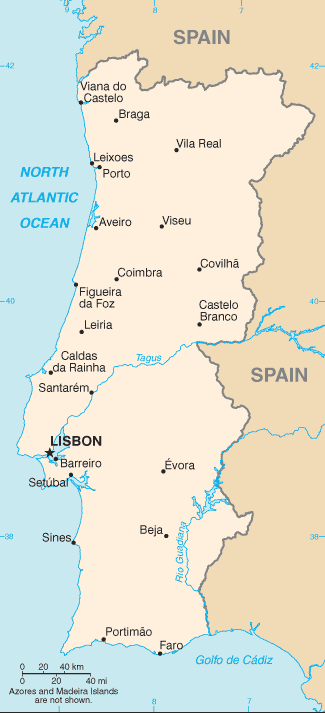
Continental Portugal
Continental Portugal ( pt, Portugal continental, ) or mainland Portugal comprises the bulk of the Portuguese Republic, namely that part on the Iberian Peninsula and so in Continental Europe, having approximately 95% of the total population and 96.6% of the country's land. Mainland Portugal is therefore commonly called by residents of the Portuguese archipelagos of the Azores and Madeira the continent ( pt, o continente) in all respects including minor elements of combined governance from Lisbon, the country's capital. Before 1975, when the Portuguese territory also stretched to several now-independent states in Africa, the designation ''metropolis'' ( pt, metrópole) was also used. Context The designation ''mainland Portugal'' is used to differentiate the continental territory of Portugal from its insular territory. The latter comprises the archipelagos of Madeira and Azores in the Atlantic Ocean. The Azores and Madeira are also commonly referred to as the autonomous region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinder Cones
A cinder cone (or scoria cone) is a steep conical hill of loose pyroclastic fragments, such as volcanic clinkers, volcanic ash, or scoria that has been built around a volcanic vent. The pyroclastic fragments are formed by explosive eruptions or lava fountains from a single, typically cylindrical, vent. As the gas-charged lava is blown violently into the air, it breaks into small fragments that solidify and fall as either cinders, clinkers, or scoria around the vent to form a cone that often is symmetrical; with slopes between 30 and 40°; and a nearly circular ground plan. Most cinder cones have a bowl-shaped crater at the summit. Mechanics of eruption Cinder cones range in size from tens to hundreds of meters tall and often have a bowl-shaped crater at the summit. They are composed of loose pyroclastic material (cinder or scoria), which distinguishes them from ''spatter cones'', which are composed of agglomerated volcanic bombs. The pyroclastic material making up a cinder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo, as well as Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha ( United Kingdom Overseas Territory).Paul R. Masson, Catherine Anne Pattillo, "Monetary union in West Africa (ECOWAS): is it desirable and how could it be achieved?" (Introduction). International Monetary Fund, 2001. The population of West Africa is estimated at about million people as of , and at 381,981,000 as of 2017, of which 189,672,000 are female and 192,309,000 male. The region is demographically and economically one of the fastest growing on the African continent. Early history in West Africa included a number of prominent regional powers that dominated different parts of both the coastal and internal trade networks, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to the east, and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to the south. Mauritania lies to the south of Western Sahara. Morocco also claims the Spanish exclaves of Ceuta, Melilla and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, and several small Spanish-controlled islands off its coast. It spans an area of or , with a population of roughly 37 million. Its official and predominant religion is Islam, and the official languages are Arabic and Berber; the Moroccan dialect of Arabic and French are also widely spoken. Moroccan identity and culture is a mix of Arab, Berber, and European cultures. Its capital is Rabat, while its largest city is Casablanca. In a region inhabited since the Paleolithic Era over 300,000 years ago, the first Moroccan s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flemish People
The Flemish or Flemings ( nl, Vlamingen ) are a Germanic ethnic group native to Flanders, Belgium, who speak Dutch. Flemish people make up the majority of Belgians, at about 60%. "''Flemish''" was historically a geographical term, as all inhabitants of the medieval County of Flanders in modern-day Belgium, France, and the Netherlands were referred to as "Flemings", irrespective of their ethnicity or language. The contemporary region of Flanders comprises a part of this historical county, as well as parts of the medieval duchy of Brabant and the medieval county of Loon, where the modern national identity and culture gradually formed. History The sense of "Flemish" identity increased significantly after the Belgian Revolution. Prior to this, the term "Vlamingen" in the Dutch language was in first place used for the inhabitants of the former County of Flanders. Flemish, however, had been used since the 14th century to refer to the language and dialects of both the peoples of Fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madeira Island
Madeira is a Portuguese island, and is the largest and most populous of the Madeira Archipelago. It has an area of , including Ilhéu de Agostinho, Ilhéu de São Lourenço, Ilhéu Mole (northwest). As of 2011, Madeira had a total population of 262,456. The island is the top of a massive submerged shield volcano that rises about from the floor of the Atlantic Ocean. The volcano formed atop an east–west rift in the oceanic crust along the African Plate, beginning during the Miocene epoch over 5 million years ago, continuing into the Pleistocene until about 700,000 years ago. This was followed by extensive erosion, producing two large amphitheatres open to south in the central part of the island. Volcanic activity later resumed, producing scoria cones and lava flows atop the older eroded shield. The most recent volcanic eruptions were on the west-central part of the island only 6,500 years ago, creating more cinder cones and lava flows. Madeira is the largest is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captain Of The Donatarie
A donatary captain was a Portuguese colonial official to whom the Crown granted jurisdiction, rights, and revenues over some colonial territory. The recipients of these grants were called (donataries), because they had been given the grant as a (donation) by the king, often as a reward for service.Johnson 1972 The term also applied as the rank title of the field officer that was in charge of a captaincy (group of companies) of the , the Portuguese territorial militia that existed from the 16th to the 19th centuries. Captaincy system Due to the impossibility of exercising direct control and sovereignty over overseas territories, the captain-major was the channel by which the monarch could delegate his powers, with certain restrictions, under the responsibility of peoples he felt he could confide. The could administer, in the sovereign's name, the lands for which he was assigned, with all the regalia, rights, and obligations, with the exception of certain limits, including milita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Don (honorific)
Don (; ; pt, Dom, links=no ; all from Latin ', roughly 'Lord'), abbreviated as D., is an honorific prefix primarily used in Spain and Hispanic America, and with different connotations also in Italy, Portugal and its former colonies, and Croatia. ''Don'' is derived from the Latin ''dominus'': a master of a household, a title with background from the Roman Republic in classical antiquity. With the abbreviated form having emerged as such in the Middle Ages, traditionally it is reserved for Catholic clergy and nobles, in addition to certain educational authorities and persons of distinction. ''Dom'' is the variant used in Portuguese. The female equivalent is Doña (), Donna (), Doamnă (Romanian) and Dona () abbreviated D.ª, Da., or simply D. It is a common honorific reserved for women, especially mature women. In Portuguese "Dona" tends to be less restricted in use to women than "Dom" is to men. In Britain and Ireland, especially at Oxford, Cambridge, and Dublin, the word is us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |