|
IK Channel
The ''I'' channel (KCa3.1), which has a conductance of 20–80 pS, is expressed mainly in peripheral tissues such as those of the haematopoietic system, colon, placenta, lung and pancreas. The KCa3.1 channel in red blood cells was the first Ca2+–sensitive K+ channel to be identified and it has been implicated in a wide range of cell functions, including vasodilation of the microvasculature, K+ flux across endothelial cells of brain capillaries and the phagocytic activity of neutrophils. KCa3.1 is of primary importance in the relationship between K+ channels and cell proliferation. In the latter case, a human ''hIKCa1'' gene encodes the channel found in T cells, which is responsible for the hyperpolarization that is required to keep Ca2+ flowing into the cell through the ''I''CRAC channels. In comparison with the large-conductance (BK) channels, KCa3.1 is much more sensitive to Ca2+ and can thus respond to the global level of Ca2+. This high affinity for Ca2+ depends upon four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haematopoietic System
The haematopoietic system is the system in the body involved in the creation of the cells of blood. Structure Stem cells Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) reside in the medulla of the bone ( bone marrow) and have the unique ability to give rise to all of the different mature blood cell types and tissues. HSCs are self-renewing cells: when they differentiate, at least some of their daughter cells remain as HSCs, so the pool of stem cells is not depleted. This phenomenon is called asymmetric division. The other daughters of HSCs ( myeloid and lymphoid progenitor cells) can follow any of the other differentiation pathways that lead to the production of one or more specific types of blood cell, but cannot renew themselves. The pool of progenitors is heterogeneous and can be divided into two groups; long-term self-renewing HSC and only transiently self-renewing HSC, also called short-terms. This is one of the main vital processes in the body. Development In developing embryos, blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperpolarization (biology)
Hyperpolarization is a change in a cell's membrane potential that makes it more negative. It is the opposite of a depolarization. It inhibits action potentials by increasing the stimulus required to move the membrane potential to the action potential threshold. Hyperpolarization is often caused by efflux of K+ (a cation) through K+ channels, or influx of Cl– (an anion) through Cl– channels. On the other hand, influx of cations, e.g. Na+ through Na+ channels or Ca2+ through Ca2+ channels, inhibits hyperpolarization. If a cell has Na+ or Ca2+ currents at rest, then inhibition of those currents will also result in a hyperpolarization. This voltage-gated ion channel response is how the hyperpolarization state is achieved. In neurons, the cell enters a state of hyperpolarization immediately following the generation of an action potential. While hyperpolarized, the neuron is in a refractory period that lasts roughly 2 milliseconds, during which the neuron is unabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Channels
Potassium channels are the most widely distributed type of ion channel found in virtually all organisms. They form potassium-selective pores that span cell membranes. Potassium channels are found in most cell types and control a wide variety of cell functions. Function Potassium channels function to conduct potassium ions down their electrochemical gradient, doing so both rapidly (up to the diffusion rate of K+ ions in bulk water) and selectively (excluding, most notably, sodium despite the sub-angstrom difference in ionic radius). Biologically, these channels act to set or reset the resting potential in many cells. In excitable cells, such as neurons, the delayed counterflow of potassium ions shapes the action potential. By contributing to the regulation of the cardiac action potential duration in cardiac muscle, malfunction of potassium channels may cause life-threatening arrhythmias. Potassium channels may also be involved in maintaining vascular tone. They also regulate ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PtdIns3P
Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns3''P'') is a phospholipid found in cell membranes that helps to recruit a range of proteins, many of which are involved in protein trafficking, to the membranes. It is the product of both the class II and III phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI 3-kinases) activity on phosphatidylinositol. PtdIns3''P'' is dephosphorylated by the myotubularin family of phosphatases, on the D3 position of the inositol ring, and can be converted to PtdIns(3,5)''P''2 by the lipid kinase PIKfyve. Both FYVE domains and PX domains – found in proteins such as SNX1, HGS, and EEA1 – bind to PtdIns3''P''. The majority of PtdIns3''P'' appears to be constitutively synthesised by the class III PI 3-kinase, PIK3C3 (Vps34), at endocytic membranes. Class II PI 3-kinases also appear to synthesise PtdIns3''P'', their activity however appears to be regulated by a range of stimuli, including growth factors. This suggests that specific pools of PtdIns3''P'' may be s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SK Channel
SK channels (small conductance calcium-activated potassium channels) are a subfamily of calcium-activated potassium channels. They are so called because of their small single channel conductance in the order of 10 pS. SK channels are a type of ion channel allowing potassium cations to cross the cell membrane and are activated (opened) by an increase in the concentration of intracellular calcium through N-type calcium channels. Their activation limits the firing frequency of action potentials and is important for regulating afterhyperpolarization in the neurons of the central nervous system as well as many other types of electrically excitable cells. This is accomplished through the hyperpolarizing leak of positively charged potassium ions along their concentration gradient into the extracellular space. This hyperpolarization causes the membrane potential to become more negative. SK channels are thought to be involved in synaptic plasticity and therefore play important roles in l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hill Coefficient
