|
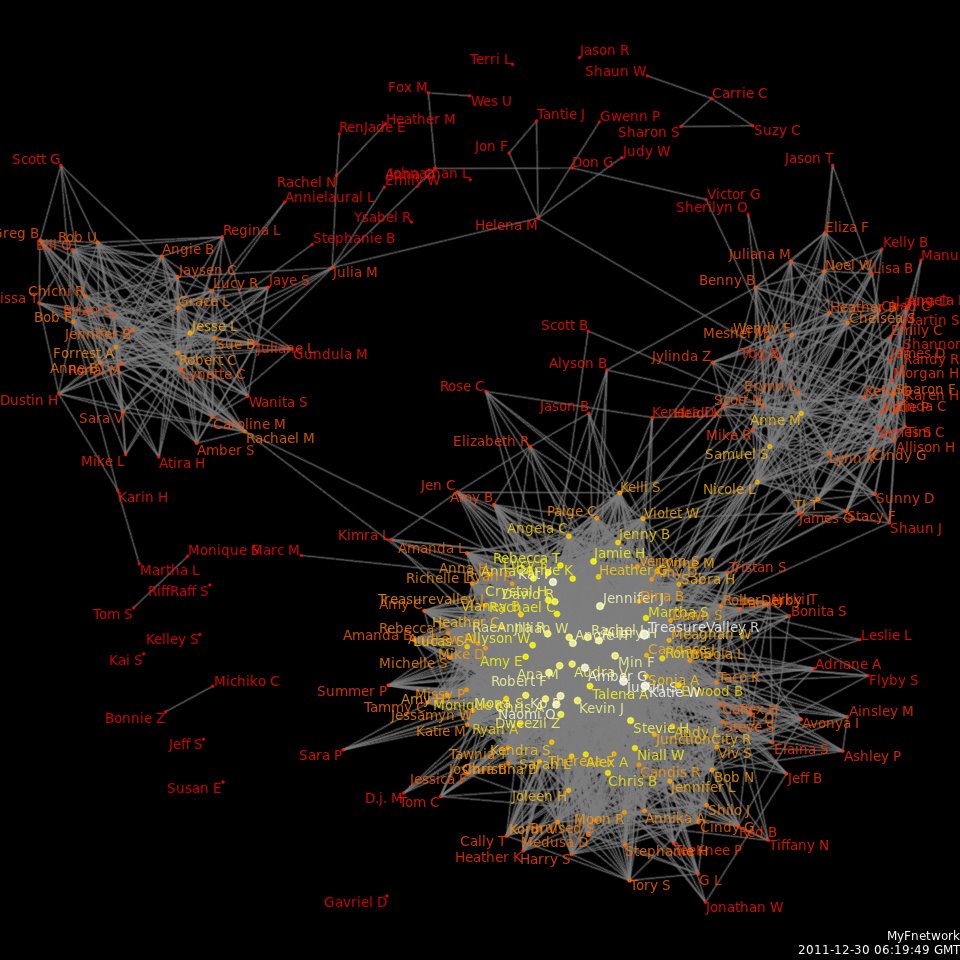
Idea Networking
Idea networking is a qualitative method of doing a cluster analysis of any collection of statements, developed by Mike Metcalfe at the University of South Australia. Networking lists of statements acts to reduce them into a handful of clusters or categories. The statements might be source from interviews, text, websites, focus groups, SWOT analysis or community consultation. Idea networking is inductive as it does not assume any prior classification system to cluster the statements. Rather keywords or issues in the statements are individually linked (paired). These links can then be entered into network software to be displayed as a network with clusters. When named, these clusters provide emergent categories, meta themes, frames or concepts which represent, structure or sense-make the collection of statements. Method An idea network can be constructed in the following way: * 60 to 200 statements are listed and assigned reference numbers. * A table is constructed showing which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cluster Analysis
Cluster analysis or clustering is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster) are more similar (in some sense) to each other than to those in other groups (clusters). It is a main task of exploratory data analysis, and a common technique for statistics, statistical data analysis, used in many fields, including pattern recognition, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning. Cluster analysis itself is not one specific algorithm, but the general task to be solved. It can be achieved by various algorithms that differ significantly in their understanding of what constitutes a cluster and how to efficiently find them. Popular notions of clusters include groups with small Distance function, distances between cluster members, dense areas of the data space, intervals or particular statistical distributions. Clustering can therefore be formulated as a multi-object ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factor Analysis
Factor analysis is a statistical method used to describe variability among observed, correlated variables in terms of a potentially lower number of unobserved variables called factors. For example, it is possible that variations in six observed variables mainly reflect the variations in two unobserved (underlying) variables. Factor analysis searches for such joint variations in response to unobserved latent variables. The observed variables are modelled as linear combinations of the potential factors plus "error" terms, hence factor analysis can be thought of as a special case of errors-in-variables models. Simply put, the factor loading of a variable quantifies the extent to which the variable is related to a given factor. A common rationale behind factor analytic methods is that the information gained about the interdependencies between observed variables can be used later to reduce the set of variables in a dataset. Factor analysis is commonly used in psychometrics, persona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognition
Cognition refers to "the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, intelligence, the formation of knowledge, memory and working memory, judgment and evaluation, reasoning and computation, problem solving and decision making, comprehension and production of language. Imagination is also a cognitive process, it is considered as such because it involves thinking about possibilities. Cognitive processes use existing knowledge and discover new knowledge. Cognitive processes are analyzed from different perspectives within different contexts, notably in the fields of linguistics, musicology, anesthesia, neuroscience, psychiatry, psychology, education, philosophy, anthropology, biology, systemics, logic, and computer science. These and other approaches to the analysis of cognition (such as embodied cognition) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis is one of the most common forms of analysis within qualitative research. It emphasizes identifying, analysing and interpreting patterns of meaning (or "themes") within qualitative data. Thematic analysis is often understood as a method or technique in contrast to most other qualitative analytic approaches - such as grounded theory, discourse analysis, narrative analysis and interpretative phenomenological analysis - which can be described as methodologies or theoretically informed frameworks for research (they specify guiding theory, appropriate research questions and methods of data collection, as well as procedures for conducting analysis). Thematic analysis is best thought of as an umbrella term for a variety of different approaches, rather than a singular method. Different versions of thematic analysis are underpinned by different philosophical and conceptual assumptions and are divergent in terms of procedure. Leading thematic analysis proponents, psychologis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Network Analysis
Social network analysis (SNA) is the process of investigating social structures through the use of networks and graph theory. It characterizes networked structures in terms of ''nodes'' (individual actors, people, or things within the network) and the ''ties'', ''edges'', or ''links'' (relationships or interactions) that connect them. Examples of social structures commonly visualized through social network analysis include social media networks, memes spread, information circulation, friendship and acquaintance networks, business networks, knowledge networks, difficult working relationships, social networks, collaboration graphs, kinship, disease transmission, and sexual relationships. These networks are often visualized through ''sociograms'' in which nodes are represented as points and ties are represented as lines. These visualizations provide a means of qualitatively assessing networks by varying the visual representation of their nodes and edges to reflect attributes of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensemaking
Sensemaking or sense-making is the process by which people give meaning to their collective experiences. It has been defined as "the ongoing retrospective development of plausible images that rationalize what people are doing" ( Weick, Sutcliffe, & Obstfeld, 2005, p. 409). The concept was introduced to organizational studies by Karl E. Weick in the 1970s and has affected both theory and practice. Weick intended to encourage a shift away from the traditional focus of organization theorists on decision-making and towards the processes that constitute the meaning of the decisions that are enacted in behavior. Definition There is no single agreed upon definition of sensemaking, but there is consensus that it is a process that allows people to understand ambiguous, equivocal or confusing issues or events. Disagreements about the meaning of sensemaking exist around whether sensemaking is a mental process within the individual, a social process or a process that occurs as part of discu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repertory Grid
The repertory grid is an interviewing technique which uses nonparametric factor analysis to determine an idiographic measure of personality. It was devised by George Kelly in around 1955 and is based on his personal construct theory of personality. Republished in 1991 as: Introduction The repertory grid is a technique for identifying the ways that a person construes (interprets or gives meaning to) his or her experience. It provides information from which inferences about personality can be made, but it is not a personality test in the conventional sense. It is underpinned by the personal construct theory developed by George Kelly, first published in 1955. A grid consists of four parts: # A ''topic'': it is about some part of the person's experience # A set of ''elements'', which are examples or instances of the ''topic''. Working as a clinical psychologist, Kelly was interested in how his clients construed people in the roles they adopted towards the client, and so, ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathfinder Network
A pathfinder network is a psychometric scaling method based on graph theory and used in the study of expertise, knowledge acquisition, knowledge engineering, scientific citation patterns, information retrieval, and data visualization. Pathfinder networks are potentially applicable to any problem addressed by network theory. Overview Several psychometric scaling methods start from proximity data and yield structures revealing the underlying organization of the data. Data clustering and multidimensional scaling are two such methods. Network scaling represents another method based on graph theory In mathematics, graph theory is the study of ''graphs'', which are mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects. A graph in this context is made up of '' vertices'' (also called ''nodes'' or ''points'') which are conn .... Pathfinder networks are derived from proximities for pairs of entities. Proximities can be obtained from similarities, correlations, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institutional Logic
Institutional logic is a core concept in sociological theory and organizational studies, with growing interest in marketing theory. It focuses on how broader belief systems shape the cognition and behavior of actors. Friedland and Alford (1991) wrote: "Institutions are supraorganizational patterns of human activity by which individuals and organizations produce and reproduce their material subsistence and organize time and space. They are also symbolic systems, ways of ordering reality, and thereby rendering experience of time and space meaningful". Friedland and Alford (1991, p. 248) elaborated: "Each of the most important orders of contemporary Western societies has a central logic – a set of material practices and symbolic constructions – which constitute its organising principles and which is available to organizations and individuals to elaborate." Thornton and Ocasio (1999: 804) define institutional logics as "the socially constructed, historical patterns of material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Concept Mapping
Group concept mapping is a structured methodology for organizing the ideas of a group on any topic of interest and representing those ideas visually in a series of interrelated maps.Kane M, Trochim WM (2007). Concept mapping for planning and evaluation. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.Trochim W (1989)An introduction to concept mapping for evaluation and planning Evaluation and Program Planning, 12(1), 1–16. It is a type of integrative mixed method, combining qualitative and quantitative approaches to data collection and analysis. Group concept mapping allows for a collaborative group process with groups of any size, including a broad and diverse array of participants. Since its development in the late 1980s by William M.K. Trochim at Cornell University, it has been applied to various fields and contexts, including community and public health, social work, health care, human services, and biomedical research and evaluation. Overview Group concept mapping integrates qualita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concept Mapping
A concept map or conceptual diagram is a diagram that depicts suggested relationships between concepts. Concept maps may be used by instructional designers, engineers, technical writers, and others to organize and structure knowledge. A concept map typically represents ideas and information as boxes or circles, which it connects with labeled arrows, often in a downward-branching hierarchical structure but also in free-form maps. The relationship between concepts can be articulated in '' linking phrases'' such as "causes", "requires", "such as" or "contributes to". The technique for visualizing these relationships among different concepts is called ''concept mapping''. Concept maps have been used to define the ontology of computer systems, for example with the object-role modeling or Unified Modeling Language formalism. Differences from other visualizations * ''Topic maps'': Both concept maps and topic maps are kinds of knowledge graph, but topic maps were developed by in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concept Driven Strategy
A concept-driven strategy is a process for formulating strategy that draws on the explanation of how humans inquire provided by linguistic pragmatic philosophy. This argues that thinking starts by selecting (explicitly or implicitly) a set of concepts (frames, patterns, lens, principles, etc.) gained from our past experiences. These are used to reflect on whatever happens, or is done, in the future. Concept-driven strategy therefore starts from agreeing and enacting a set of strategic concepts ( organizing principles) that "works best" for an organisation. For example, a hospital might set its strategy as intending to be Caring, World Class, Local, Evidence Based, and Team Based. A University might set its strategy as intending to be Ranked, Problem Solving, Online, Equis, and Offering Pathways. A commercial corporation might set its strategy as intending to be Innovative, Global, Have Visible Supply Chains, Agile and Market Share Dominant. These strategic concepts make up its ''S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |