|
IMac (Apple Silicon)
The iMac with Apple silicon, also known as the iMac M1, is a Macintosh all-in-one desktop computer designed, developed and marketed by Apple Inc. The first iMac with Apple silicon, a redesigned 24-inch model based on the Apple M1 ARM-based system on a chip, was released on May 21, 2021. Overview On June 22, 2020, Apple CEO Tim Cook announced the Mac would shift from Intel processors to Apple's own in-house designed processors that use the ARM64 architecture, branded as Apple silicon. On April 20, 2021, Apple announced a 24-inch iMac based on the Apple M1 system on a chip. The iMac with M1 features a 4480-by-2520 (4.5K) built-in display, 1080p FaceTime camera with an improved image signal processor and three-microphone array, and a six-driver stereo speaker system with a pair of force-canceling woofers and a tweeter per side, that supports Dolby Atmos and spatial audio. It also adds support for Wi-Fi 6, USB4/ Thunderbolt 3, and 6K output to run the Pro Display XDR. Ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
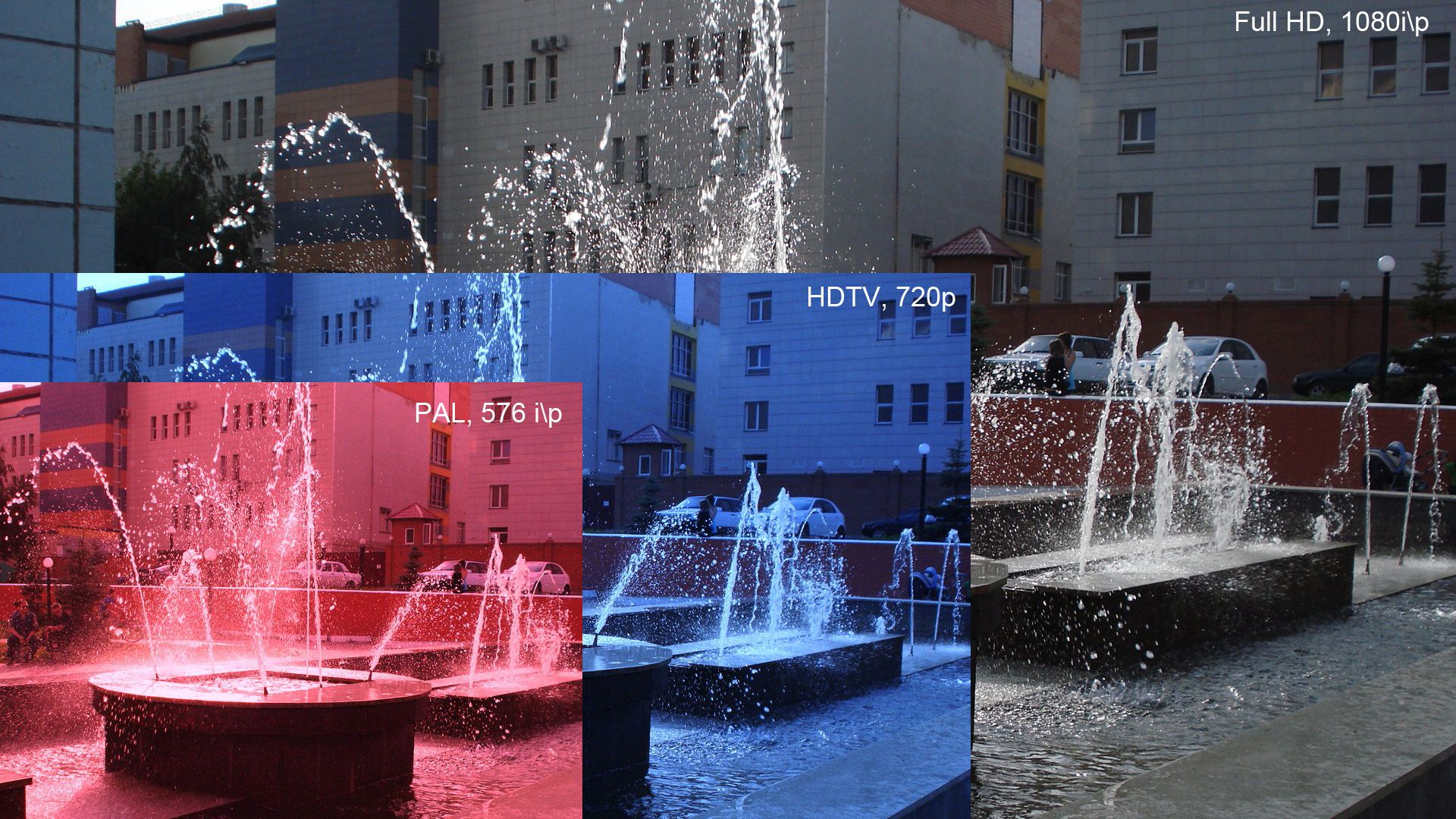
1080p
1080p (1920×1080 progressively displayed pixels; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709) is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the ''p'' stands for progressive scan, ''i.e.'' non-interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixels. It is often marketed as Full HD or FHD, to contrast 1080p with 720p resolution screens. Although 1080p is sometimes informally referred to as 2K, these terms reflect two distinct technical standards, with differences including resolution and aspect ratio. 1080p video signals are supported by ATSC standards in the United States and DVB standards in Europe. Applications of the 1080p standard include television broadcasts, Blu-ray Discs, smartphones, Internet content such as YouTube videos and Netflix TV shows and movies, consumer-grade televisions and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magic Keyboard (Mac)
The Magic Keyboard is a family of wireless computer keyboards produced by Apple Inc. The keyboards are bundled with the iMac and Mac Pro and sold as standalone products, replacing the Apple Wireless Keyboard product line. Each Magic Keyboard model combination has a compact or full-size key layout for a specific region, a function key or Touch ID sensor next to F12, and color scheme variant. Apple also refers to the internal keyboards in MacBooks released after November 2019 as the Magic Keyboard, which uses an identical scissor-mechanism with slightly shallower keys. Features First generation The original Magic Keyboard design was available in two models: * (A1644) Magic Keyboard, first available in October 2015 * (A1843) Magic Keyboard with Numeric Keypad, first available in June 2017 This keyboard's design was similar to its predecessor, but had a lower profile. Apple re-engineered the scissor mechanism to increase key stability by 33 percent and reduce key travel. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magic Trackpad 2
The second-generation Magic Trackpad (initially marketed as Magic Trackpad 2) is a multi-touch and Force Touch trackpad produced by Apple Inc. It was announced on October 13, 2015 alongside the Magic Keyboard and second-generation Magic Mouse, and replaces the first-generation Magic Trackpad. Description The second-generation Magic Trackpad is similar to its predecessor, with the key differences being a larger form factor, rechargeable lithium-ion battery and Force Touch. The trackpad also provides haptic feedback via Apple's built-in Taptic Engine that is also used in MacBook trackpads. The Lightning connector is used for charging and pairing. The second-generation Magic Trackpad has been made available in a large variety of colors. A space gray color was introduced with the iMac Pro in 2017, alongside a color-matching Magic Keyboard; both were later made available as standalone purchases. iPadOS iPadOS is a mobile operating system developed by Apple Inc. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magic Mouse 2
Magic or Magick most commonly refers to: * Magic (supernatural), beliefs and actions employed to influence supernatural beings and forces * Ceremonial magic, encompasses a wide variety of rituals of magic * Magical thinking, the belief that unrelated events are causally connected, particularly as a result of supernatural effects * Magic (illusion), the art of appearing to perform supernatural feats Magic(k) may also refer to: Art and entertainment Film and television * ''Magic'' (1917 film), a silent Hungarian drama * ''Magic'' (1978 film), an American horror film * ''Magic'' (soap opera), 2013 Indonesian soap opera * Magic (TV channel), a British music television station Literature * Magic in fiction, the genre of fiction that uses supernatural elements as a theme * ''Magic'' (Chesterton play), 1913 * ''Magic'' (short story collection), 1996 short story collection by Isaac Asimov * ''Magic'' (novel), 1976 novel by William Goldman * ''The Magic Comic'', a 1939–1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gigabit Ethernet
In computer networking, Gigabit Ethernet (GbE or 1 GigE) is the term applied to transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second. The most popular variant, 1000BASE-T, is defined by the IEEE 802.3ab standard. It came into use in 1999, and has replaced Fast Ethernet in wired local networks due to its considerable speed improvement over Fast Ethernet, as well as its use of cables and equipment that are widely available, economical, and similar to previous standards. History Ethernet was the result of research conducted at Xerox PARC in the early 1970s, and later evolved into a widely implemented physical and link layer protocol. Fast Ethernet increased the speed from 10 to 100 megabits per second (Mbit/s). Gigabit Ethernet was the next iteration, increasing the speed to 1000 Mbit/s. * The initial standard for Gigabit Ethernet was produced by the IEEE in June 1998 as IEEE 802.3z, and required optical fiber. 802.3z is commonly referred to as 1000BASE-X, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4K Resolution
4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. Digital television and digital cinematography commonly use several different 4K resolutions. In television and consumer media, 38402160 (4K UHD) is the dominant 4K standard, whereas the movie projection industry uses 40962160 (DCI 4K). The 4K television market share increased as prices fell dramatically during 2014 and 2015. 4K standards and terminology The term "4K" is generic and refers to any resolution with a horizontal pixel count of approximately 4,000. Several different 4K resolutions have been standardized by various organizations. The terms "4K" and "Ultra HD" are used more widely in marketing than "2160p". While typically referring to motion pictures, some digital camera vendors have used the term "4K photo" for still photographs, making it appear like an especially high resolution even though 3840×2160 pixels equal approximately 8.3 megapixels, which is not considered to be es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USB-C
USB-C (properly known as USB Type-C) is a 24-pin USB connector system with a rotationally symmetrical connector. The designation C refers only to the connector's physical configuration or form factor and should not be confused with the connector's specific capabilities, which are designated by its transfer specifications (such as USB 3.2). A notable feature of the USB-C connector is its ''reversibility''; a plug may be inserted into a receptacle in either orientation. The ''USB Type-C Specification 1.0'' was published by the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF) and was finalized in August 2014. It was developed at roughly the same time as the USB 3.1 specification. In July 2016, it was adopted by the IEC as "IEC 62680-1-3". A device with a Type-C connector does not necessarily implement USB, USB Power Delivery, or any Alternate Mode: the Type-C connector is common to several technologies while mandating only a few of them. USB 3.2, released in September 2017, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pro Display XDR
The Pro Display XDR is a 32-inch flat panel computer monitor created by Apple, based on an LG supplied display, and released on December 10, 2019. It was announced at the Apple Worldwide Developers Conference on June 3, 2019 along with the third-generation Mac Pro. It is the first Apple-branded display since the Apple Thunderbolt Display was discontinued in 2016. It is sold alongside the consumer Apple Studio Display. "XDR" stands for "Extreme Dynamic Range." Overview The Pro Display XDR contains a 6016 × 3384 6K color-calibrated panel, and its rear cover contains a similar lattice pattern to the third-generation Mac Pro. To improve its contrast ratio and HDR capabilities, it uses blue-colored LEDs for its backlight instead of white, at a higher refresh rate than the display itself, and contains a system of "custom lenses and reflectors". The aforementioned lattice serves as a heatsink: Apple stated that this design gave the display sufficient thermal management to ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunderbolt (interface)
Thunderbolt is the brand name of a hardware interface for the connection of external peripherals to a computer. It has been developed by Intel, in collaboration with Apple. It was initially marketed under the name Light Peak, and first sold as part of an end-user product on 24 February 2011. Thunderbolt combines PCI Express (PCIe) and DisplayPort (DP) into two serial signals, and additionally provides DC power, all in one cable. Up to six peripherals may be supported by one connector through various topologies. Thunderbolt 1 and 2 use the same connector as Mini DisplayPort (MDP), whereas Thunderbolt 3 and 4 reuse the USB-C connector from USB. Description Thunderbolt controllers multiplex one or more individual data lanes from connected PCIe and DisplayPort devices for transmission via two duplex Thunderbolt lanes, then de-multiplex them for use by PCIe and DisplayPort devices on the other end. A single Thunderbolt port supports up to six Thunderbolt devices via hubs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USB4
USB4 (aka: USB 4.0) is a specification by the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), which was released in version 1.0 on 29 August 2019. The USB4 protocol is based on the Thunderbolt 3 protocol; the Thunderbolt 3 specification was donated to the USB-IF by Intel Corp. The USB4 architecture can share a single high-speed link with multiple end-device types dynamically, best serving each transfer by data type and application. In contrast to prior USB protocol standards, USB4 ''mandates'' the exclusive use of the Type-C connector, and ''mandates'' the use of USB PD for power delivery. USB4 products must support 20 Gbit/s throughput and can support 40 Gbit/s throughput, but due to tunneling even nominal 20 Gbit/s can result in higher effective data rates in USB4, compared to USB 3.2, when sending mixed data. In contrast to USB 3.2, it allows tunneling of DisplayPort and PCI Express. Support of interoperability with Thunderbolt 3 products is required for USB4 hosts an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wi-Fi 6
IEEE 802.11ax, officially marketed by the Wi-Fi Alliance as (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) and (6 GHz), is an IEEE standard for wireless local-area networks (WLANs) and the successor of 802.11ac. It is also known as ''High Efficiency'' , for the overall improvements to clients under dense environments. It is designed to operate in license-exempt bands between 1 and 7.125 GHz, including the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands already in common use as well as the much wider 6 GHz band (5.925–7.125 GHz in the US). The main goal of this standard is enhancing throughput-per-area in high-density scenarios, such as corporate offices, shopping malls and dense residential apartments. While the nominal data rate improvement against 802.11ac is only 37%, the overall throughput increase (over an entire network) is 300% (hence ''High Efficiency''). This also translates to 75% lower latency. The quadrupling of overall throughput is made possible by a higher spectral efficiency. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_-_2.jpg)