In biochemistry and pharmacology, the Hill equation refers to two closely related equations that reflect the binding of ligands to macromolecules, as a function of the ligand concentration. A ligand is "a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose" ( ligand definition), and a macromolecule is a very large molecule, such as a protein, with a complex structure of components ( macromolecule definition). Protein-ligand binding typically changes the structure of the target protein, thereby changing its function in a cell. The distinction between the two Hill equations is whether they measure ''occupancy'' or ''response''. The Hill–Langmuir equation reflects the occupancy of macromolecules: the fraction that is saturated or bound by the ligand.For clarity, this article will use the International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology convention of distinguishing between the Hill-Langmuir equation (for receptor saturation) and Hill equation (for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell's internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance or cytoplasmic matrix which remains after exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, the plant plastids, lipid droplets, and vacuoles. Most cellular activities take place within the cytoplasm, such as many metabolic pathways including glycolysis, and proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calmodulin
Calmodulin (CaM) (an abbreviation for calcium-modulated protein) is a multifunctional intermediate calcium-binding messenger protein expressed in all eukaryotic cells. It is an intracellular target of the secondary messenger Ca2+, and the binding of Ca2+ is required for the activation of calmodulin. Once bound to Ca2+, calmodulin acts as part of a calcium signal transduction pathway by modifying its interactions with various target proteins such as kinases or phosphatases. Structure Calmodulin is a small, highly conserved protein that is 148 amino acids long (16.7 kDa). The protein has two approximately symmetrical globular domains (the N- and C- domains) each containing a pair of EF hand motifs separated by a flexible linker region for a total of four Ca2+ binding sites, two in each globular domain. In the Ca2+-free state, the helices that form the four EF-hands are collapsed in a compact orientation, and the central linker is disordered; in the Ca2+-saturated state, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
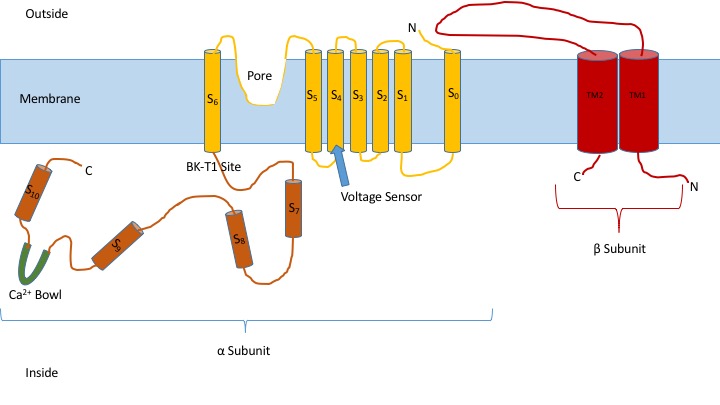
BK Channel
BK channels (big potassium), are large conductance calcium-activated potassium channels, also known as Maxi-K, slo1, or Kca1.1. BK channels are voltage-gated potassium channels that conduct large amounts of potassium ions (K+) across the cell membrane, hence their name, ''big potassium''. These channels can be activated (opened) by either electrical means, or by increasing Calcium in biology, Ca2+ concentrations in the cell. BK channels help regulate physiological processes, such as Circadian rhythm, circadian behavioral rhythms and neuronal excitability. BK channels are also involved in many processes in the body, as it is a ubiquitous channel. They have a tetrameric structure that is composed of a transmembrane domain, voltage sensing domain, potassium channel domain, and a cytoplasmic C-terminal domain, with many X-ray structures for reference. Their function is to repolarize the membrane potential by allowing for potassium to flow outward, in response to a depolarization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins CD8 or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Intestine
The large intestine, also known as the large bowel, is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract and of the digestive system in tetrapods. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored in the rectum as feces before being removed by defecation. The colon is the longest portion of the large intestine, and the terms are often used interchangeably but most sources define the large intestine as the combination of the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal. Some other sources exclude the anal canal. In humans, the large intestine begins in the right iliac region of the pelvis, just at or below the waist, where it is joined to the end of the small intestine at the cecum, via the ileocecal valve. It then continues as the colon ascending the abdomen, across the width of the abdominal cavity as the transverse colon, and then descending to the rectum and its endpoint at the anal canal. Overall, in humans, the large intestine is about long, which is about one-fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrophil
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in different animals. They are formed from stem cells in the bone marrow and Cellular differentiation, differentiated into #Subpopulations, subpopulations of neutrophil-killers and neutrophil-cagers. They are short-lived and highly mobile, as they can enter parts of tissue where other cells/molecules cannot. Neutrophils may be subdivided into segmented neutrophils and banded neutrophils (or Band cell, bands). They form part of the polymorphonuclear cells family (PMNs) together with basophils and eosinophils. The name ''neutrophil'' derives from staining characteristics on hematoxylin and eosin (H&E stain, H&E) histology, histological or cell biology, cytological preparations. Whereas basophilic white blood cells stain dark blue and eosinoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |